Hormones(荷尔蒙)
The word Hormone comes means, "to spur on" which reflects how hormones acts as catalysts for other chemical changes at the cellular level necessary for growth, development, and energy.
Hormones are chemical messengers that carry and travel signals in the blood stream from 1 cell or glands to other tissues and organsto maintain chemical levels in the bloodstream that achieve homeostasis. All cellular organisms produce hormones.
Hormones also regulate the function of their target cells whicht express a receptor for the hormone. The action of hormones is determined by numerous factors such as its pattern of secretion and the response of the receiving tissue (signal transduction response).
Though few hormones circulate dissolved in the blood-stream, most are carried in the blood, bound to plasma proteins. For example, steroid hormones which are highly hydrophobic, are transported bound to plasma proteins.
An Example of antagonistic pairs of hormones is the Insulin, which causes the level of glucose to drop when it has risen and Glucagon causes blood sugar to rise when it has fallen.
There are two major classes of hormones 1. Proteins, Peptides, and modified amino acids 2. Steroids. In general, steroids are sex hormones related to sexual maturation and fertility. Steroids are made from cholesterol by placenta by our adrenal gland or gonads (testes or ovaries). Peptides regulate functions such as sleep and sugar concentration. They are made from long strings of amino acids, so sometimes they are referred to as "protein" hormones. Growth hormone, for example, helps us burn fat and build up muscles. Another peptide hormone, insulin, starts the process to convert sugar into cellular energy.
Hormones so perfectly and efficiently manage homeostasis due to negative feedback cycles. Our goal is to keep the concentration of a certain chemical, such as testosterone, at a constant level for a certain period of time, the way that a thermostat works. Using negative feedback, a change in conditions causes a response that returns the conditions to their original state. When a room's temperature drops, the thermostat responds by turning the heat on. The room returns to the ideal temperature, and the heater turns off, keeping the conditions relatively constant.
Endocrine hormone are secreted into the blood and carried by blood and tissue fluids to the cells they act upon, while exocrine hormones are secreted into a duct, and then into the bloodstream. Exocrine hormones are transferred from cell to cell by diffusion (paracrine signaling).
Hormones work slowly, over time, and affect many different processes in the body, such as Growth & development, Metabolism, Sexual function, Reproduction Mood,
Endocrine glands, etc… The major endocrine glands are the pituitary, pineal, thymus, thyroid, adrenal glands and pancreas. In addition, men produce hormones in their testes and women produce them in their ovaries.
Hormones have large effects and it takes picogram amounts to cause big changes in cells or even your whole body. That is why too much or too little of a certain hormone can cause harsh problems and complications. In Laboratory experiments, one can measure hormone levels in blood, urine or saliva.
The hormone levels circulating in the blood stream are controlled by a homeostatic mechanism, such as 1 hormone stimulates the production of a 2nd, the 2nd suppresses the production of the 1st .
For Instance, FSH stimulates the release of estrogens from the ovarian follicle but at high levels of estrogen itsuppresses the further production of FSH.
1 major class of hormones is the Proteins, Peptides and modified amino acids which are hydrophilic (and mostly large) hormone molecules that bind to receptors on the surface of "target" cells, cells are able to respond to the presence of the hormone. These receptors are transmembrane proteins. Binding of the hormone to its receptor initiates a sequence of intracellular signals that alters the behavior of the cell (opening or closing of the membrane channels) or stimulate (or repress) gene expression in the nucleus by turning on (or off) the promoters and enhancers of the genes.
A hormone binds to a site on the extracellular portion of the receptor which acts as transmembrane protein that pass through the plasma membrane x7, with theN-terminal exposed at the exterior of the cell and the C-terminal projecting into the cytoplasm.
Once the hormone binds to the receptor it activates a G protein associated with the cytoplasmic C-terminal which initiates production of a 2nd messenger such as cyclic AMP, (cAMP)which is produced by adenylyl cyclase from ATP, and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)
The 2nd messenger initiates a series of intracellular events such as phosphorylation and activation of enzymes, release of Ca2+ into the cytosol from stores within the endoplasmic reticulum.
cAMP activates the transcription factor CREB (cAMP response element binding protein) which turns on gene transcription. The cell begins to produce the appropriate gene products in response to the hormonal signal it had received at its surface.
Steroid hormones are hydrophobic proteins/peptides and diffuse freely into cells. However, their "target" cells contain cytoplasmic and/or nuclear proteins that serve as receptors of the hormone. The hormone binds to the receptor and the complex binds to hormone response elements - stretches of DNA within the promoters of genes responsive to the hormone. The hormone/receptor complex acts as a transcription factor turning target genes "on" (or "off"). Hormones circulate freely in the bloodstream, waiting to be recognized by a target cell, their intended destination. The target cell has a receptor that can only be activated by a specific type of hormone. Once activated, the cell knows to start a certain function within its walls. Genes might get activated, or energy production resumed. As special categories, autocrine hormones act on the cells of the secreting gland, while paracrine hormones act on nearby, but unrelated, cells.
Hormone secretion is increased (or decreased) by the same substance whose level is decreased (or increased) by the hormone. The rising level of Ca2+ in the blood stream suppresses the production of PTH but a low level of Ca2+ stimulates it.
Products for Hormones
- Endothelin(3)
- Exendin(1)
- FSH(3)
- GHRP(7)
- GLP(4)
- Glucagon(4)
- HCG(2)
- Inhibin A(3)
- LHRH(3)
- Other Hormones(11)
- Peptide Hormones(114)
- Procalcitonin(7)
- PTH(9)
- Stanniocalcin(4)
- Thymosin(3)
- Thyrostimulin(2)
- TSH(2)
- Thyroid Hormones(2)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP26106
CRHBP (22-322), Human
CRHBP Human Recombinant produced in E

-
GP21236
CRHBP Human
Corticotropin Releasing Hormone Binding Protein Human Recombinant

-
GC92092
CTX-1211 (trifluoroacetate salt)
Acetyl-Arg-cyclo(Cys-D-Ala-Arg-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Cys)-NH2
CTX-1211 (trifluoroacetate salt)是黑皮质素受体的肽激动剂。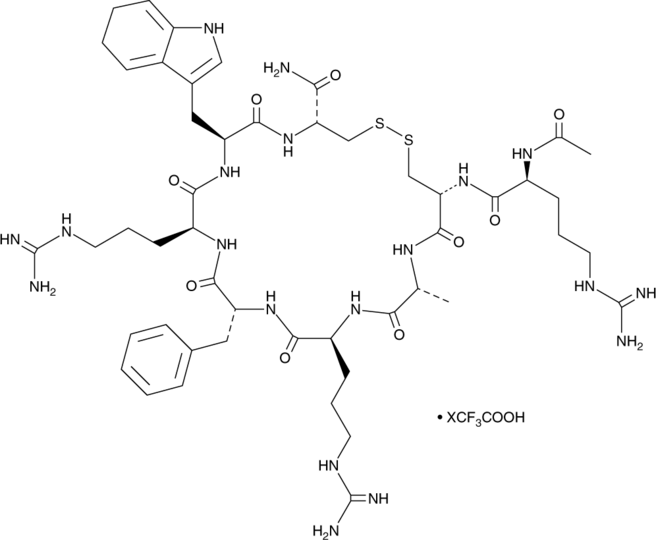
-
GC92128
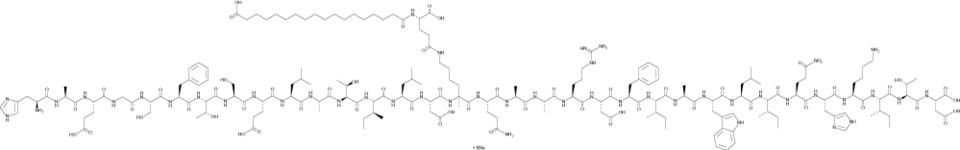
Dapiglutide (sodium salt)
Dapiglutide (sodium salt)是一种双胰高血糖素样肽1受体GLP-1R和GLP-2R激动剂。
-
GP21237
DDAVP
Desmopressin

-
GP21238
Deslorelin
Deslorelin

-
GC49143
Deslorelin (acetate)
D-Trp6-Pro9-des-Gly10-GnRH ethylamide, pGlu-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-D-Trp-Leu-Arg-Pro-NHEt
A peptide agonist of GnRH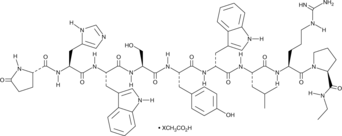
-
GC49459
Desmopressin (trifluoroacetate salt)
Adiuretin, DDAVP
A vasopressin receptor agonist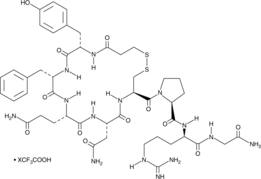
-
GP21239
EDN2 Human
Endothelin-2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21240
EDN3
Human Endothelin-3

-
GP21241
EDN3 Human
Endothelin-3 Human Recombinant

-
GP21242
Elcatonin
Elcatonin

-
GP21243
Exenatide
Exenatide

-
GP21245
FSH
FSH 是窦状卵泡的主要存活因子,已被认为可以提高 GC 对卵泡闭锁期间氧化应激的抵抗力。

-
GP21246
FSH Human
FSH Human是人重组卵泡刺激激素

-
GP21247
FSH Porcine
猪卵泡刺激素

-
GP21248
Ganirelix
Ganirelix 是一种竞争性和选择性促性腺激素释放激素 (GnRH) 拮抗剂。

-
GC90534
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (1-39) (porcine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
GIP (1-39), Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (1-39)
一种促进胰岛素分泌的物质。

-
GC90545
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (1-42) (porcine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
GIP (1-42), Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (1-42)
一种肽类胰高血糖素激素。
-
GC90547
Gastric Inhibitory Peptide 1 (3-42) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
GIP-1 (3-42), Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide 3-42
GIP的肽段和GIP受体拮抗剂

-
GP21261
GCGR Human
Glucagon Receptor Human Recombinant

-
GC43752
Ghrelin (rat) (acetyl) (trifluoroacetate salt)
An acetylated form of ghrelin

-
GC43753
Ghrelin (rat) (palmitoyl) (trifluoroacetate salt)
A palmitoylated form of ghrelin
-
GC43754
Ghrelin (rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
A peptide hormone

-
GP21249
GHRH Human
生长激素释放激素人类

-
GP21251
GHRL Human
Ghrelin Human Recombinant

-
GP21252
GHRP 2 Human
Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-2 Human

-
GP21253
GHRP 6
Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-6

-
GP26107
GHRP1
Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-1 Synthetic is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 5 amino acids, having a molecular mass of 955

-
GP26108
GHRP4
Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-4 Synthetic is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 4 amino acids, having a molecular mass of 607

-
GP26109
GHRP5
Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-5 Synthetic is a single, non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 5 amino acids, having a molecular mass of 770

-
GP21256
GLP 1 Human
人胰高血糖素样肽-1

-
GP21255
GLP 1 Human (37 a.a.)
Human Glucagon Like Peptide-1 (37 a.a.)

-
GC91863
GLP-1 (1-32) (bullfrog) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (1-32)
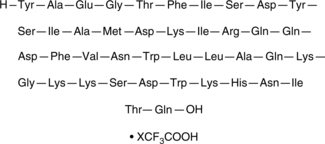
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) (1-32) is an endogenous incretin hormone.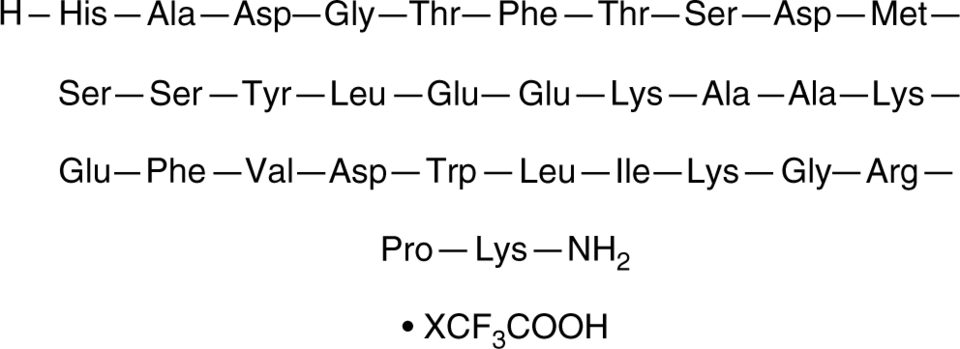
-
GC45462
GLP-1 (1-36) amide (human, rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (1-36) amide (human, rat)
A peptide hormone
-
GC92088
GLP-1 (28-36) amide (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (28-36) amide; Phe-Ile-Ala-Trp-Leu-Val-Lys-Gly-Arg-NH2
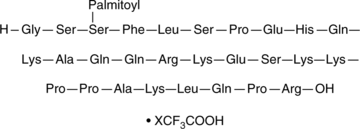
胰高血糖素样肽1GLP-1 (28-36) amide (trifluoroacetate salt)是内源性GLP-1R激动剂GLP-1(7-36)酰胺的肽和活性代谢产物。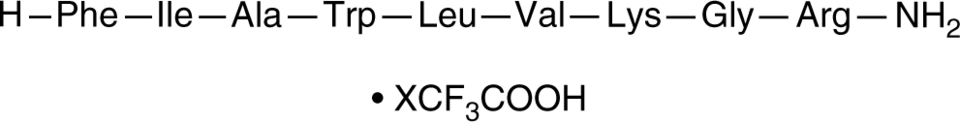
-
GC92058
GLP-1 (7-13) (human, mouse, rat, bovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (7-13); His-Ala-Glu-Gly-Thr-Phe-Thr-OH
GLP-1 (7-13) (human, mouse, rat, bovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)是内源性肠促胰岛素激素GLP-1的肽片段。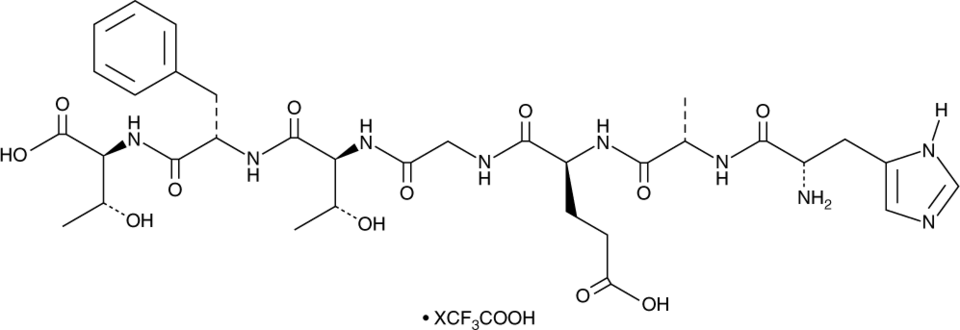
-
GC92079
GLP-1 (7-15) (human, mouse, rat, porcine, bovine, ovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (7-15)
GLP-1 (7-15) (human, mouse, rat, porcine, bovine, ovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)是内源性肠促胰岛素激素GLP-1的肽片段。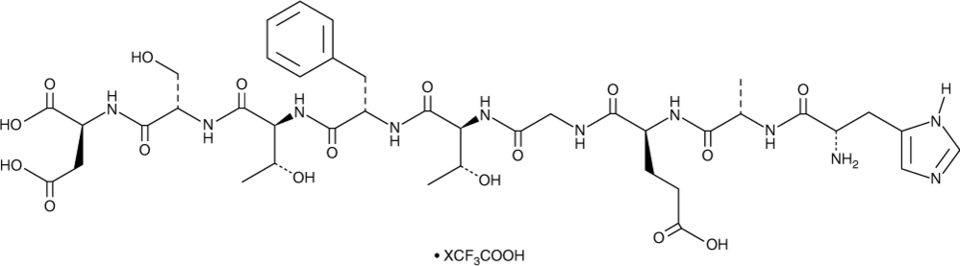
-
GC92093
GLP-1 (7-17) (human, mouse, rat, porcine, bovine, ovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (7-17)
GLP-1 (7-17) (human, mouse, rat, porcine, bovine, ovine) (trifluoroacetate salt)是内源性肠促胰岛素GLP-1的肽片段。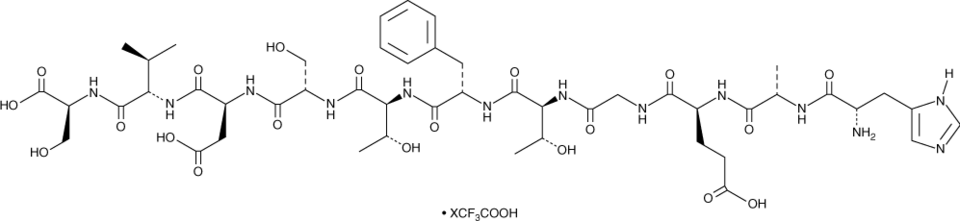
-
GC43762
GLP-1 (7-36) amide (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (7-36) amide
A GLP-1R agonist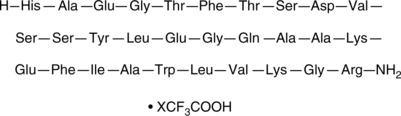
-
GC43763
GLP-1 (7-37) (human, bovine, guinea pig, mouse, rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (7-37) (human, bovine, guinea pig, mouse, rat)
An incretin hormone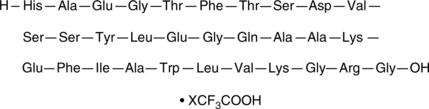
-
GP21254
GLP-1 Human (31 a.a.)
Glucagon Like Peptide-1 (31 a.a.) Human Recombinant

-
GC90250
GLP-2 (1-34) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 2 (1-34)
一种合成的GLP-2肽形式。

-
GC45463
GLP-2 (1-34) (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 2 (1-34)
A synthetic form of the peptide GLP-2
-
GC43764
GLP-2 (human) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide-2
A peptide hormone
-
GC90251
GLP-2 (rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 2
一种肠道多肽激素GLP-2R的拮抗剂

-
GC45464
GLP-2 (rat) (trifluoroacetate salt)
Glucagon-like Peptide 2
A gut peptide hormone antagonist of GLP-2R
-
GP26110
GLP1R Human
GLP1R Human Recombinant produced in E

-
GP21258
Glucagon (1-29), bovine, human, porcine
胰高血糖素; Porcine glucagon
胰高血糖素是一种由 29 个氨基酸组成的肽,由胰腺 α 细胞分泌,以响应低血糖水平。
-
GP21259
Glucagon Human
Glucagon Human Recombinant





