Enzymes(酶)
Enzymes are very efficient and specific catalyst proteins which react with 1 or few types of substrates in biochemical reactions and are responsible for bringing about almost all of the chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes speed up reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Without enzymes, reactions take place at a rate far too slow for the pace of metabolism which means that they speed up the chemical reactions in living things.
There are 2 types of enzymes, ones that help join specific molecules together to form new molecules & others that help break specific molecules apart into separate molecules. Enzymes play many important roles ouside the cell as well. One of the best examples of this is the digestive system. For instance, it is enzymes in your digestive system that break food down in your digestive system break food down into small molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Some enzymes in your digestive system break down starch, some proteins and others break down fats. The enzymes used to digest our food are extra-cellular since they are located outside our cells & enzymes inside our cells are intra-cellular enzymes. Enzymes are used in ALL chemical reactions in living things; this includes respiration, photosynthesis, movement growth, getting rid of toxic chemicals in the liver and so on. Enzymes are proteins that must have the correct structure to be active. They are very easily affected by heat, pH and heavy metal ions.
Ribonucleoprotein enzyme catalytic activity is located in the protein part but for some the catalytic activity is in the RNA part. A catalyst is any substance which makes a chemical reaction go faster, without itself being changed. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction and does not get used up.
Enzymes lower the amount of activation energy needed by binding to the reactants of the reaction they catalyze, thus speed up the reaction and can process millions of molecules per second. Enzymes are typically large proteins with high molecular weight that permit reactions to go at conditions that the body can tolerate.
Enzyme nomenclature is based on what the enzyme reacts with & how it reacts along with the ending ase.
Enzymes must get over the activation energy hurdle.
Enzymes change how a reaction will proceed which reduces the activation energy and makes it faster. The more we increase the enzyme concentration the faster the reaction rate for non-catalyzed reactions. Enzymes that are catalyzed reactions also increase reaction rate at higher level of concentration but up to a certain point called Vmax which means that the enzyme has reached its maximum point. The reaction is limited by both the concentrations of the enzyme and substrate. Enzymes as catalysts take part in reactions which provide an alternative reaction pathway. Enzymes do not undergo permanent changes and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. They only change the rate of reaction, not the position of the equilibrium.Enzymes as catalysts are highly selective by only catalysing specific reactions due to the shapes of the enzyme’s molecule.
Enzymes contain a globular protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named cofactor or prosthetic group or metal-ion-activator. Changes in temperature and pH have great influence on the intra- and intermolecular bonds that hold the protein part in their secondary and tertiary structures.
Examples of cofactors are 1. Prosthetic group that are permanently bound to the enzyme. 2. Activator group which are cations (positively charged metal ions) & temporarily bind to the active site of the enzyme. 3.Coenzymes, usually vitamins or made from vitamins which are not permanently bound to the enzyme molecule, but combine with the enzyme-substrate complex temporarily. Enzymes require the presence cofactors before their catalytic activity can be exerted. This entire active complex is referred to as the holoenzyme.
Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks to digest our food, our muscles, nerves and bones would not work properly and so on…
Main Enzyme category groups:
Oxidoreductases:
All enzymes that catalyse oxido-reductions belong in this class. The substrate oxidized is regarded as a hydrogen or electron donor. The classification is based on 'donor:acceptor oxidoreductase'. The common name is 'dehydrogenase', wherever this is possible; as an alternative, 'acceptor reductase' can be used. 'Oxidase' is used only where O2 is an acceptor. Classification is difficult in some cases, because of the lack of specificity towards the acceptor.
Transferases:
Transferases are enzymes that transfer a group, for example, the methyl group or a glycosyl group, from one compound (generally regarded as donor) to another compound (generally regarded as acceptor). The classification is based on the scheme 'donor:acceptor grouptransferase'. The common names are normally formed as 'acceptor grouptransferase' or 'donor grouptransferase'. In many cases, the donor is a cofactor (coenzyme) that carries the group to be transferred. The aminotransferases constitute a special case.
Hydrolases:
These enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of various bonds. Some of these enzymes pose problems because they have a very wide specificity, and it is not easy to decide if two preparations described by different authors are the same, or if they should be listed under different entries. While the systematic name always includes 'hydrolase', the common name is, in most cases, formed by the name of the substrate with the suffix -ase. It is understood that the name of the substrate with this suffix, and no other indicator, means a hydrolytic enzyme. It should be noted that peptidases have recommended names rather than common names.
Lyases:
Lyases are enzymes that cleave C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by means other than by hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzymes in that two (or more) substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but there is one compound fewer in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring. The systematic name is formed according to 'substrate group-lyase'. In common names, expressions like decarboxylase, aldolase, etc. are used. 'Dehydratase' is used for those enzymes that eliminate water. In cases where the reverse reaction is the more important, or the only one to be demonstrated, 'synthase' may be used in the name.
Ligases:
Ligases are enzymes that catalyse the joining of two molecules with concomitant hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond in ATP or a similar triphosphate. 'Ligase' is often used for the common name, but, in a few cases, 'synthase' or 'carboxylase' is used. 'Synthetase' may be used in place of 'synthase' for enzymes in this class.
Products for Enzymes
- 41701(11)
- Activating Transcription Factor(3)
- Adenylate Kinase(10)
- AHCY(3)
- Aldolase(9)
- Asparaginase(5)
- Aurora Kinase(18)
- Beta Lactamase(3)
- Calcium and Integrin Binding(2)
- Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase(4)
- Carbonic Anhydrase(49)
- Casein Kinase(36)
- Cathepsin(52)
- Chitinase(5)
- Creatin Kinases(9)
- Cyclin(7)
- Cyclin-Dependent Kinase(18)
- Cyclophilin(23)
- Deaminase(14)
- Decarboxylase(12)
- Dehydrogenase(96)
- Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase(2)
- DNA Polymerase(4)
- EGF Receptor(3)
- Endonuclease(6)
- Enolase(10)
- Enterokinase(5)
- Epimerase(3)
- Esterase(15)
- FGF Receptors(12)
- FK506 Binding Protein(10)
- Fructosamine 3 Kinase(2)
- Galactosidase(5)
- Glucosidase(32)
- Gluteradoxin(7)
- Glycogen synthase kinase(2)
- Glycosylase(10)
- Glyoxalase(3)
- Granzyme(7)
- Guanylate Kinase(2)
- Heparanase(2)
- Histone Deacetylase(3)
- Hydratase(10)
- Hydrolase(33)
- Hydroxylase(6)
- Isomerase(26)
- Jun N-terminal Kinase(1)
- Jun Proto-Oncogene(2)
- Kallikrein(26)
- Ligase(4)
- Lipase(14)
- Lipocalin(6)
- Lyase(9)
- LYVE1(3)
- Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase(16)
- MMP(68)
- Mutase(11)
- Natural Enzymes(4)
- Nuclease(18)
- Nucleotidase(4)
- Nudix Type Motif(11)
- Other Enzymes(63)
- Oxidase(23)
- Oxygenase(12)
- Paraoxonase(3)
- Peptidase(41)
- Peroxiredoxin(10)
- Phosphatase(150)
- Phosphorylase(9)
- PI3-kinase(5)
- Polymerase(13)
- PPARG(2)
- Protease(15)
- Proteasome(54)
- Protein Kinase Akt1/PKB alpha(4)
- Protein Kinase-A(7)
- Protein Kinase-C(3)
- Protein Kinases(86)
- Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase(10)
- Reductase(60)
- Secreted Phospholipase A2(10)
- Serine Threonine Kinase(4)
- Sulfatase(8)
- Synthase(23)
- Synthetase(33)
- TGFBR(3)
- TGM2(3)
- TIMP(10)
- TPA(4)
- Transferase(156)
- Tyrosine Kinase(9)
- Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme(39)
- Uromodulin(4)
- VEGF Receptors(14)
- Transaminase(19)
- Hexokinase(6)
- TIE1(6)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP21834
KARS Human
Lysyl-tRNA Synthetase Human Recombinant

-
GP21835
KAT2A Human
K (lysine) Acetyltransferase 2A Human Recombinant

-
GP21836
KDSR Human
3-Ketodihydrosphingosine Reductase Human Recombinant

-
GP26160
KEL Mouse
KEL Mouse produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 674 amino acids (49-713 aa) and having a molecular mass of 76

-
GP22538
Ketohexokinase Human
Ketohexokinase Human Recombinant

-
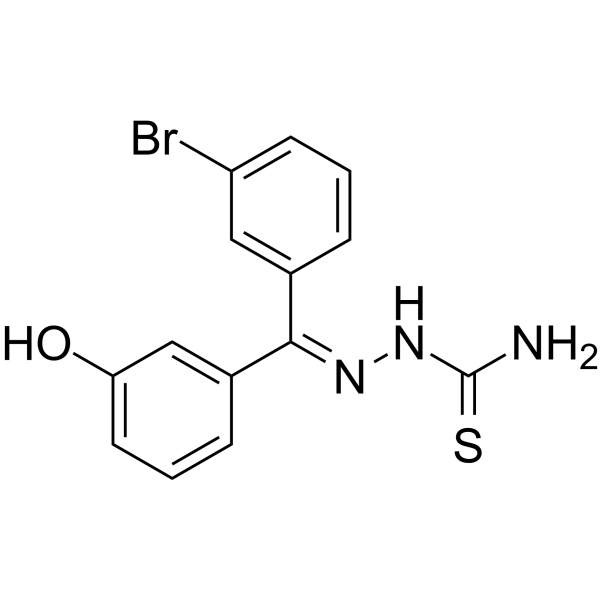
GC65153
KGP94
KGP94 是一种特异的 cathepsin L 抑制剂,IC50为 189 nM。KGP94 抑制转移癌的运动性和侵袭性,对人类细胞的毒性低 (GI50=26.9µM)。
-
GP22539
KIT Human
KIT Proto-Oncogene Receptor Tyrosine Human Recombinant

-
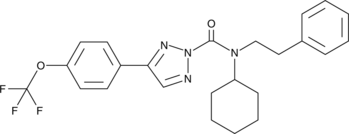
GC44008
KLH45
An inhibitor of DDHD2
-
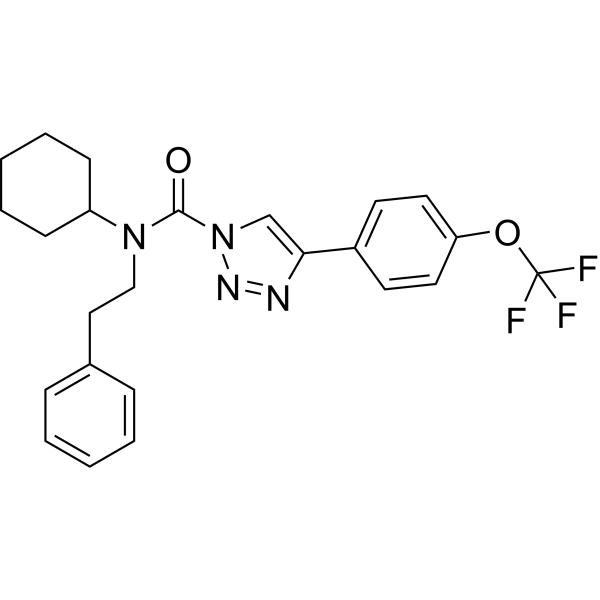
GC70408
KLH45b
KLH45b是DDHD2(含有2个DDHD结构域)的抑制剂。
-
GP21837
KLK1 Human
Kallikrein-1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21838
KLK1 Human, His
Kallikrein-1 Human Recombinant, His Tag

-
GP21848
KLK10 Human
Kallikrein-10 Human Recombinant

-
GP21849
KLK10 Human, Sf9
Kallikrein-10 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP21850
KLK11 Human
Kallikrein-11 Human Recombinant

-
GP21851
KLK11 Human, Sf9
Kallikrein-11, 4 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP21852
KLK13 Human
Kallikrein-13 Human Recombinant

-
GP21853
KLK13 Human, sf9
Kallikrein-13 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP21854
KLK15 Human
Kallikrein-15 Human Recombinant

-
GP21855
KLK15 Human, sf9
Kallikrein-15 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP21839
KLK2 Human
Kallikrein-2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21840
KLK2 Human, sf9
Kallikrein-2 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP21841
KLK3
Kallikrein-3 Human Recombinant

-
GP21842
KLK3 Human
Kallikrein-3 Human

-
GP26162
KLK3 Human, HEK
KLK3 Human Recombinant produced in HEK cells is a single, glycosylated, polypeptide chain (18-261 a

-
GP26163
KLK3 Human, Native
Human Kallikrein-3 produced in Human seminal fluid having a molecular mass of approximately 30kD

-
GP26161
KLK3 Protein
Kallikrein-3 Human Recombinant produced in E

-
GP21843
KLK5 Human
Kallikrein-5 Human Recombinant

-
GP21844
KLK5 Human, Sf9
Kallikrein-5 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP21845
KLK7 Human
Kallikrein-7 Human Recombinant

-
GP21846
KLK7 Human, sf9
Kallikrein-7 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP21847
KLK8 Mouse
Kallikrein-8 Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21856
KMT5A Human
Lysine Methyltransferase 5A Human Recombinant

-
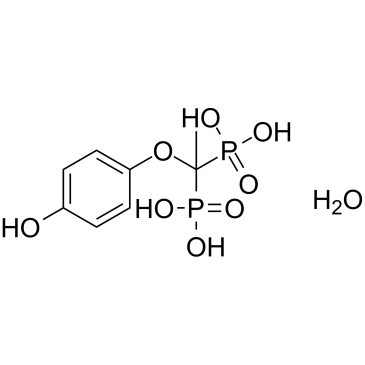
GC61578
L-690330 hydrate
L-690330hydrate是一种竞争性的肌醇单磷酸酶(inositolmonophosphatase(IMPase))抑制剂,对重组人和牛IMPase的Ki值为0.27μM和0.19μM,对人和牛前脑皮层IMPase的为Ki值为0.30μM和0.42μM。L-690330hydrate对其敏感性是大鼠和小鼠的IMPase的10倍。
-
GC19511
L-Ascorbic Acid 2-phosphate (magnesium salt)
维生素C磷酸酯镁; 2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid magnesium
L-Ascorbic Acid 2-phosphate (magnesium salt) (AA2P)是一种稳定的VC(维生素C)衍生物。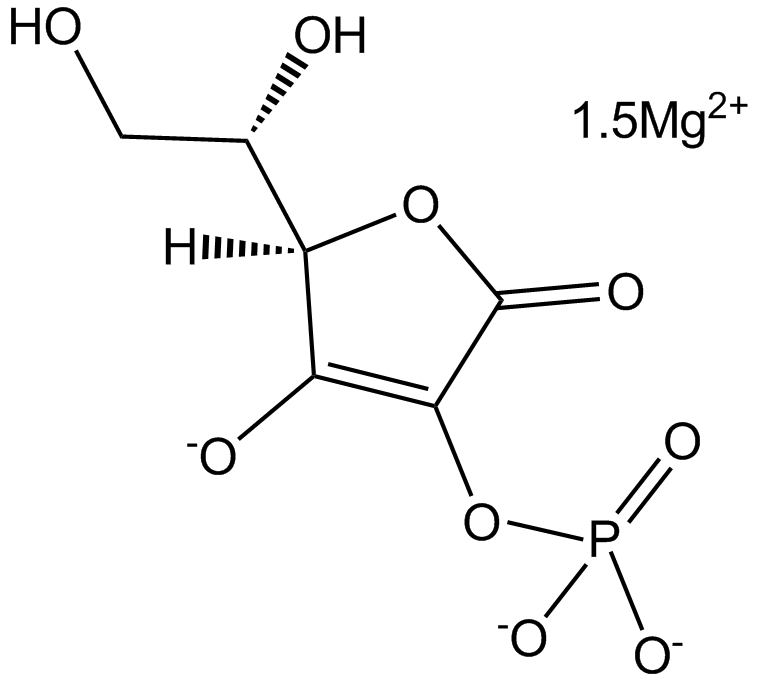
-
GP21861
L-Asparaginase
L-天冬酰胺酶(L-ASNase)是一种脱酰胺酶,催化L-天冬酰胺和L-谷氨酰胺的水解,可用于急性淋巴细胞白血病的研究。 L-天冬酰胺酶从血浆中消耗 L-天冬酰胺,导致 RNA 和 DNA 合成受到抑制,随后发生胚细胞凋亡。

-
GP21857
LACTB E.coli
Beta Lactamase E.coli Recombinant

-
GP21858
LACTB E.coli, His
Beta Lactamase E.coli Recombinant, His Tag

-
GP21859
LACTB E.Coli, His Active
Beta Lactamase E.Coli Recombinant, His Active

-
GC72335
Lanadelumab
Lanadelumab(SHP643)是一种针对血浆激肽释放酶(pKal)的人IgG1单克隆抗体,Ki值为0.12 nM。

-
GP21860
LAP3 Human
Leucine Aminopeptidase 3 Human Recombinant

-
GP21862
Latexin Human
Latexin Human Recombinant

-
GP21863
LCAT Human
Lecithin-Cholesterol Acyltransferase Human Recombinant

-
GP21864
LCAT Human, HEK
Lecithin-Cholesterol Acyltransferase Human Recombinant, HEK

-
GP21865
LCMT1 Human
Leucine Carboxyl Methyltransferase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21866
LCN1 Human
Lipocalin-1 人类重组体

-
GP21867
LCN2 Human
中性粒细胞明胶酶相关 Lipocalin/Lipocalin-2 人重组体

-
GP21868
LCN2 Human, His
Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin/Lipocalin-2 Human Recombinant, His Tag

-
GP21869
LCN2 Human, Pichia
Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin/Lipocalin-2 Human Recombinant, Pichia

-
GP21870
LCN2 Mouse
Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin/Lipocalin-2 Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21871
LCN2 Rat
Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin/Lipocalin-2 Rat Recombinant





