Hormones(荷尔蒙)
The word Hormone comes means, "to spur on" which reflects how hormones acts as catalysts for other chemical changes at the cellular level necessary for growth, development, and energy.
Hormones are chemical messengers that carry and travel signals in the blood stream from 1 cell or glands to other tissues and organsto maintain chemical levels in the bloodstream that achieve homeostasis. All cellular organisms produce hormones.
Hormones also regulate the function of their target cells whicht express a receptor for the hormone. The action of hormones is determined by numerous factors such as its pattern of secretion and the response of the receiving tissue (signal transduction response).
Though few hormones circulate dissolved in the blood-stream, most are carried in the blood, bound to plasma proteins. For example, steroid hormones which are highly hydrophobic, are transported bound to plasma proteins.
An Example of antagonistic pairs of hormones is the Insulin, which causes the level of glucose to drop when it has risen and Glucagon causes blood sugar to rise when it has fallen.
There are two major classes of hormones 1. Proteins, Peptides, and modified amino acids 2. Steroids. In general, steroids are sex hormones related to sexual maturation and fertility. Steroids are made from cholesterol by placenta by our adrenal gland or gonads (testes or ovaries). Peptides regulate functions such as sleep and sugar concentration. They are made from long strings of amino acids, so sometimes they are referred to as "protein" hormones. Growth hormone, for example, helps us burn fat and build up muscles. Another peptide hormone, insulin, starts the process to convert sugar into cellular energy.
Hormones so perfectly and efficiently manage homeostasis due to negative feedback cycles. Our goal is to keep the concentration of a certain chemical, such as testosterone, at a constant level for a certain period of time, the way that a thermostat works. Using negative feedback, a change in conditions causes a response that returns the conditions to their original state. When a room's temperature drops, the thermostat responds by turning the heat on. The room returns to the ideal temperature, and the heater turns off, keeping the conditions relatively constant.
Endocrine hormone are secreted into the blood and carried by blood and tissue fluids to the cells they act upon, while exocrine hormones are secreted into a duct, and then into the bloodstream. Exocrine hormones are transferred from cell to cell by diffusion (paracrine signaling).
Hormones work slowly, over time, and affect many different processes in the body, such as Growth & development, Metabolism, Sexual function, Reproduction Mood,
Endocrine glands, etc… The major endocrine glands are the pituitary, pineal, thymus, thyroid, adrenal glands and pancreas. In addition, men produce hormones in their testes and women produce them in their ovaries.
Hormones have large effects and it takes picogram amounts to cause big changes in cells or even your whole body. That is why too much or too little of a certain hormone can cause harsh problems and complications. In Laboratory experiments, one can measure hormone levels in blood, urine or saliva.
The hormone levels circulating in the blood stream are controlled by a homeostatic mechanism, such as 1 hormone stimulates the production of a 2nd, the 2nd suppresses the production of the 1st .
For Instance, FSH stimulates the release of estrogens from the ovarian follicle but at high levels of estrogen itsuppresses the further production of FSH.
1 major class of hormones is the Proteins, Peptides and modified amino acids which are hydrophilic (and mostly large) hormone molecules that bind to receptors on the surface of "target" cells, cells are able to respond to the presence of the hormone. These receptors are transmembrane proteins. Binding of the hormone to its receptor initiates a sequence of intracellular signals that alters the behavior of the cell (opening or closing of the membrane channels) or stimulate (or repress) gene expression in the nucleus by turning on (or off) the promoters and enhancers of the genes.
A hormone binds to a site on the extracellular portion of the receptor which acts as transmembrane protein that pass through the plasma membrane x7, with theN-terminal exposed at the exterior of the cell and the C-terminal projecting into the cytoplasm.
Once the hormone binds to the receptor it activates a G protein associated with the cytoplasmic C-terminal which initiates production of a 2nd messenger such as cyclic AMP, (cAMP)which is produced by adenylyl cyclase from ATP, and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)
The 2nd messenger initiates a series of intracellular events such as phosphorylation and activation of enzymes, release of Ca2+ into the cytosol from stores within the endoplasmic reticulum.
cAMP activates the transcription factor CREB (cAMP response element binding protein) which turns on gene transcription. The cell begins to produce the appropriate gene products in response to the hormonal signal it had received at its surface.
Steroid hormones are hydrophobic proteins/peptides and diffuse freely into cells. However, their "target" cells contain cytoplasmic and/or nuclear proteins that serve as receptors of the hormone. The hormone binds to the receptor and the complex binds to hormone response elements - stretches of DNA within the promoters of genes responsive to the hormone. The hormone/receptor complex acts as a transcription factor turning target genes "on" (or "off"). Hormones circulate freely in the bloodstream, waiting to be recognized by a target cell, their intended destination. The target cell has a receptor that can only be activated by a specific type of hormone. Once activated, the cell knows to start a certain function within its walls. Genes might get activated, or energy production resumed. As special categories, autocrine hormones act on the cells of the secreting gland, while paracrine hormones act on nearby, but unrelated, cells.
Hormone secretion is increased (or decreased) by the same substance whose level is decreased (or increased) by the hormone. The rising level of Ca2+ in the blood stream suppresses the production of PTH but a low level of Ca2+ stimulates it.
Products for Hormones
- Endothelin(3)
- Exendin(1)
- FSH(3)
- GHRP(7)
- GLP(4)
- Glucagon(4)
- HCG(2)
- Inhibin A(3)
- LHRH(3)
- Other Hormones(11)
- Peptide Hormones(114)
- Procalcitonin(7)
- PTH(9)
- Stanniocalcin(4)
- Thymosin(3)
- Thyrostimulin(2)
- TSH(2)
- Thyroid Hormones(2)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP21260
Glucagon Human, His
Glucagon Human Recombinant, His Tag

-
GC49342
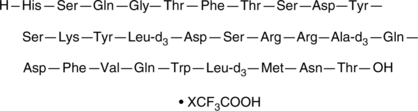
Glucagon-d9 (trifluoroacetate salt)
An internal standard for the quantification of glucagon
-
GC91868
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (1-39) (porcine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (1-39),GIP (1-39)
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) (1-39) is an endogenous 39-amino acid peptide hormone that induces insulin secretion.
-
GC92133
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (1-42) (porcine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (1-42); GIP (1-42)
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (1-42) (porcine) (trifluoroacetate salt)是一种内源性42个氨基酸的肽肠促胰岛素激素,可诱导胰岛素分泌。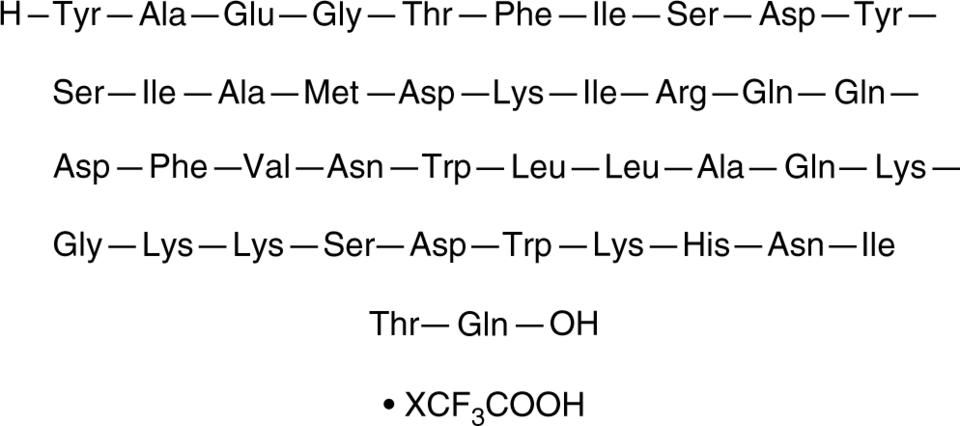
-
GC91870
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (3-42) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide 1 (3-42),GIP-1 (3-42)
Gastric inhibitory peptide 1 (GIP-1) (3-42) is a peptide fragment of the incretin hormone GIP and a GIP receptor antagonist.
-
GC92134
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide; GIP
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)是一种内源性42个氨基酸的肽促胰岛素素激素,在葡萄糖反应中诱导胰岛素分泌。
-
GC43781
GnRH (free acid; trifluoroacetate salt)
Gonadorelin, Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone, LHRH
A biologically inactive form of GnRH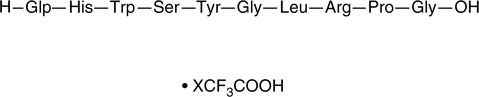
-
GC43782
GnRH II (trifluoroacetate salt)
Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone II, LHRH II
A GnRHR agonist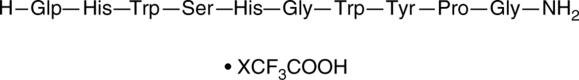
-
GP21262
Goserelin
Goserelin (ICI 118630) 是促性腺激素释放激素 (GnRH/LHRH) 的十肽类似物,可作为 GnRH 激动剂发挥作用。

-
GP21263
GPHA2 Human
Thyrostimulin Alpha Human Recombinant

-
GP21264
GPHB5 Human
Thyrostimulin Beta Human Recombinant

-
GC49048
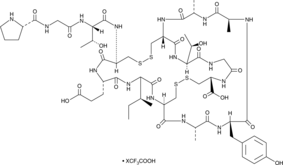
Guanylin (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
A peptide hormone activator of GC-C
-
GP21265
GUCA2B Human
Prouroguanylin Human Recombinant

-
GP21266
hCG Protein
人绒毛膜促性腺激素

-
GC49543
Hepcidin-25 (trifluoroacetate salt)
H-DTHFPICIFCCGCCHRSKCGMCCKT-OH
A peptide hormone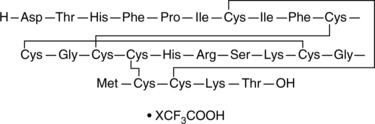
-
GP21267
Hexarelin
Hexarelin

-
GP21268
Histrelin
Histrelin 是一种 GnRH 类似物,是一种 GnRH 受体激动剂。 Histrelin 增加血清黄体生成素 (LH)、促卵泡激素 (FSH) 和睾酮水平。 Histrelin 可用于前列腺癌、子宫内膜异位症的研究。

-
GC92091
hMC1R Agonist 1 (acetate)
Ac-Nle-[CHfRWC]-NH2; Ac-Nle-[Cys-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Cys]-NH2
hMC1R Agonist 1 (acetate)是黑皮质素受体1(MC1R)的肽激动剂和黑素蛋白II的衍生物。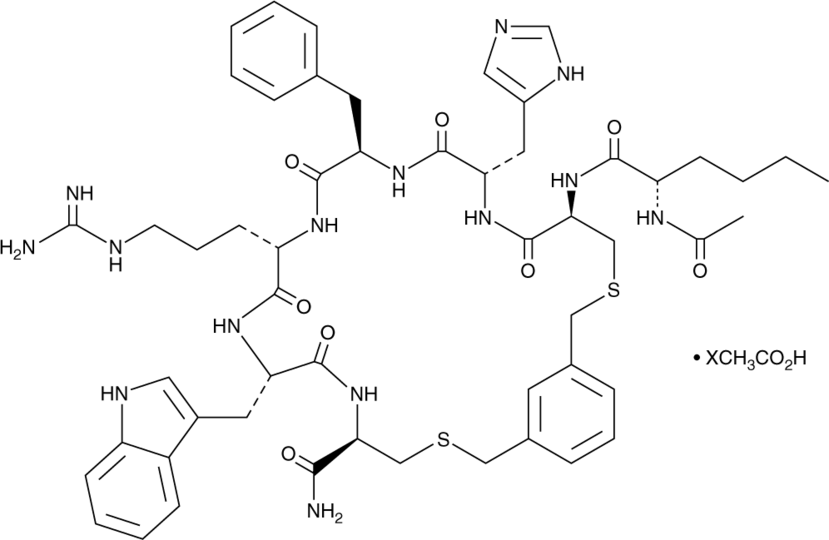
-
GC92103
HS-014 (trifluoroacetate salt)
Cyclic [Ac-Cys11, D-Nal14, Cys18, Asp-NH2]-β-MSH(11-22)
HS-014 (trifluoroacetate salt)是黑素皮质素受体4mc4r的拮抗剂;Ki = 3.16 nM。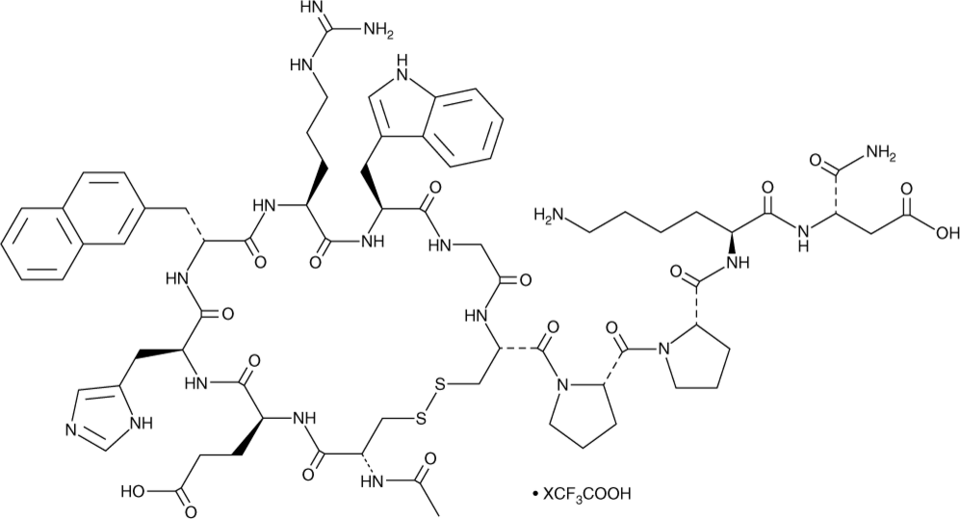
-
GC92098
HS-024 (trifluoroacetate salt)
Ac-Cys-Nle-Arg-His-D-Nal-Arg-Trp-Gly-Cys-NH2; cyclic [AcCys3,Nle4,Arg5,D-Nal7,Cys-NH211]α-MSH-(3-11)
HS-024 (trifluoroacetate salt)是黑皮质素受体4的环肽拮抗剂(MC4R;Ki=0.29nM)。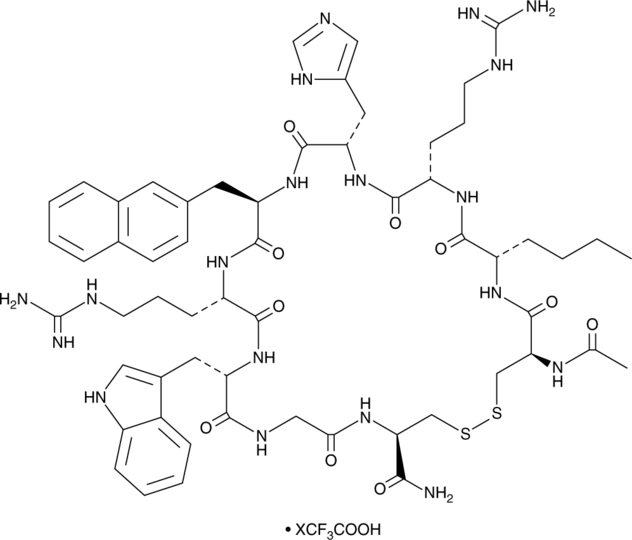
-
GP21271
INHBC Human
Inhibin-Beta C Chain Human Recombinant

-
GP21269
Inhibin a Human
Inhibin Alpha Human Recombinant

-
GP21270
Inhibin alpha A Chain Human
Inhibin-Alpha A Chain Human Recombinant

-
GP26111
Ipamorelin
Ipamorelin Synthetic is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 4 amino acids, having a molecular mass of 711

-
GC92122
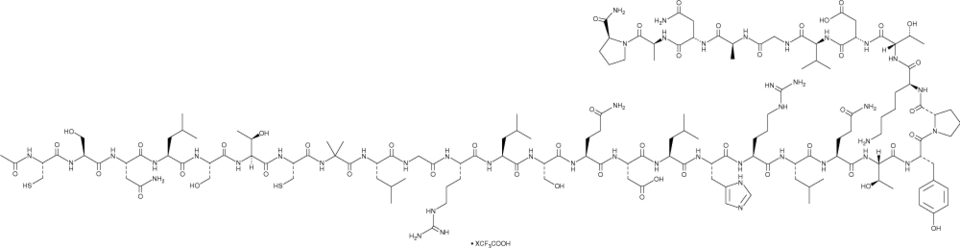
KBP-066 (trifluoroacetate salt)
KBP-066 (trifluoroacetate salt)是一种胰淀素和降钙素双重CT受体激动剂。
-
GC91889
L-Tyrosine (sodium salt hydrate)
L-4-Hydroxyphenylalanine; p-Hydroxyphenylalanine; (-)-Tyrosine; p-Tyrosine
L-Tyrosine (sodium salt hydrate)是一种条件必需氨基酸。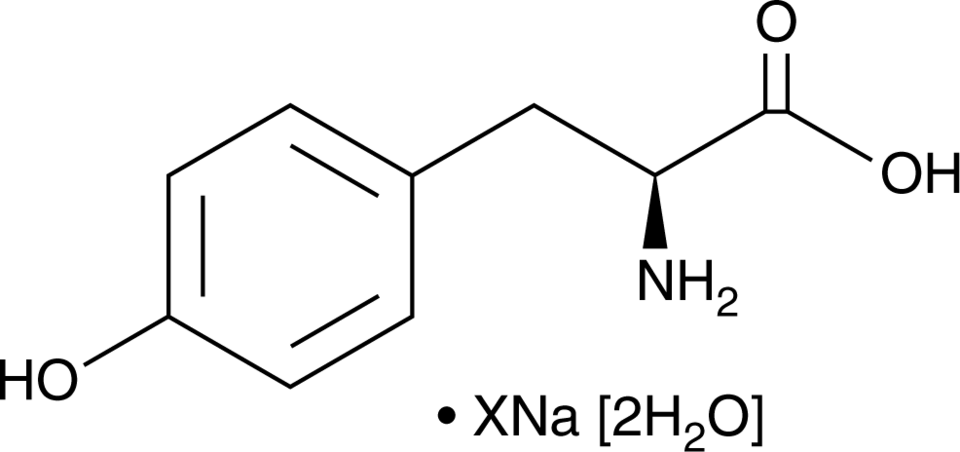
-
GP21272
Lanreotide
Lanreotide (BIM 23014) 是一种具有抗肿瘤活性的生长抑素类似物。

-
GP21273
Leuprorelin Human
Leuprolide Human

-
GP21283
LH Porcine
促黄体激素猪

-
GP21275
LHRH Human
Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone Human

-
GP21274
LHRH Protein
Luteinizing Hormone Releasing Hormone Human Recombinant

-
GC92125
Liraglutide (acetate)
NN 2211
Liraglutide (acetate)是胰高血糖素样肽1(GLP-1)受体的强效激动剂,也是含有棕榈酸基团的GLP-1(7-37)的合成衍生物。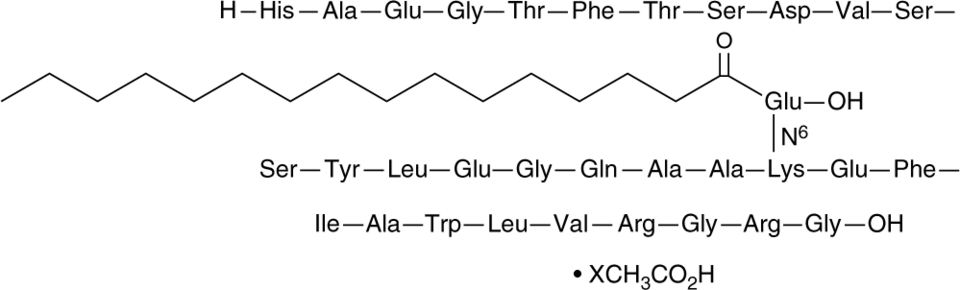
-
GC92038
Lotiglipron (hydrochloride)
PF-07081532
Lotiglipron (hydrochloride)是一种胰高血糖素样肽1受体GLP-1R激动剂。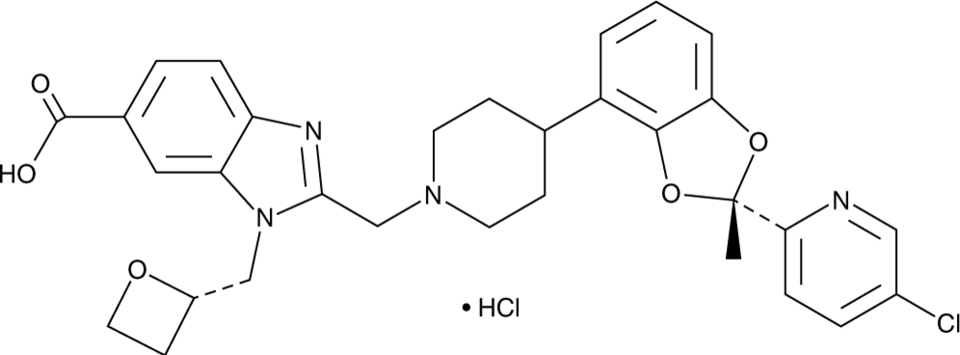
-
GP21276
Lypressin
Lypressin

-
GC92036
MCL0020 (trifluoroacetate salt)
Ac-D-2Nal-Arg-2-Nal-NH2
MCL0020 (trifluoroacetate salt)是一种黑素皮质素受体4mc4r拮抗剂。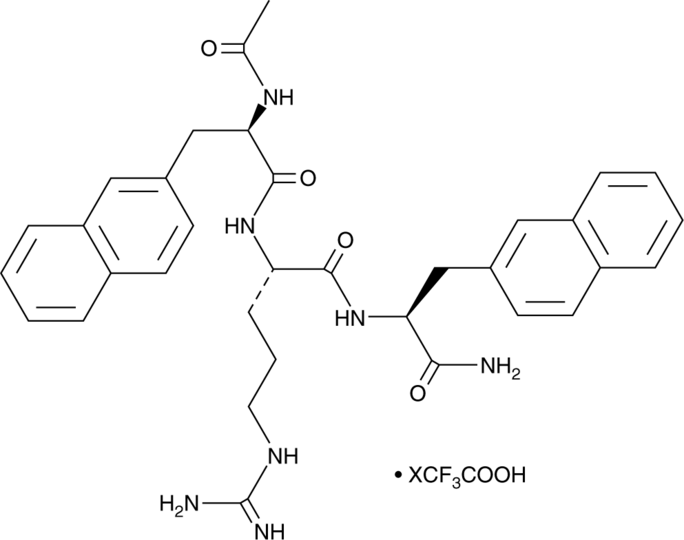
-
GC92129
Melanostatin (frog, eel) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Neuropeptide Y; NPY
Melanostatin (frog, eel) (trifluoroacetate salt)是一种内源性肽。
-
GP21277
MG Human
Menopausal Gonadotropin Human

-
GC18349
Motilin (porcine)
A polypeptide hormone

-
GP21278
MT I
Melanotan-I

-
GP21279
MT II
Melanotan-II

-
GC44293
N-Acetyl ACTH (1-17) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Ac-SYSMEHFRWGKPVGKKR, N-Acetyl Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (1-17)
An N-terminal peptide fragment of ACTH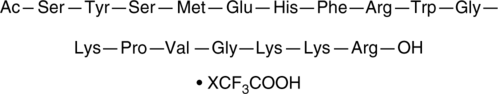
-
GP21280
NAF
Nafarelin Acetate

-
GC92100
Neuropeptide EI (rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
NEI; Neuropeptide-Glutamic Acid-Isoleucine
Neuropeptide EI (rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)是大鼠前黑色素浓缩激素MCH的内源性肽片段,参与激素释放、梳理行为和运动活动。
-
GC92131
NN1177 (trifluoroacetate salt)
NN1177 (trifluoroacetate salt)是胰高血糖素受体(GCGR)和胰高血糖激素样肽1受体(GLP-1R)的双肽激动剂。
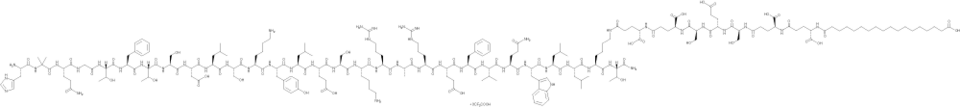
-
GC48328
Obestatin (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
A peptide hormone

-
GC44484
Obestatin (rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
A peptide hormone

-
GP21281
OCT Human
Octreotide Human

-
GP21282
OT Human
Oxytocin Human

-
GP21285
OXM Porcine
Oxyntomodulin Porcine Recombinant

-
GC44525
Oxyntomodulin (human, mouse, rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glicentin (33-69), Proglucagon (33-69)
A peptide hormone




