Apoptosis(凋亡)
As one of the cellular death mechanisms, apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, can be defined as the process of a proper death of any cell under certain or necessary conditions. Apoptosis is controlled by the interactions between several molecules and responsible for the elimination of unwanted cells from the body.
Many biochemical events and a series of morphological changes occur at the early stage and increasingly continue till the end of apoptosis process. Morphological event cascade including cytoplasmic filament aggregation, nuclear condensation, cellular fragmentation, and plasma membrane blebbing finally results in the formation of apoptotic bodies. Several biochemical changes such as protein modifications/degradations, DNA and chromatin deteriorations, and synthesis of cell surface markers form morphological process during apoptosis.
Apoptosis can be stimulated by two different pathways: (1) intrinsic pathway (or mitochondria pathway) that mainly occurs via release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria and (2) extrinsic pathway when Fas death receptor is activated by a signal coming from the outside of the cell.
Different gene families such as caspases, inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, B cell lymphoma (Bcl)-2 family, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene superfamily, or p53 gene are involved and/or collaborate in the process of apoptosis.
Caspase family comprises conserved cysteine aspartic-specific proteases, and members of caspase family are considerably crucial in the regulation of apoptosis. There are 14 different caspases in mammals, and they are basically classified as the initiators including caspase-2, -8, -9, and -10; and the effectors including caspase-3, -6, -7, and -14; and also the cytokine activators including caspase-1, -4, -5, -11, -12, and -13. In vertebrates, caspase-dependent apoptosis occurs through two main interconnected pathways which are intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic or mitochondrial apoptosis pathway can be activated through various cellular stresses that lead to cytochrome c release from the mitochondria and the formation of the apoptosome, comprised of APAF1, cytochrome c, ATP, and caspase-9, resulting in the activation of caspase-9. Active caspase-9 then initiates apoptosis by cleaving and thereby activating executioner caspases. The extrinsic apoptosis pathway is activated through the binding of a ligand to a death receptor, which in turn leads, with the help of the adapter proteins (FADD/TRADD), to recruitment, dimerization, and activation of caspase-8 (or 10). Active caspase-8 (or 10) then either initiates apoptosis directly by cleaving and thereby activating executioner caspase (-3, -6, -7), or activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway through cleavage of BID to induce efficient cell death. In a heat shock-induced death, caspase-2 induces apoptosis via cleavage of Bid.
Bcl-2 family members are divided into three subfamilies including (i) pro-survival subfamily members (Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, Bcl-W, MCL1, and BFL1/A1), (ii) BH3-only subfamily members (Bad, Bim, Noxa, and Puma9), and (iii) pro-apoptotic mediator subfamily members (Bax and Bak). Following activation of the intrinsic pathway by cellular stress, pro‑apoptotic BCL‑2 homology 3 (BH3)‑only proteins inhibit the anti‑apoptotic proteins Bcl‑2, Bcl-xl, Bcl‑W and MCL1. The subsequent activation and oligomerization of the Bak and Bax result in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). This results in the release of cytochrome c and SMAC from the mitochondria. Cytochrome c forms a complex with caspase-9 and APAF1, which leads to the activation of caspase-9. Caspase-9 then activates caspase-3 and caspase-7, resulting in cell death. Inhibition of this process by anti‑apoptotic Bcl‑2 proteins occurs via sequestration of pro‑apoptotic proteins through binding to their BH3 motifs.
One of the most important ways of triggering apoptosis is mediated through death receptors (DRs), which are classified in TNF superfamily. There exist six DRs: DR1 (also called TNFR1); DR2 (also called Fas); DR3, to which VEGI binds; DR4 and DR5, to which TRAIL binds; and DR6, no ligand has yet been identified that binds to DR6. The induction of apoptosis by TNF ligands is initiated by binding to their specific DRs, such as TNFα/TNFR1, FasL /Fas (CD95, DR2), TRAIL (Apo2L)/DR4 (TRAIL-R1) or DR5 (TRAIL-R2). When TNF-α binds to TNFR1, it recruits a protein called TNFR-associated death domain (TRADD) through its death domain (DD). TRADD then recruits a protein called Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD), which then sequentially activates caspase-8 and caspase-3, and thus apoptosis. Alternatively, TNF-α can activate mitochondria to sequentially release ROS, cytochrome c, and Bax, leading to activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and thus apoptosis. Some of the miRNAs can inhibit apoptosis by targeting the death-receptor pathway including miR-21, miR-24, and miR-200c.
p53 has the ability to activate intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis by inducing transcription of several proteins like Puma, Bid, Bax, TRAIL-R2, and CD95.
Some inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) can inhibit apoptosis indirectly (such as cIAP1/BIRC2, cIAP2/BIRC3) or inhibit caspase directly, such as XIAP/BIRC4 (inhibits caspase-3, -7, -9), and Bruce/BIRC6 (inhibits caspase-3, -6, -7, -8, -9).
Any alterations or abnormalities occurring in apoptotic processes contribute to development of human diseases and malignancies especially cancer.
References:
1.Yağmur Kiraz, Aysun Adan, Melis Kartal Yandim, et al. Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis[J]. Tumor Biology, 2016, 37(7):8471.
2.Aggarwal B B, Gupta S C, Kim J H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey.[J]. Blood, 2012, 119(3):651.
3.Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother W J, Leverson J D, et al. From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors[J]. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2017.
4.McIlwain D R, Berger T, Mak T W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease[J]. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 2013, 5(4): a008656.
5.Ola M S, Nawaz M, Ahsan H. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis[J]. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 2011, 351(1-2): 41-58.
Products for Apoptosis
- Caspase(99)
- 14.3.3 Proteins(1)
- Apoptosis Inducers(43)
- Bax(7)
- Bcl-2 Family(120)
- Bcl-xL(8)
- c-RET(9)
- IAP(27)
- KEAP1-Nrf2(66)
- MDM2(12)
- p53(123)
- PC-PLC(4)
- PKD(7)
- RasGAP (Ras- P21)(1)
- Survivin(8)
- Thymidylate Synthase(10)
- TNF-α(145)
- Other Apoptosis(883)
- APC(6)
- PD-1/PD-L1 interaction(90)
- ASK1(3)
- PAR4(2)
- RIP kinase(52)
- FKBP(20)
- Pyroptosis(31)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GC41183
α-Carotene
α-胡萝卜素
A precursor of vitamin A
-
GC45204
α-Ecdysone
蜕皮激素; α-Ecdysone
蜕皮激素(α-蜕皮激素)是一种存在于昆虫和植物中的类固醇蜕皮激素,可激活盐皮质激素受体(MR),从而导致肾小球疾病。
-
GC48292
α-MSH (human, mouse, rat, porcine, bovine, ovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Α-促黑激素,α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone TFA
A peptide hormone
-
GC45213
α-NETA
2-(BETA-萘甲酰基)乙基三甲基碘化铵
An inhibitor of choline acetyltransferase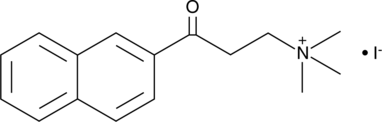
-
GC41499
α-Phellandrene
水芹烯
A monoterpene with diverse biological activities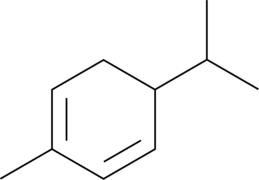
-
GC63941
α-Solanine
α-茄碱
α-solanine 是马铃薯中的一种生物活性成分,是主要的甾体类生物碱之一,可抑制癌细胞的生长并诱导其凋亡 (apoptosis)。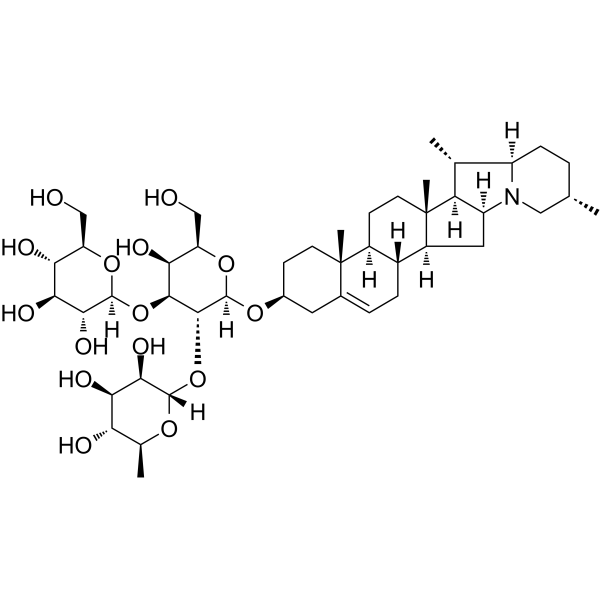
-
GC67618
α-Tocopherol phosphate disodium
alpha-Tocopherol phosphate disodium; TocP disodium; Vitamin E phosphate disodium
α-Tocopherol phosphate (alpha-Tocopherol phosphate) 是一种抗氧化剂,可以保护长波 UVA1 诱导的细胞死亡,并清除 UVA1 诱导的活性氧 (ROS)。α-Tocopherol phosphate disodium 可抑制内皮祖细胞凋亡 (apoptosis),增加高糖/低氧条件下内皮祖细胞迁移能力,促进血管生成。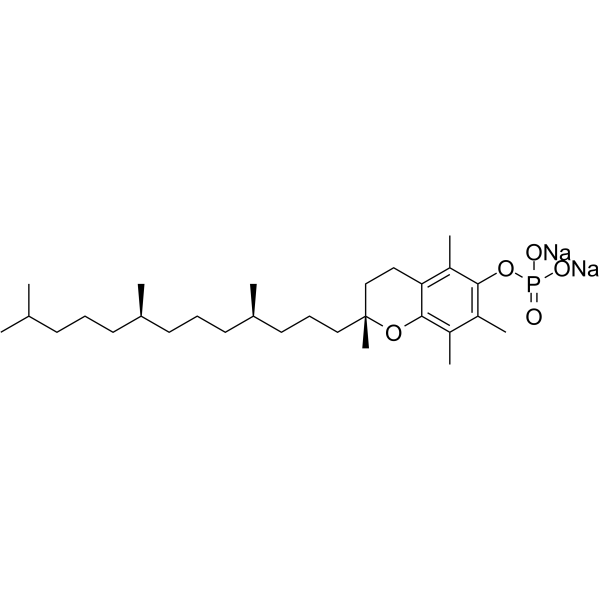
-
GC48920
β-Carboline-1-carboxylic Acid
1-Formic Acid-β-carboline
An alkaloid with diverse biological activities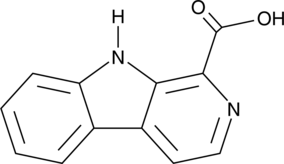
-
GC41623
β-Elemonic Acid
β-岚香酮酸
A triterpene with anticancer activity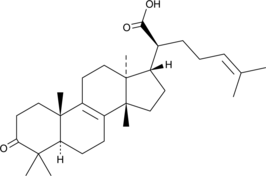
-
GC64619
β-Ionone
β-紫罗兰酮
β-Ionone 可有效诱导胃腺癌细胞 SGC7901 凋亡 (apoptosis)。具有抗肿瘤活性。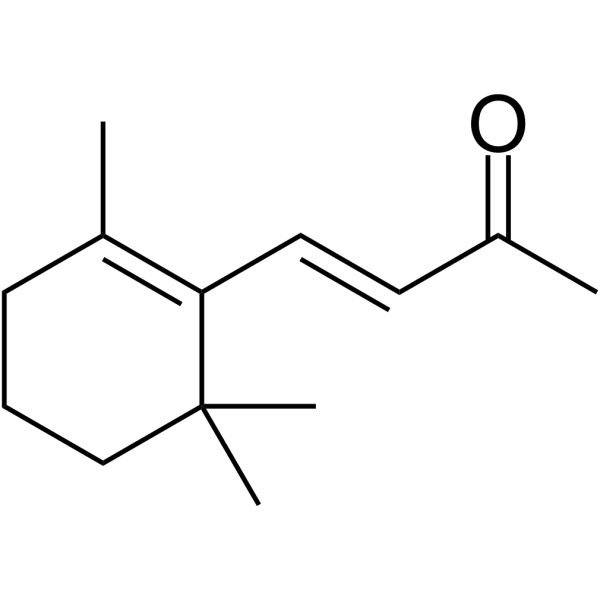
-
GC72061
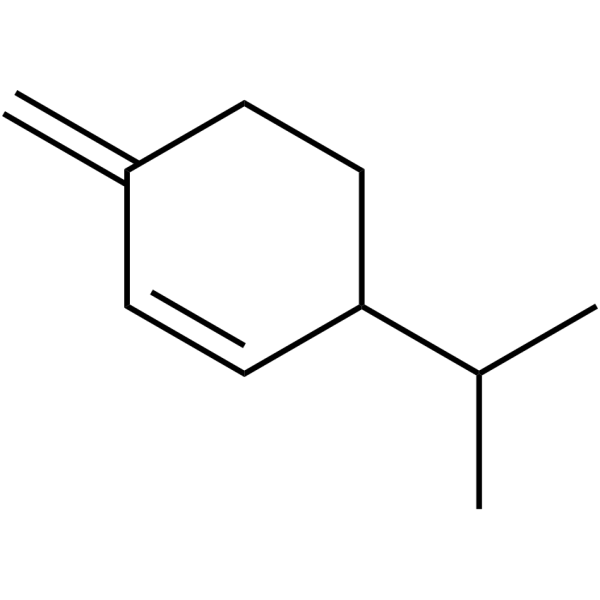
β-Phellandrene
β-Phellandrene是从岩骨中获得的。
-
GC66048
δ-Secretase inhibitor 11
Compound 11, a non-toxic and selective δ-secretase inhibitor (IC50=0.7 μM, in fluorescence-based assay) that interacts with both the active site and allosteric site of δ-secretase in Co-crystal structure analysis. The IC50 value of the compound 11 towards δ-secretase in Pala cells is 0.8 μM.
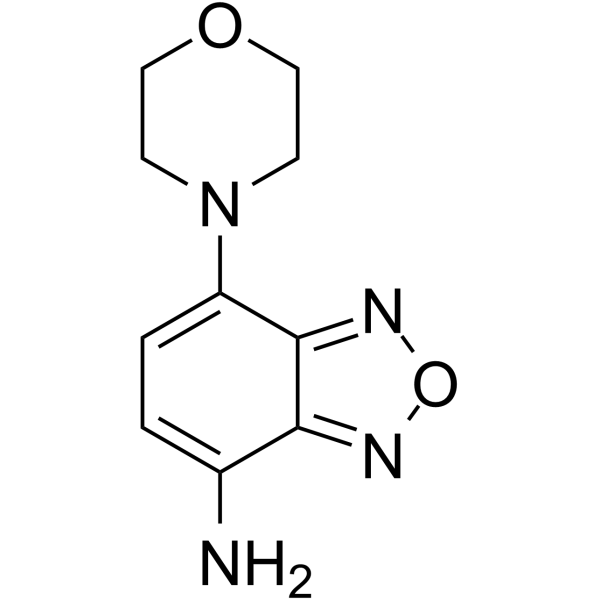
-
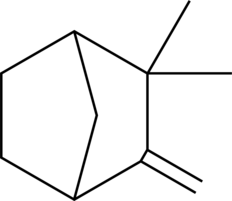
GC45277
(±)-Camphene
DL-Camphene, NSC 4165
-
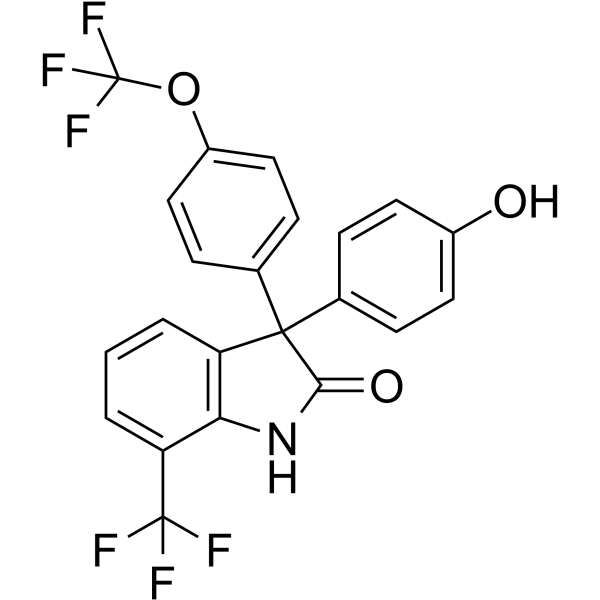
GC62383
(±)-ErSO
(±)-ErSO 是 ErSO 的消旋体。ErSO 是选择性预期未折叠蛋白反应 (a-UPR) 激活物。
-
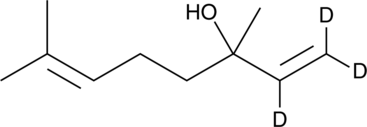
GC91298
(±)-Linalool-d3
dl-Linalool-d3
一种用于量化(±)-芳樟醇的内部标准。
-
GC46008
(±)-Thalidomide-d4
沙利度胺 D4
An internal standard for the quantification of (±)-thalidomide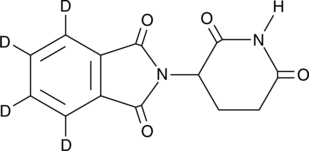
-
GC45618
(±)-trans-GK563
GK563
A GVIA iPLA2 inhibitor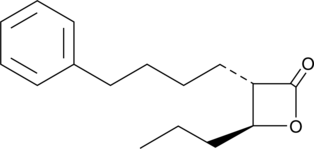
-
GC45270
(±)10(11)-EDP Ethanolamide
10,11-EDP-EA, 10,11-EDP epoxide, 10,11-epoxy Docosapentaenoic Ethanolamide
An ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and CB receptor agonist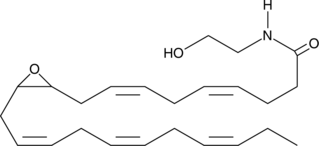
-
GC49268
(+)-δ-Cadinene
Δ-杜松烯
A sesquiterpene with antimicrobial and anticancer activities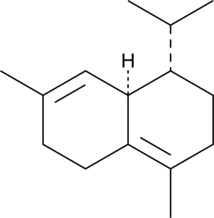
-
GC18516
(+)-Aeroplysinin-1
(+)-Aeroplysinin-1
A sea sponge metabolite with diverse biological activities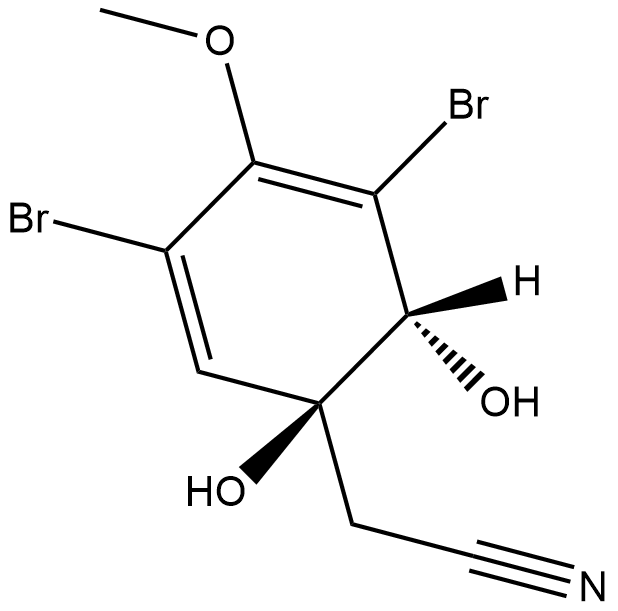
-
GC17008
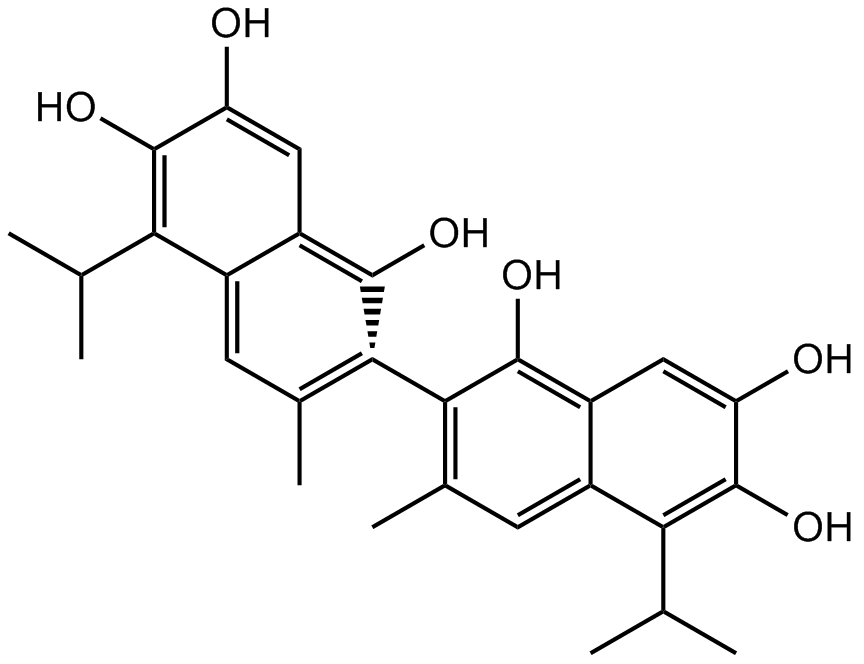
(+)-Apogossypol
變棉子酚,Apogossypol; NSC736630
(+)-Apogossypol 是一种泛 BCL-2 拮抗剂。 (+)-Apogossypol 与 Mcl-1、Bcl-2 和 Bcl-xL 结合,EC50 分别为 2.6、2.8 和 3.69 μM。
-
GC45256
(+)-ar-Turmerone
(6S)-2-甲基-6-(4-甲基苯基)-2-庚烯-4-酮,(+)-ar-Turmerone
A natural compound with immunomodulatory activities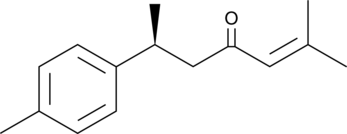
-
GN10654
(+)-Corynoline
紫蓳灵
An isoquinoline alkaloid with diverse biological activities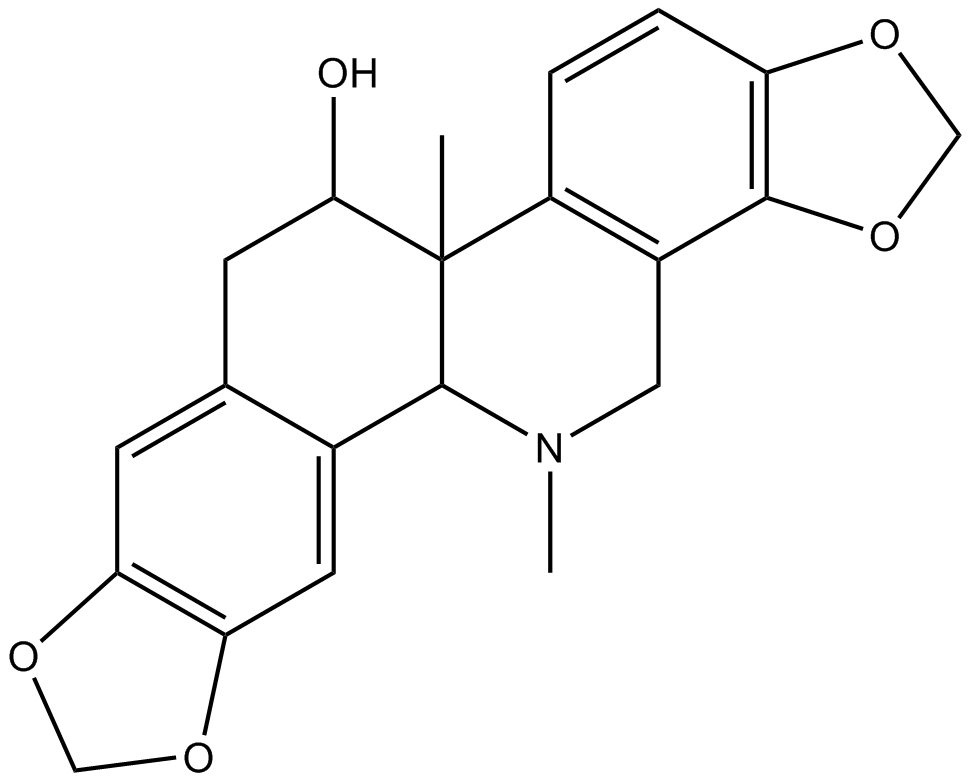
-
GC31691
(+)-DHMEQ
(1R,2R,6R)-Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin; (1R,2R,6R)-DHMEQ
(+)-DHMEQ 是抗氧化转录因子 Nrf2 的激活剂。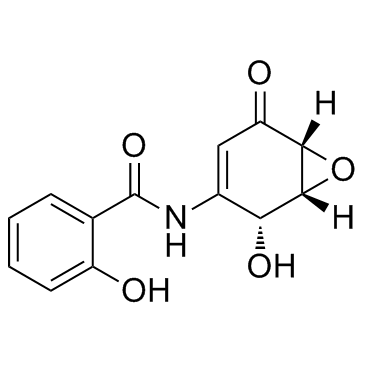
-
GC70332
(+)-Erinacin A
(+)-Erinacin A是一种抗癌化合物,可以从蘑菇猴头菇中分离出来。
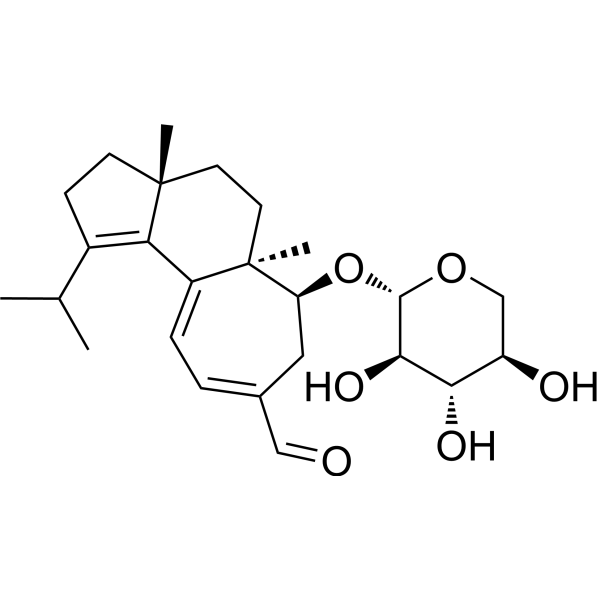
-
GC45265
(+)-Goniothalesdiol
A natural product with cytotoxic activity
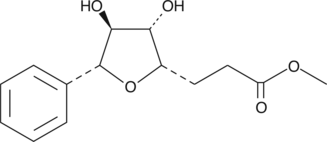
-
GC45274
(+)-Pinoresinol
松脂素,(+)-Pinoresinol
A lignan with diverse biological activities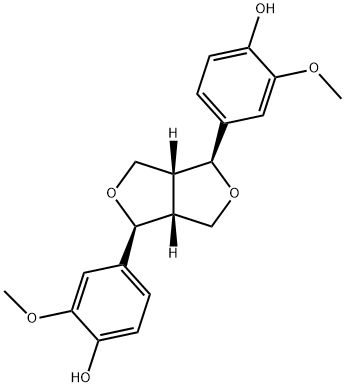
-
GC18749
(+)-Rugulosin
细皱青霉素+FORM,(+)-Rugulosin
A mycotoxin
-
GC41345
(-)-α-Bisabolol
没药醇; (-)-α-Bisabolol
A sesquiterpene alcohol with diverse biological activities
-
GC49502
(-)-β-Sesquiphellandrene
Β-倍半水芹烯
A sesquiterpene with antiviral and anticancer activities
-
GC45244
(-)-(α)-Kainic Acid (hydrate)
红藻氨酸
An L-glutamate analog with neuroexcitatory activities
-
GC45246
(-)-Chaetominine
(-)-Chaetominine
A cytotoxic alkaloid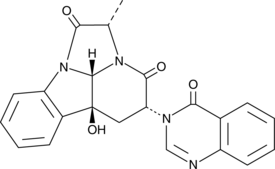
-
GC40218
(-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate-d3/d4
EGCG-d3/d4
An internal standard for the quantification of (–)-epigallocatechin gallate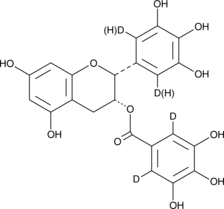
-
GC40698
(-)-Perillyl Alcohol
紫苏醇
A monoterpene alcohol with diverse biological activities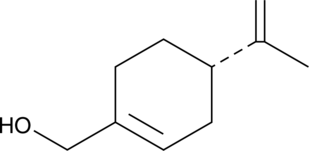
-
GC40076
(-)-Voacangarine
NSC 306219, (-)-Voacristine
A cytotoxic indole alkaloid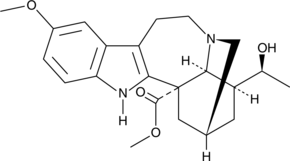
-
GC62193
(1S,2S)-Bortezomib
硼替佐米杂质E
(1S,2S)-Bortezomib 是 Bortezomib 的对映异构体。Bortezomib 是一种细胞渗透性、可逆性和选择性的蛋白酶体抑制剂,通过靶向苏氨酸残基有效抑制 20S 蛋白酶体 (Ki 为 0.6 nM)。Bortezomib 破坏细胞周期、诱导细胞凋亡以及抑制核因子 NF-κB。Bortezomib 是一种抗癌药物,也是第一种用于人类的蛋白酶体抑制剂。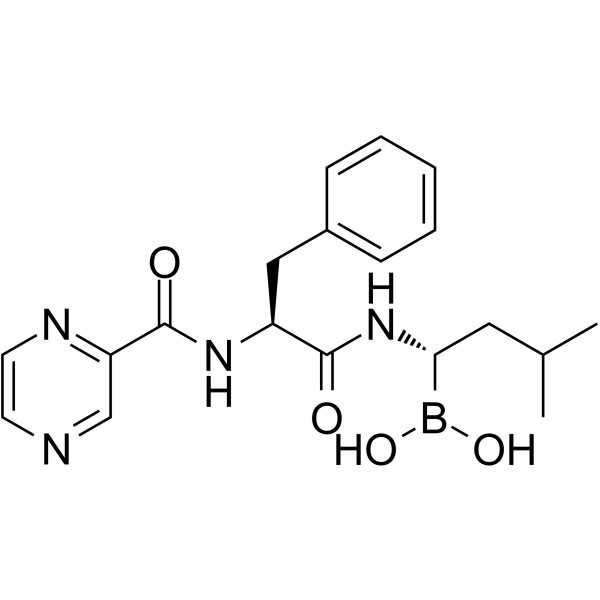
-
GC34965
(20S)-Protopanaxatriol
20 (S)-原人参三醇; 20(S)-APPT; g-PPT
An active ginsenoside metabolite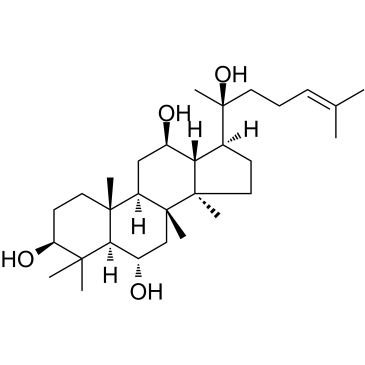
-
GC60397
(5Z,2E)-CU-3
A DGK-α inhibitor
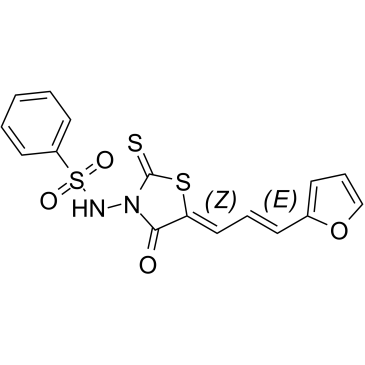
-
GC60398
(6R)-FR054
(3AR,7AR)-5-(乙酰氧基甲基)-2-甲基-5,6,7,7A-四氢-3AH-吡喃并[3,2-D]噁唑-6,7-叉基二醋酸盐
(6R)-FR054是FR054的一个活性异构体。FR054是HBP酶PGM3的抑制剂,具有显著的抗乳腺癌活性。FR054可诱导内质网应激和ROS依赖的细胞凋亡。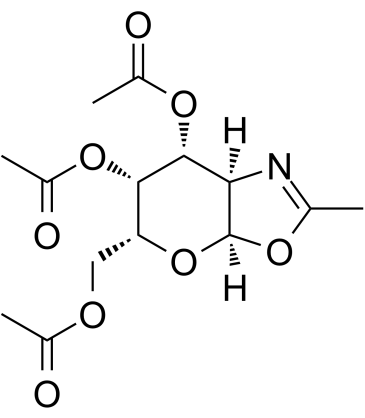
-
GC50482
(D)-PPA 1
An inhibitor of the PD-1-PD-L1 protein-protein interaction
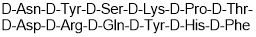
-
GC69009
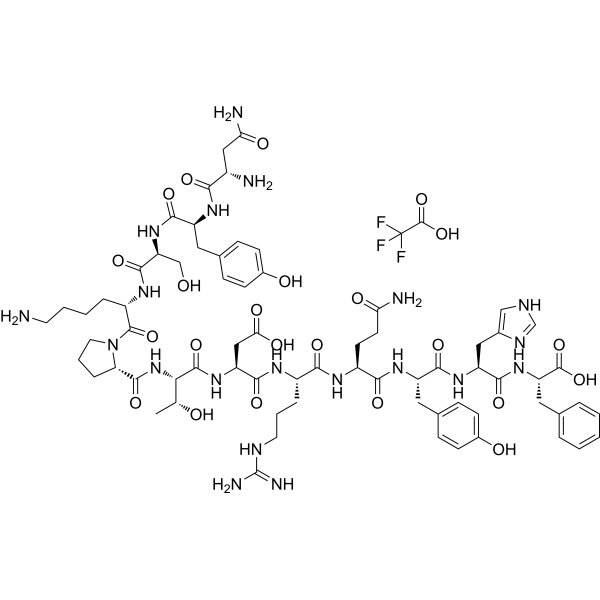
(D)-PPA 1 TFA
(D)-PPA 1 TFA 是一种抗水解 D 肽拮抗剂。(D)-PPA 1 TFA 是一种有效的 PD-1/PD-L1 抑制剂。(D)-PPA 1 TFA 与 PD-1 结合的亲和力为 0.51 μM,体内外均有效。
-
GC41698
(D)2-Rh 110 (trifluoroacetate salt)
D2R, (Asp)2-Rhodamine 110, Rhodamine 110 bis-(L-aspartic acid amide)
A fluorogenic caspase substrate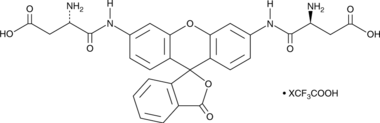
-
GA20156
(D-Ser(tBu)⁶,Azagly¹⁰)-LHRH (free base)
戈舍瑞林; ICI 118630

-
GC41700
(E)-2-(2-Chlorostyryl)-3,5,6-trimethylpyrazine
CSTMP
A stilbene derivative with antioxidant and anticancer activities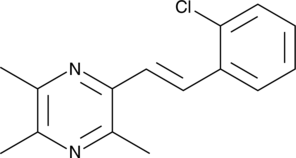
-
GC41268
(E)-2-Hexadecenal
trans-2-Hexadecenal
A long-chain fatty aldehyde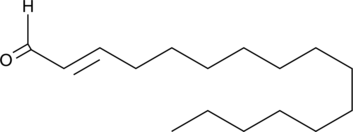
-
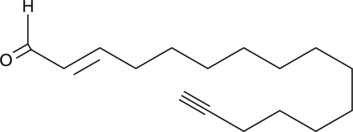
GC41701
(E)-2-Hexadecenal Alkyne
A click chemistry probe for a sphingolipid degradation product
-
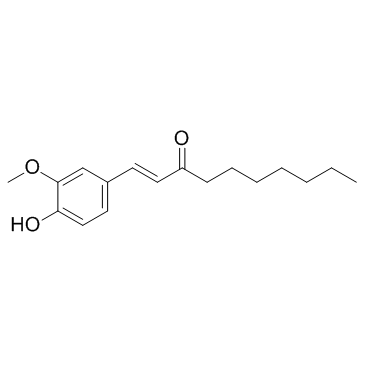
GC34125
(E)-[6]-Dehydroparadol
(E)-[6]-Dehydroparadol来自专利US9272994化合物M15,能够抑制人体癌细胞生长并且诱导细胞凋亡。在HCT-116和H-1299细胞中的IC50值分别为43.02和41.59μM。
-
GC34980
(E)-Ferulic acid
反式阿魏酸,(E)-Coniferic acid
Trans-ferulic acid is a potent activator of AMPKunder high glucose condition.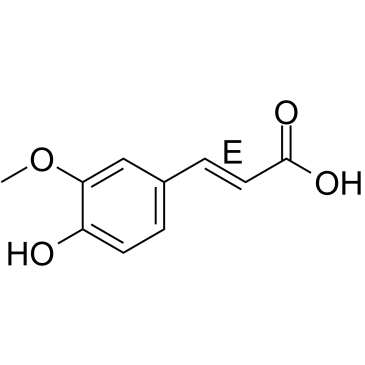
-
GC34981
(E)-Flavokawain A
卡瓦胡椒素A
A chalcone with diverse biological activities
-
GC61437
(E)-Methyl 4-coumarate
4-羟基肉桂酸甲酯; Methyl trans-p-coumarate
A phenol with diverse biological activities