Enzymes(酶)
Enzymes are very efficient and specific catalyst proteins which react with 1 or few types of substrates in biochemical reactions and are responsible for bringing about almost all of the chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes speed up reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Without enzymes, reactions take place at a rate far too slow for the pace of metabolism which means that they speed up the chemical reactions in living things.
There are 2 types of enzymes, ones that help join specific molecules together to form new molecules & others that help break specific molecules apart into separate molecules. Enzymes play many important roles ouside the cell as well. One of the best examples of this is the digestive system. For instance, it is enzymes in your digestive system that break food down in your digestive system break food down into small molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Some enzymes in your digestive system break down starch, some proteins and others break down fats. The enzymes used to digest our food are extra-cellular since they are located outside our cells & enzymes inside our cells are intra-cellular enzymes. Enzymes are used in ALL chemical reactions in living things; this includes respiration, photosynthesis, movement growth, getting rid of toxic chemicals in the liver and so on. Enzymes are proteins that must have the correct structure to be active. They are very easily affected by heat, pH and heavy metal ions.
Ribonucleoprotein enzyme catalytic activity is located in the protein part but for some the catalytic activity is in the RNA part. A catalyst is any substance which makes a chemical reaction go faster, without itself being changed. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction and does not get used up.
Enzymes lower the amount of activation energy needed by binding to the reactants of the reaction they catalyze, thus speed up the reaction and can process millions of molecules per second. Enzymes are typically large proteins with high molecular weight that permit reactions to go at conditions that the body can tolerate.
Enzyme nomenclature is based on what the enzyme reacts with & how it reacts along with the ending ase.
Enzymes must get over the activation energy hurdle.
Enzymes change how a reaction will proceed which reduces the activation energy and makes it faster. The more we increase the enzyme concentration the faster the reaction rate for non-catalyzed reactions. Enzymes that are catalyzed reactions also increase reaction rate at higher level of concentration but up to a certain point called Vmax which means that the enzyme has reached its maximum point. The reaction is limited by both the concentrations of the enzyme and substrate. Enzymes as catalysts take part in reactions which provide an alternative reaction pathway. Enzymes do not undergo permanent changes and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. They only change the rate of reaction, not the position of the equilibrium.Enzymes as catalysts are highly selective by only catalysing specific reactions due to the shapes of the enzyme’s molecule.
Enzymes contain a globular protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named cofactor or prosthetic group or metal-ion-activator. Changes in temperature and pH have great influence on the intra- and intermolecular bonds that hold the protein part in their secondary and tertiary structures.
Examples of cofactors are 1. Prosthetic group that are permanently bound to the enzyme. 2. Activator group which are cations (positively charged metal ions) & temporarily bind to the active site of the enzyme. 3.Coenzymes, usually vitamins or made from vitamins which are not permanently bound to the enzyme molecule, but combine with the enzyme-substrate complex temporarily. Enzymes require the presence cofactors before their catalytic activity can be exerted. This entire active complex is referred to as the holoenzyme.
Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks to digest our food, our muscles, nerves and bones would not work properly and so on…
Main Enzyme category groups:
Oxidoreductases:
All enzymes that catalyse oxido-reductions belong in this class. The substrate oxidized is regarded as a hydrogen or electron donor. The classification is based on 'donor:acceptor oxidoreductase'. The common name is 'dehydrogenase', wherever this is possible; as an alternative, 'acceptor reductase' can be used. 'Oxidase' is used only where O2 is an acceptor. Classification is difficult in some cases, because of the lack of specificity towards the acceptor.
Transferases:
Transferases are enzymes that transfer a group, for example, the methyl group or a glycosyl group, from one compound (generally regarded as donor) to another compound (generally regarded as acceptor). The classification is based on the scheme 'donor:acceptor grouptransferase'. The common names are normally formed as 'acceptor grouptransferase' or 'donor grouptransferase'. In many cases, the donor is a cofactor (coenzyme) that carries the group to be transferred. The aminotransferases constitute a special case.
Hydrolases:
These enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of various bonds. Some of these enzymes pose problems because they have a very wide specificity, and it is not easy to decide if two preparations described by different authors are the same, or if they should be listed under different entries. While the systematic name always includes 'hydrolase', the common name is, in most cases, formed by the name of the substrate with the suffix -ase. It is understood that the name of the substrate with this suffix, and no other indicator, means a hydrolytic enzyme. It should be noted that peptidases have recommended names rather than common names.
Lyases:
Lyases are enzymes that cleave C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by means other than by hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzymes in that two (or more) substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but there is one compound fewer in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring. The systematic name is formed according to 'substrate group-lyase'. In common names, expressions like decarboxylase, aldolase, etc. are used. 'Dehydratase' is used for those enzymes that eliminate water. In cases where the reverse reaction is the more important, or the only one to be demonstrated, 'synthase' may be used in the name.
Ligases:
Ligases are enzymes that catalyse the joining of two molecules with concomitant hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond in ATP or a similar triphosphate. 'Ligase' is often used for the common name, but, in a few cases, 'synthase' or 'carboxylase' is used. 'Synthetase' may be used in place of 'synthase' for enzymes in this class.
Products for Enzymes
- 41701(11)
- Activating Transcription Factor(3)
- Adenylate Kinase(10)
- AHCY(3)
- Aldolase(9)
- Asparaginase(5)
- Aurora Kinase(18)
- Beta Lactamase(3)
- Calcium and Integrin Binding(2)
- Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase(4)
- Carbonic Anhydrase(49)
- Casein Kinase(36)
- Cathepsin(52)
- Chitinase(5)
- Creatin Kinases(9)
- Cyclin(7)
- Cyclin-Dependent Kinase(18)
- Cyclophilin(23)
- Deaminase(14)
- Decarboxylase(12)
- Dehydrogenase(96)
- Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase(2)
- DNA Polymerase(4)
- EGF Receptor(3)
- Endonuclease(6)
- Enolase(10)
- Enterokinase(5)
- Epimerase(3)
- Esterase(15)
- FGF Receptors(12)
- FK506 Binding Protein(10)
- Fructosamine 3 Kinase(2)
- Galactosidase(5)
- Glucosidase(32)
- Gluteradoxin(7)
- Glycogen synthase kinase(2)
- Glycosylase(10)
- Glyoxalase(3)
- Granzyme(7)
- Guanylate Kinase(2)
- Heparanase(2)
- Histone Deacetylase(3)
- Hydratase(10)
- Hydrolase(33)
- Hydroxylase(6)
- Isomerase(26)
- Jun N-terminal Kinase(1)
- Jun Proto-Oncogene(2)
- Kallikrein(26)
- Ligase(4)
- Lipase(14)
- Lipocalin(6)
- Lyase(9)
- LYVE1(3)
- Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase(16)
- MMP(68)
- Mutase(11)
- Natural Enzymes(4)
- Nuclease(18)
- Nucleotidase(4)
- Nudix Type Motif(11)
- Other Enzymes(63)
- Oxidase(23)
- Oxygenase(12)
- Paraoxonase(3)
- Peptidase(41)
- Peroxiredoxin(10)
- Phosphatase(150)
- Phosphorylase(9)
- PI3-kinase(5)
- Polymerase(13)
- PPARG(2)
- Protease(15)
- Proteasome(54)
- Protein Kinase Akt1/PKB alpha(4)
- Protein Kinase-A(7)
- Protein Kinase-C(3)
- Protein Kinases(86)
- Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase(10)
- Reductase(60)
- Secreted Phospholipase A2(10)
- Serine Threonine Kinase(4)
- Sulfatase(8)
- Synthase(23)
- Synthetase(33)
- TGFBR(3)
- TGM2(3)
- TIMP(10)
- TPA(4)
- Transferase(156)
- Tyrosine Kinase(9)
- Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme(39)
- Uromodulin(4)
- VEGF Receptors(14)
- Transaminase(19)
- Hexokinase(6)
- TIE1(6)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP21821
ldhA E. coli
Fermentative D-lactate Dehydrogenase, NAD-Dependent E.Coli Recombinant

-
GP21872
LDHA Human
Lactate Dehydrogenase A Human Recombinant

-
GP21873
LDHA Mouse
Lactate Dehydrogenase A Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21874
LDHA Rat
Lactate Dehydrogenase A, Rat Recombinant

-
GP26164
LDHA, E.Coli Active
LDHA E

-
GP21875
LDHB
Lactate Dehydrogenase B Recombinant

-
GP21877
LDHB Human
Lactate Dehydrogenase B Human Recombinant

-
GP21876
LDHB Human, His
Lactate Dehydrogenase B Human Recombinant, His Tag

-
GP21878
LDHB Mouse
Lactate Dehydrogenase B Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21879
LGMN Human
Legumain Human Recombinant

-
GP21880
LGMN Mouse
Legumain Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21881
LHPP Human
Phospholysine Phosphohistidine Inorganic Pyrophosphate Phosphatase Human Recombinant

-
GP21882
Lipase A
Lipase-A Recombinant

-
GP21883
LIPG Human
Lipase Endothelial Human Recombinant

-
GP21884
LIPG Human, HEK
Lipase Endothelial Human Recombinant, HEK

-
GP21885
lldD E. coli
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase E.Coli Recombinant

-
GC73242
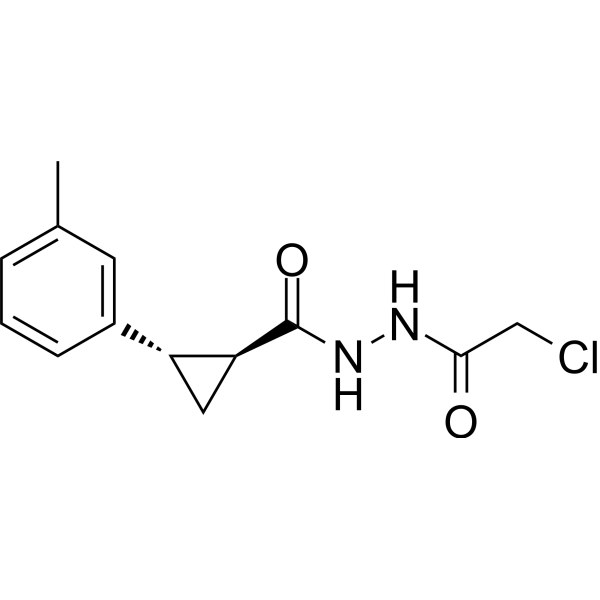
LN5P45
LN5P45是OTUB2抑制剂(IC50: 2.3 μM)。
-
GP21886
LOX Human
Lysyl Oxidase Human Recombinant

-
GP21887
LPCAT1 Human
Lysophosphatidylcholine Acyltransferase Human Recombinant

-
GP21888
LPL Human
Lipoprotein Lipase Human Recombinant

-
GP21889
LPL Human, HEK
Lipoprotein Lipase Human Recombinant, HEK

-
GP21890
LTA4H Human
Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase Human Recombinant

-
GC71416
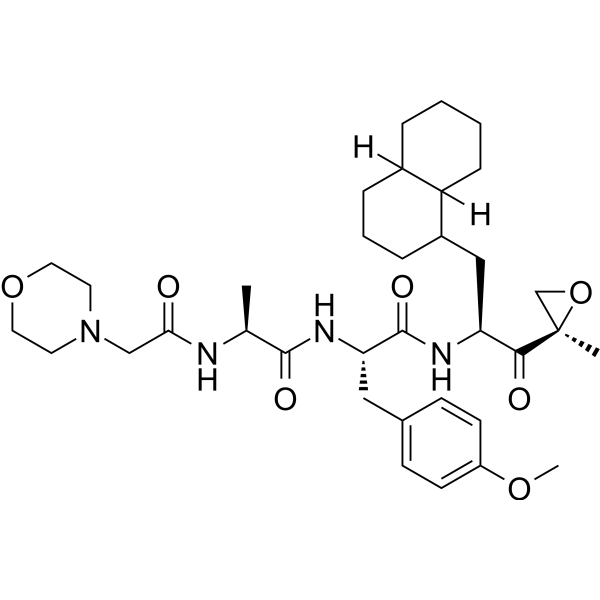
LU-002i
LU-002i是一种亚基选择性的人蛋白酶体β2c和β2i抑制剂,对β2i的IC50值为220 nM。
-
GP21892
Luciferase Firefly, Active
荧光素 4-单加氧酶萤火虫重组体,活性

-
GC65432
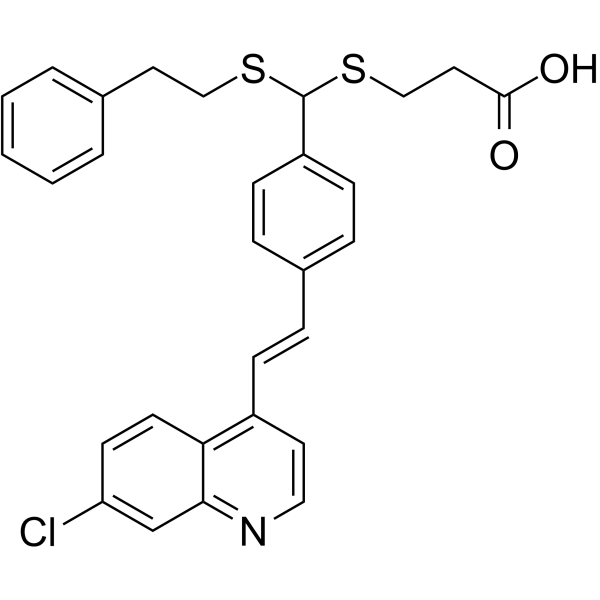
LV-320
LV-320 是一种有效且非竞争性的 ATG4B 抑制剂,其 IC50 值为 24.5 μM,Kd 值为 16 μM。 LV-320 抑制 ATG4B 的酶促活性,阻断细胞自噬,并且在体内稳定,无毒且有活性。
-
GC64282
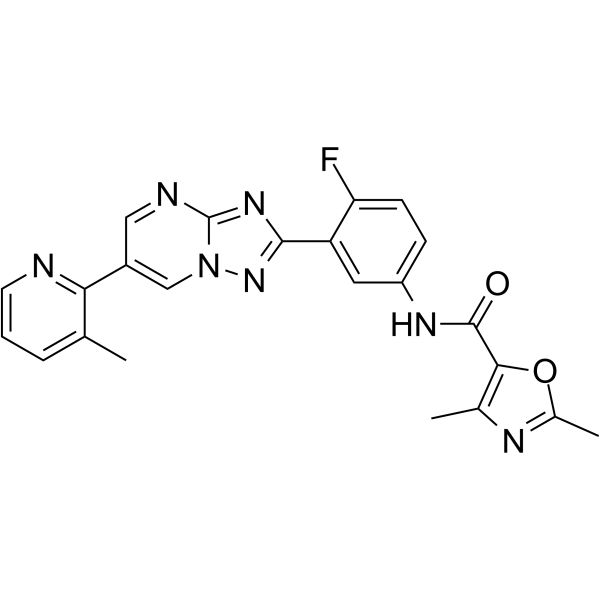
LXE408
LXE408 是一种口服有效的,非竞争性的,动素体选择性蛋白酶体 (proteasome) 抑制剂。LXE408 抑制 L. donovani 蛋白酶体 (IC50=0.04 μM) 和 L. donovani (EC50=0.04 μM)。LXE408 具有较弱的透过血脑屏障能力。LXE408 具有用于内脏利什曼病 (VL) 研究的潜力。
-
GC50009
LY 294002 hydrochloride
Prototypical PI 3-kinase inhibitor; also inhibits other kinases
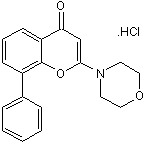
-
GC64338
LYP-IN-1
LYP-IN-1 是一种有效、选择性和特异性的 LYP 抑制剂,其 Ki,IC50 的值分别为 110 nM 和 0.259 μM。LYP-IN-1 对一些 PTPs 也有选择性,如 SHP1 (IC50=5 μM) 和 SHP2 (IC50=2.5 μM)。LYP-IN-1 在 T 细胞和肥大细胞中表现出高效的细胞活性。LYP-IN-1 可用于研究自身免疫性疾病。
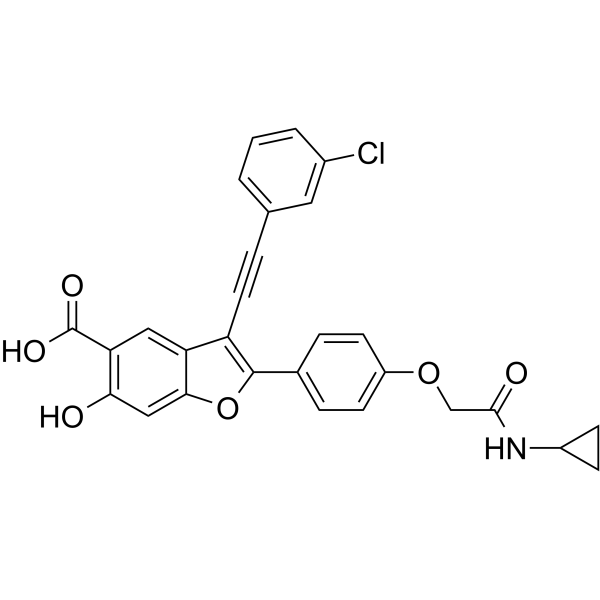
-
GC73595
LYP-IN-3
LYP-IN-3(化合物D34)是淋巴-酪氨酸磷酸酶(LYP)选择性抑制剂(Ki=0.93 μM),在肿瘤发展过程中调控t细胞受体(TCR)信号通路。
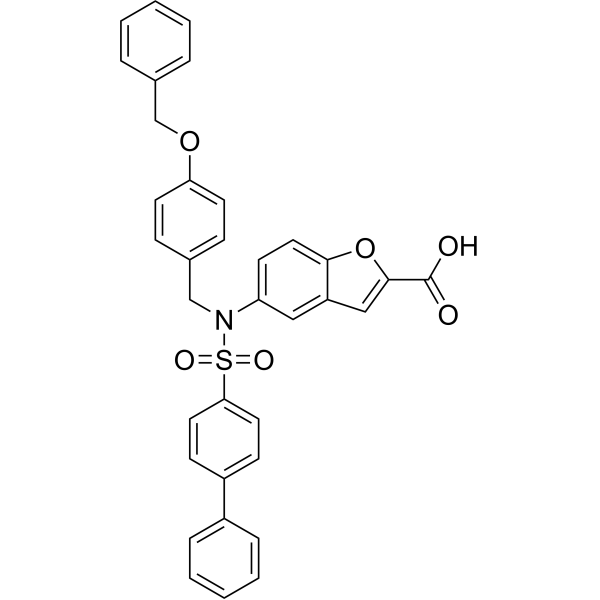
-
GP21895
LYPLA1 Mouse
Lysophospholipase I Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21893
LYPLA2 Human
Lysophospholipase II Human Recombinant

-
GP21894
LYPLAL1 Human
Lysophospholipase Like I Human Recombinant

-
GP21896
Lysostaphin
溶葡萄球菌素是一种抗葡萄球菌剂。

-
GP26165
Lysozyme Human
Recombinant Human Lysozyme produced in Plant is a non-glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 130 amino acids and having a molecular mass of 14kDa

-
GC72176
Lysyl endopeptidase, Achromobacter sp
Lysyl endopeptidase, Achromobacter sp(Lys-C)催化羧基氧交换反应。
-
GP22541
LYVE1 Human
Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Hyaluronic Acid Receptor 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22540
LYVE1 Human 25-235 a.a.
Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Hyaluronic Acid Receptor 1 (25-235 a.a) Human Recombinant

-
GP22542
LYVE1 Mouse Sf9
Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Hyaluronic Acid Receptor 1 Mouse Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP21897
M2 Human
DLAT/DLST/BCOADC Recombinant Human

-
GC73020
M5N36
M5N36是一种有效的选择性Cdc25C抑制剂,对Cdc25A、Cdc25B、Cdc25C的IC50值分别为0.15、0.19、0.06µM。
-
GP21899
MAO B Human
单胺氧化酶 B 人重组体

-
GP21898
MAOA Human
Monoamine Oxidase A Human Recombinant

-
GP21900
MAP E.coli
Methionine Aminopeptidase E.Coli Recombinant

-
GP22543
MAP2K1 Human
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22544
MAP2K2 Human
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP22545
MAP2K3 Human
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 3 Human Recombinant

-
GP22546
MAP2K6 Human
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 6 Human Recombinant

-
GP22547
MAP2K6 Human, sf9
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 6 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP22548
MAPK1 Human
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22549
MAPK1 Human, Active
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 1 Human Recombinant, Active





