Enzymes(酶)
Enzymes are very efficient and specific catalyst proteins which react with 1 or few types of substrates in biochemical reactions and are responsible for bringing about almost all of the chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes speed up reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Without enzymes, reactions take place at a rate far too slow for the pace of metabolism which means that they speed up the chemical reactions in living things.
There are 2 types of enzymes, ones that help join specific molecules together to form new molecules & others that help break specific molecules apart into separate molecules. Enzymes play many important roles ouside the cell as well. One of the best examples of this is the digestive system. For instance, it is enzymes in your digestive system that break food down in your digestive system break food down into small molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Some enzymes in your digestive system break down starch, some proteins and others break down fats. The enzymes used to digest our food are extra-cellular since they are located outside our cells & enzymes inside our cells are intra-cellular enzymes. Enzymes are used in ALL chemical reactions in living things; this includes respiration, photosynthesis, movement growth, getting rid of toxic chemicals in the liver and so on. Enzymes are proteins that must have the correct structure to be active. They are very easily affected by heat, pH and heavy metal ions.
Ribonucleoprotein enzyme catalytic activity is located in the protein part but for some the catalytic activity is in the RNA part. A catalyst is any substance which makes a chemical reaction go faster, without itself being changed. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction and does not get used up.
Enzymes lower the amount of activation energy needed by binding to the reactants of the reaction they catalyze, thus speed up the reaction and can process millions of molecules per second. Enzymes are typically large proteins with high molecular weight that permit reactions to go at conditions that the body can tolerate.
Enzyme nomenclature is based on what the enzyme reacts with & how it reacts along with the ending ase.
Enzymes must get over the activation energy hurdle.
Enzymes change how a reaction will proceed which reduces the activation energy and makes it faster. The more we increase the enzyme concentration the faster the reaction rate for non-catalyzed reactions. Enzymes that are catalyzed reactions also increase reaction rate at higher level of concentration but up to a certain point called Vmax which means that the enzyme has reached its maximum point. The reaction is limited by both the concentrations of the enzyme and substrate. Enzymes as catalysts take part in reactions which provide an alternative reaction pathway. Enzymes do not undergo permanent changes and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. They only change the rate of reaction, not the position of the equilibrium.Enzymes as catalysts are highly selective by only catalysing specific reactions due to the shapes of the enzyme’s molecule.
Enzymes contain a globular protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named cofactor or prosthetic group or metal-ion-activator. Changes in temperature and pH have great influence on the intra- and intermolecular bonds that hold the protein part in their secondary and tertiary structures.
Examples of cofactors are 1. Prosthetic group that are permanently bound to the enzyme. 2. Activator group which are cations (positively charged metal ions) & temporarily bind to the active site of the enzyme. 3.Coenzymes, usually vitamins or made from vitamins which are not permanently bound to the enzyme molecule, but combine with the enzyme-substrate complex temporarily. Enzymes require the presence cofactors before their catalytic activity can be exerted. This entire active complex is referred to as the holoenzyme.
Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks to digest our food, our muscles, nerves and bones would not work properly and so on…
Main Enzyme category groups:
Oxidoreductases:
All enzymes that catalyse oxido-reductions belong in this class. The substrate oxidized is regarded as a hydrogen or electron donor. The classification is based on 'donor:acceptor oxidoreductase'. The common name is 'dehydrogenase', wherever this is possible; as an alternative, 'acceptor reductase' can be used. 'Oxidase' is used only where O2 is an acceptor. Classification is difficult in some cases, because of the lack of specificity towards the acceptor.
Transferases:
Transferases are enzymes that transfer a group, for example, the methyl group or a glycosyl group, from one compound (generally regarded as donor) to another compound (generally regarded as acceptor). The classification is based on the scheme 'donor:acceptor grouptransferase'. The common names are normally formed as 'acceptor grouptransferase' or 'donor grouptransferase'. In many cases, the donor is a cofactor (coenzyme) that carries the group to be transferred. The aminotransferases constitute a special case.
Hydrolases:
These enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of various bonds. Some of these enzymes pose problems because they have a very wide specificity, and it is not easy to decide if two preparations described by different authors are the same, or if they should be listed under different entries. While the systematic name always includes 'hydrolase', the common name is, in most cases, formed by the name of the substrate with the suffix -ase. It is understood that the name of the substrate with this suffix, and no other indicator, means a hydrolytic enzyme. It should be noted that peptidases have recommended names rather than common names.
Lyases:
Lyases are enzymes that cleave C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by means other than by hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzymes in that two (or more) substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but there is one compound fewer in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring. The systematic name is formed according to 'substrate group-lyase'. In common names, expressions like decarboxylase, aldolase, etc. are used. 'Dehydratase' is used for those enzymes that eliminate water. In cases where the reverse reaction is the more important, or the only one to be demonstrated, 'synthase' may be used in the name.
Ligases:
Ligases are enzymes that catalyse the joining of two molecules with concomitant hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond in ATP or a similar triphosphate. 'Ligase' is often used for the common name, but, in a few cases, 'synthase' or 'carboxylase' is used. 'Synthetase' may be used in place of 'synthase' for enzymes in this class.
Products for Enzymes
- 41701(11)
- Activating Transcription Factor(3)
- Adenylate Kinase(10)
- AHCY(3)
- Aldolase(9)
- Asparaginase(5)
- Aurora Kinase(18)
- Beta Lactamase(3)
- Calcium and Integrin Binding(2)
- Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase(4)
- Carbonic Anhydrase(49)
- Casein Kinase(36)
- Cathepsin(52)
- Chitinase(5)
- Creatin Kinases(9)
- Cyclin(7)
- Cyclin-Dependent Kinase(18)
- Cyclophilin(23)
- Deaminase(14)
- Decarboxylase(12)
- Dehydrogenase(96)
- Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase(2)
- DNA Polymerase(4)
- EGF Receptor(3)
- Endonuclease(6)
- Enolase(10)
- Enterokinase(5)
- Epimerase(3)
- Esterase(15)
- FGF Receptors(12)
- FK506 Binding Protein(10)
- Fructosamine 3 Kinase(2)
- Galactosidase(5)
- Glucosidase(32)
- Gluteradoxin(7)
- Glycogen synthase kinase(2)
- Glycosylase(10)
- Glyoxalase(3)
- Granzyme(7)
- Guanylate Kinase(2)
- Heparanase(2)
- Histone Deacetylase(3)
- Hydratase(10)
- Hydrolase(33)
- Hydroxylase(6)
- Isomerase(26)
- Jun N-terminal Kinase(1)
- Jun Proto-Oncogene(2)
- Kallikrein(26)
- Ligase(4)
- Lipase(14)
- Lipocalin(6)
- Lyase(9)
- LYVE1(3)
- Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase(16)
- MMP(68)
- Mutase(11)
- Natural Enzymes(4)
- Nuclease(18)
- Nucleotidase(4)
- Nudix Type Motif(11)
- Other Enzymes(63)
- Oxidase(23)
- Oxygenase(12)
- Paraoxonase(3)
- Peptidase(41)
- Peroxiredoxin(10)
- Phosphatase(150)
- Phosphorylase(9)
- PI3-kinase(5)
- Polymerase(13)
- PPARG(2)
- Protease(15)
- Proteasome(54)
- Protein Kinase Akt1/PKB alpha(4)
- Protein Kinase-A(7)
- Protein Kinase-C(3)
- Protein Kinases(86)
- Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase(10)
- Reductase(60)
- Secreted Phospholipase A2(10)
- Serine Threonine Kinase(4)
- Sulfatase(8)
- Synthase(23)
- Synthetase(33)
- TGFBR(3)
- TGM2(3)
- TIMP(10)
- TPA(4)
- Transferase(156)
- Tyrosine Kinase(9)
- Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme(39)
- Uromodulin(4)
- VEGF Receptors(14)
- Transaminase(19)
- Hexokinase(6)
- TIE1(6)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP21776
HARS Human, His
Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase Human Recombinant, His Tag

-
GP21777
HARS Human, Sf9
Histidyl-tRNA Synthetase Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP21778
HAT1 Human
Histone Acetyltransferase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GC73573
hCA/Wnt/β-catenin-IN-1
hCA/Wnt/β-catenin-IN-1 (Compd 15)是hCA的抑制剂(Ki: 33.6, 24.1, 6.8 nM对hCA II, hCA IX, hCA XII) hCA/Wnt/β-catenin-IN-1降低P-gp活性。
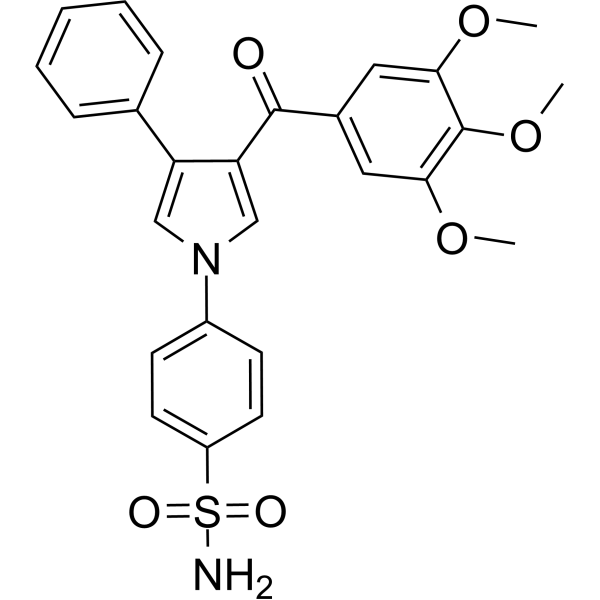
-
GC66029
hCAI/II-IN-6
hCAI/II-IN-6 是一种具有口服活性的 human carbonic anhydrase (CA) 抑制剂。hCAI/II-IN-6 选择性地抑制 hCA II 和 hCA VII,对 hCA I,hCA II,hCA VII 和 hCA XII 的 Ki 值分别为 220,4.9,6.5 和 >50000 nM。hCAI/II-IN-6 在体内显示抗惊厥活性和抗最大电击 (MES) 活性。hCAI/II-IN-6 可以用于癫痫的研究。
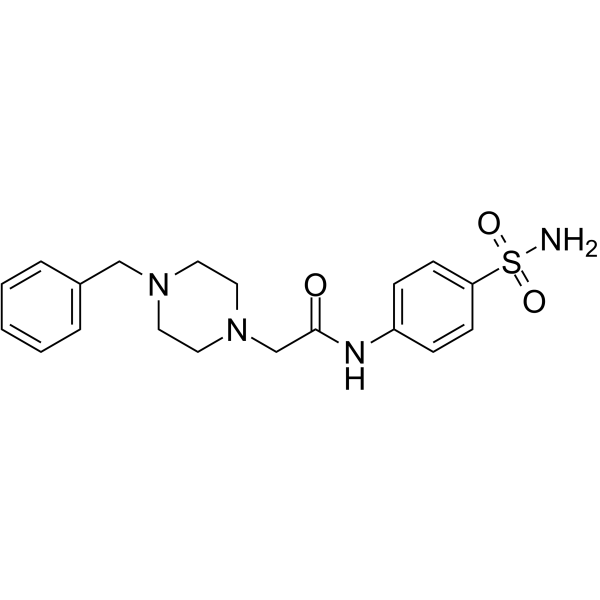
-
GC69209
hCAII-IN-8
hCAII-IN-8 是一种酰胺,是一种高选择性碳酸酐酶 (CA) 抑制剂,对 hCA II 的 IC50 值为 0.18 μM。
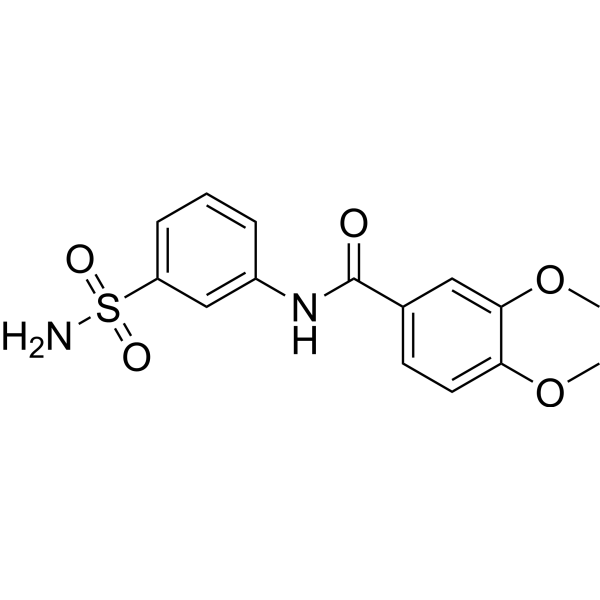
-
GC73227
hCAIX-IN-18
hCAIX-IN-18(化合物30)是碳酸酐酶(CA)的抑制剂,hCAI、hCAII、hCAIX、hCAXII的Kis分别为3.5 nM、9.4 nM、43.0 nM和8.2 nM。
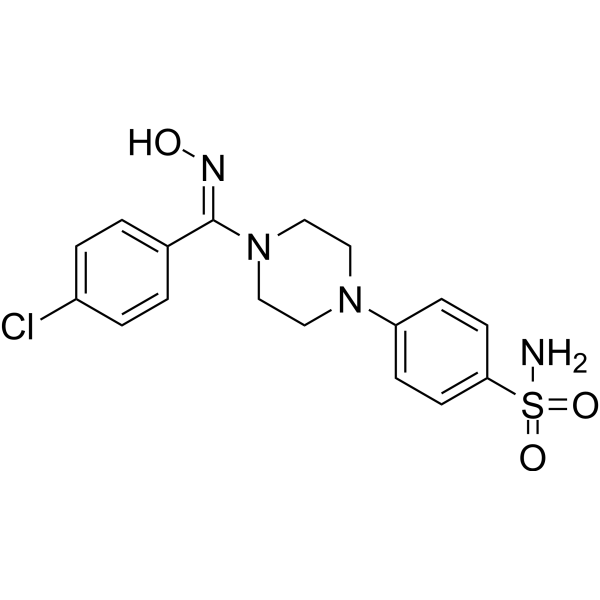
-
GP21779
HDAC2 Human
Histone Deacetylase 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21780
HDAC8 Human
组蛋白脱乙酰酶 8 人重组体

-
GP21781
HDAC8 Mouse
Histone Deacetylase 8 Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21782
HDDC2 Human
HD Domain Containing 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21783
HDDC3 Human
包含 3 个人类重组体的 HD 结构域

-
GP21784
HDHD1 Human
Haloacid Dehalogenase-Like Hydrolase Domain Containing 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21785
HDHD2 Human
Haloacid Dehalogenase-Like Hydrolase Domain Containing 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21786
HDHD3 Human
Haloacid Dehalogenase-Like Hydrolase Domain Containing 3 Human Recombinant

-
GC39266
Hematein
氧化苏木精
Hematein inhibits casein kinase II activity in a selective, dose-dependent and ATP non-competitive manner in vitro, with IC50 of 0.55 μM in the presence of 10 μM ATP.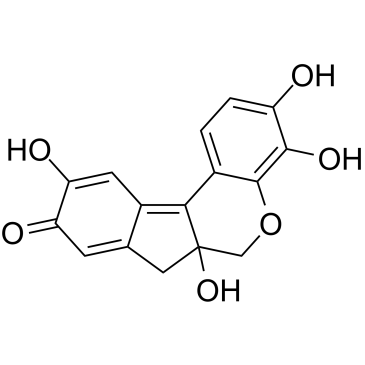
-
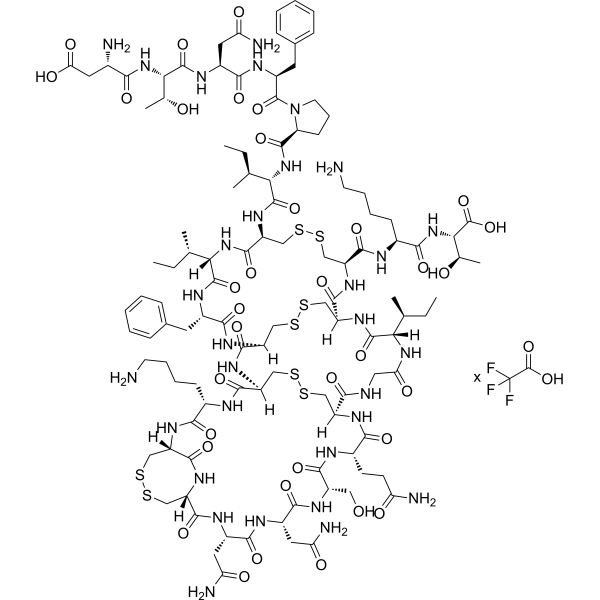
GC72231
Hepcidin-1 (mouse) (TFA)
Hepcidin-1 (mouse) (TFA)是一种参与调节铁稳态的内源性肽激素。
-
GP21787
HERC5 Human
HECT and RLD Domain Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 5 Human Recombinant

-
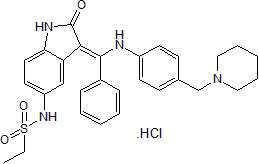
GC50050
Hesperadin hydrochloride
A multi-kinase inhibitor
-
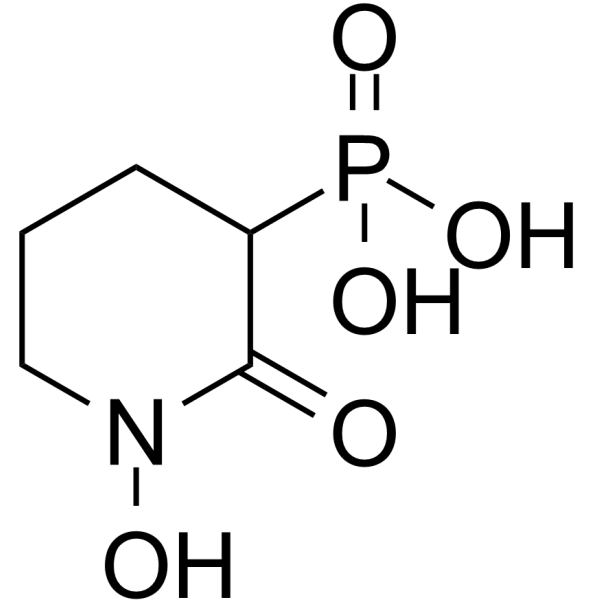
GC63451
Hex
Hex 是烯醇酶 (enolase) 的抑制剂,其对 ENO2 和 ENO1 的 Ki 值分别为 74.4 nM 和 269.4 nM。
-
GP21788
HEXA Human
Hexosaminidase A Human Recombinant

-
GP21789
HEXA Human, Sf9
Hexosaminidase A Human Recombinant, SF9

-
GC70717
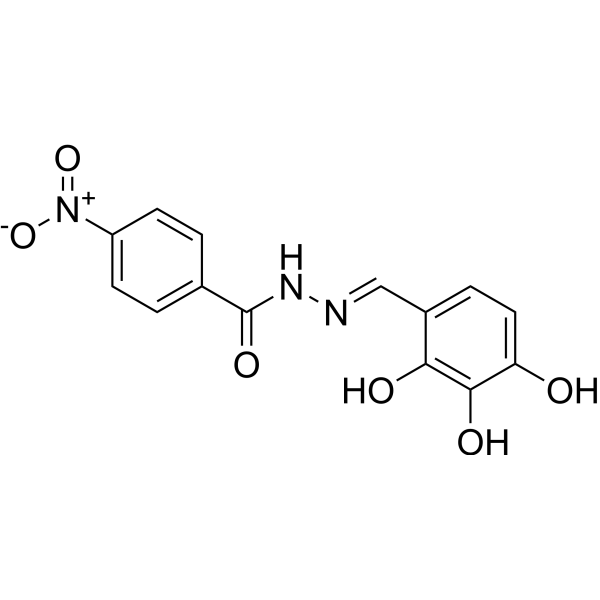
Hexokinase 2 inhibitor 1
Hexokinase 2 inhibitor 1(化合物2a)是一种具有抗肿瘤活性的己糖激酶2 (HK2)抑制剂,可用于癌症研究。
-
GP21790
HIBCH Human
3-Hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA Hydrolase Human Recombinant

-
GP22528
HK1 Human
Hexokinase-1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22529
HK2 Human
Hexokinase-2 Human Recombinant

-
GP22530
HK3 Human
Hexokinase-3 Human Recombinant

-
GC69231
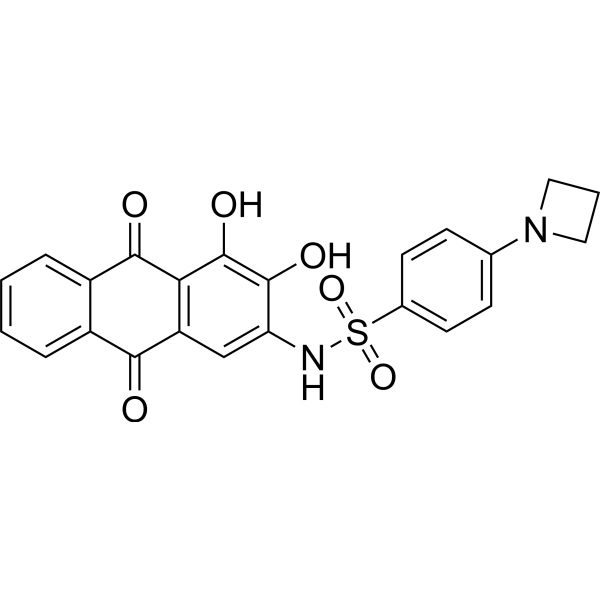
HKB99
HKB99 是磷酸甘油酸突变酶 1 的变构抑制剂 (PGAM1)。HKB99 抑制侵袭性伪足的形成,提高 PAI-2 水平。HKB99 增加氧化应激,激活 JNK/c-Jun,抑制 AKT 和 ERK。HKB99 可用于非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC) 的研究。
-
GP21791
HMBS Human
Hydroxymethylbilane Synthase Human Recombinant

-
GP21792
HMGCL Human
3-Hydroxymethyl-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Lyase Human Recombinant

-
GP21793
HMGCL Human, Sf9
3-羟甲基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶 A 裂解酶人类重组,Sf9

-
GP21794
HMGCS1 Human
3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21795
HMOX1 Human
Heme Oxygenase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21796
HMOX2 Human
Heme Oxygenase-2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21797
HNMT Human
Histamine N-Methyltransferase Human Recombinant

-
GP21798
HNMT Human, Active
Histamine N-Methyltransferase Human Recombinant, Active

-
GP21802
HPD Human
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Human Recombinant

-
GP21803
HPD Mouse
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21804
HPGD Human
Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase 15-(NAD) Human Recombinant

-
GP21805
HPGD Mouse
Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase 15-(NAD) Mouse Recombinant

-
GP21806
HPGDS Human
Hematopoietic Prostaglandin D Synthase Human Recombinant

-
GP21807
HPRT1 Human
Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phosphoribosyltransferase Human Recombinant

-
GP21808
HPRT1 Human, Active
Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phosphoribosyltransferase, Human Recombinant, Active

-
GP21800
HPSE Human
Heparanase-1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21799
HPSE WB
Recombinant Human Heparanase-1 WB Control

-
GP21809
HRASLS3 Human
HRAS-Like Suppressor 3 Human Recombinant (PLA2G16)

-
GP21810
HRP
HRP作为神经元连接的逆行和顺行示踪物,提高了检测色氨酸的敏感性

-
GP21811
HS3ST1 Human
Heparan Sulfate 3-O-Sulfotransferase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21812
HSD17B1 Human
Hydroxysteroid (17-beta) Dehydrogenase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP23680
HSD17B10 Human
Hydroxysteroid (17-beta) Dehydrogenase 10 Human Recombinant





