Enzymes(酶)
Enzymes are very efficient and specific catalyst proteins which react with 1 or few types of substrates in biochemical reactions and are responsible for bringing about almost all of the chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes speed up reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Without enzymes, reactions take place at a rate far too slow for the pace of metabolism which means that they speed up the chemical reactions in living things.
There are 2 types of enzymes, ones that help join specific molecules together to form new molecules & others that help break specific molecules apart into separate molecules. Enzymes play many important roles ouside the cell as well. One of the best examples of this is the digestive system. For instance, it is enzymes in your digestive system that break food down in your digestive system break food down into small molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Some enzymes in your digestive system break down starch, some proteins and others break down fats. The enzymes used to digest our food are extra-cellular since they are located outside our cells & enzymes inside our cells are intra-cellular enzymes. Enzymes are used in ALL chemical reactions in living things; this includes respiration, photosynthesis, movement growth, getting rid of toxic chemicals in the liver and so on. Enzymes are proteins that must have the correct structure to be active. They are very easily affected by heat, pH and heavy metal ions.
Ribonucleoprotein enzyme catalytic activity is located in the protein part but for some the catalytic activity is in the RNA part. A catalyst is any substance which makes a chemical reaction go faster, without itself being changed. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction and does not get used up.
Enzymes lower the amount of activation energy needed by binding to the reactants of the reaction they catalyze, thus speed up the reaction and can process millions of molecules per second. Enzymes are typically large proteins with high molecular weight that permit reactions to go at conditions that the body can tolerate.
Enzyme nomenclature is based on what the enzyme reacts with & how it reacts along with the ending ase.
Enzymes must get over the activation energy hurdle.
Enzymes change how a reaction will proceed which reduces the activation energy and makes it faster. The more we increase the enzyme concentration the faster the reaction rate for non-catalyzed reactions. Enzymes that are catalyzed reactions also increase reaction rate at higher level of concentration but up to a certain point called Vmax which means that the enzyme has reached its maximum point. The reaction is limited by both the concentrations of the enzyme and substrate. Enzymes as catalysts take part in reactions which provide an alternative reaction pathway. Enzymes do not undergo permanent changes and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. They only change the rate of reaction, not the position of the equilibrium.Enzymes as catalysts are highly selective by only catalysing specific reactions due to the shapes of the enzyme’s molecule.
Enzymes contain a globular protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named cofactor or prosthetic group or metal-ion-activator. Changes in temperature and pH have great influence on the intra- and intermolecular bonds that hold the protein part in their secondary and tertiary structures.
Examples of cofactors are 1. Prosthetic group that are permanently bound to the enzyme. 2. Activator group which are cations (positively charged metal ions) & temporarily bind to the active site of the enzyme. 3.Coenzymes, usually vitamins or made from vitamins which are not permanently bound to the enzyme molecule, but combine with the enzyme-substrate complex temporarily. Enzymes require the presence cofactors before their catalytic activity can be exerted. This entire active complex is referred to as the holoenzyme.
Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks to digest our food, our muscles, nerves and bones would not work properly and so on…
Main Enzyme category groups:
Oxidoreductases:
All enzymes that catalyse oxido-reductions belong in this class. The substrate oxidized is regarded as a hydrogen or electron donor. The classification is based on 'donor:acceptor oxidoreductase'. The common name is 'dehydrogenase', wherever this is possible; as an alternative, 'acceptor reductase' can be used. 'Oxidase' is used only where O2 is an acceptor. Classification is difficult in some cases, because of the lack of specificity towards the acceptor.
Transferases:
Transferases are enzymes that transfer a group, for example, the methyl group or a glycosyl group, from one compound (generally regarded as donor) to another compound (generally regarded as acceptor). The classification is based on the scheme 'donor:acceptor grouptransferase'. The common names are normally formed as 'acceptor grouptransferase' or 'donor grouptransferase'. In many cases, the donor is a cofactor (coenzyme) that carries the group to be transferred. The aminotransferases constitute a special case.
Hydrolases:
These enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of various bonds. Some of these enzymes pose problems because they have a very wide specificity, and it is not easy to decide if two preparations described by different authors are the same, or if they should be listed under different entries. While the systematic name always includes 'hydrolase', the common name is, in most cases, formed by the name of the substrate with the suffix -ase. It is understood that the name of the substrate with this suffix, and no other indicator, means a hydrolytic enzyme. It should be noted that peptidases have recommended names rather than common names.
Lyases:
Lyases are enzymes that cleave C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by means other than by hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzymes in that two (or more) substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but there is one compound fewer in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring. The systematic name is formed according to 'substrate group-lyase'. In common names, expressions like decarboxylase, aldolase, etc. are used. 'Dehydratase' is used for those enzymes that eliminate water. In cases where the reverse reaction is the more important, or the only one to be demonstrated, 'synthase' may be used in the name.
Ligases:
Ligases are enzymes that catalyse the joining of two molecules with concomitant hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond in ATP or a similar triphosphate. 'Ligase' is often used for the common name, but, in a few cases, 'synthase' or 'carboxylase' is used. 'Synthetase' may be used in place of 'synthase' for enzymes in this class.
Products for Enzymes
- 41701(11)
- Activating Transcription Factor(3)
- Adenylate Kinase(10)
- AHCY(3)
- Aldolase(9)
- Asparaginase(5)
- Aurora Kinase(18)
- Beta Lactamase(3)
- Calcium and Integrin Binding(2)
- Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase(4)
- Carbonic Anhydrase(49)
- Casein Kinase(36)
- Cathepsin(52)
- Chitinase(5)
- Creatin Kinases(9)
- Cyclin(7)
- Cyclin-Dependent Kinase(18)
- Cyclophilin(23)
- Deaminase(14)
- Decarboxylase(12)
- Dehydrogenase(96)
- Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase(2)
- DNA Polymerase(4)
- EGF Receptor(3)
- Endonuclease(6)
- Enolase(10)
- Enterokinase(5)
- Epimerase(3)
- Esterase(15)
- FGF Receptors(12)
- FK506 Binding Protein(10)
- Fructosamine 3 Kinase(2)
- Galactosidase(5)
- Glucosidase(32)
- Gluteradoxin(7)
- Glycogen synthase kinase(2)
- Glycosylase(10)
- Glyoxalase(3)
- Granzyme(7)
- Guanylate Kinase(2)
- Heparanase(2)
- Histone Deacetylase(3)
- Hydratase(10)
- Hydrolase(33)
- Hydroxylase(6)
- Isomerase(26)
- Jun N-terminal Kinase(1)
- Jun Proto-Oncogene(2)
- Kallikrein(26)
- Ligase(4)
- Lipase(14)
- Lipocalin(6)
- Lyase(9)
- LYVE1(3)
- Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase(16)
- MMP(68)
- Mutase(11)
- Natural Enzymes(4)
- Nuclease(18)
- Nucleotidase(4)
- Nudix Type Motif(11)
- Other Enzymes(63)
- Oxidase(23)
- Oxygenase(12)
- Paraoxonase(3)
- Peptidase(41)
- Peroxiredoxin(10)
- Phosphatase(150)
- Phosphorylase(9)
- PI3-kinase(5)
- Polymerase(13)
- PPARG(2)
- Protease(15)
- Proteasome(54)
- Protein Kinase Akt1/PKB alpha(4)
- Protein Kinase-A(7)
- Protein Kinase-C(3)
- Protein Kinases(86)
- Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase(10)
- Reductase(60)
- Secreted Phospholipase A2(10)
- Serine Threonine Kinase(4)
- Sulfatase(8)
- Synthase(23)
- Synthetase(33)
- TGFBR(3)
- TGM2(3)
- TIMP(10)
- TPA(4)
- Transferase(156)
- Tyrosine Kinase(9)
- Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme(39)
- Uromodulin(4)
- VEGF Receptors(14)
- Transaminase(19)
- Hexokinase(6)
- TIE1(6)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GC70181
α-Glucosidase-IN-22
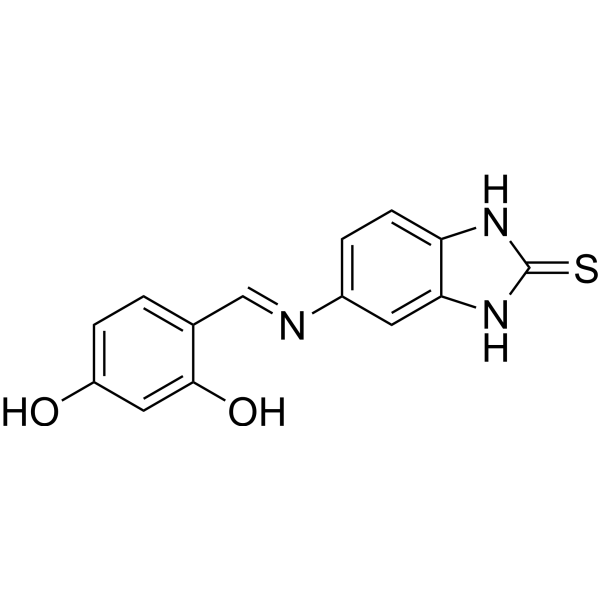
α-Glucosidase-IN-22 (compound 7i) 是一种苯并咪唑,一种有效的 α-葡萄糖苷酶 (α-glucosidase) 抑制剂,IC50 为 0.64 μM。α-Glucosidase-IN-22 是一种有效的抗糖尿病活性分子,具有用于 2 型糖尿病 (T2DM) 研究的潜力。
-
GC72710
α-Glucosidase-IN-35
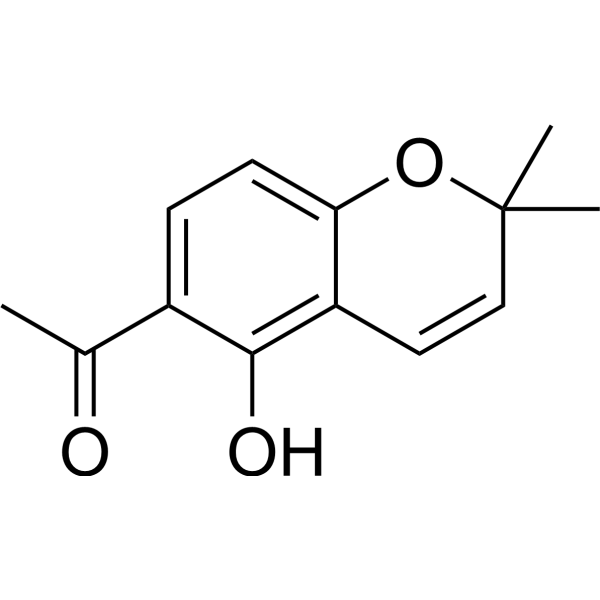
α-Glucosidase-IN-35(化合物1)是一种苯并二氢吡喃。
-
GC62551
β-Hydroxypropiovanillone
3,4'-二羟基-3'-甲氧基苯丙酮
β-Hydroxypropiovanillone 是一种天然化合物,对 α-葡萄糖苷酶 (α-glucosidase) 具有明显的浓度依赖性抑制作用 (IC50=257.8 μg/mL)。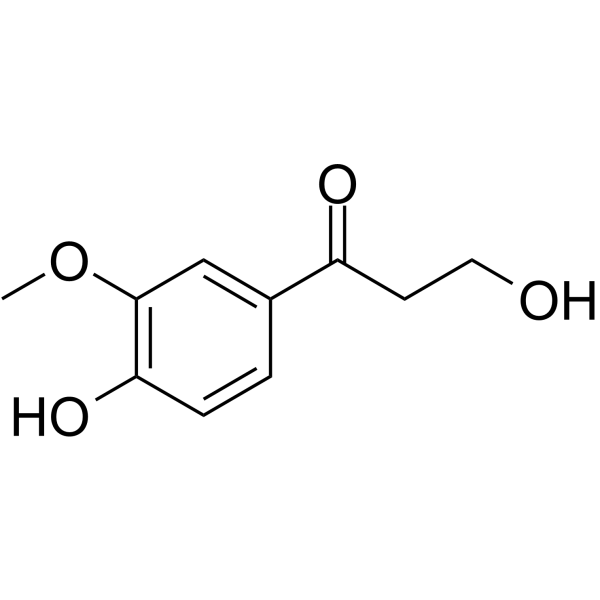
-
GC39795
(+)-Afzelechin
(+)-阿夫儿茶精
(+)-Afzelechin 是从佛手根的根茎中分离出来的,是一种 α-葡萄糖苷酶 (alpha-glucosidase) 活性抑制剂,ID50 值为 0.13 mM。(+)-Afzelechin 可以延迟食物中碳水化合物的吸收,从而抑制餐后高血糖和高胰岛素血症。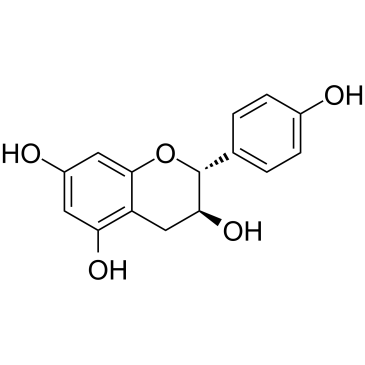
-
GC65547
(1S,2R)-Alicapistat
(1S,2R)-ABT-957
(1S,2R)-Alicapistat ((1S,2R)-ABT-957) 是一种具有口服活性的人钙激活中性蛋白酶 (calpains 1 和 2) 的选择性抑制剂,可能用于阿尔茨海默病 (AD) 的研究。 Alicapistat 可减轻羰基还原的代谢倾向,对 calpain 1 的 IC50 为 395 nM。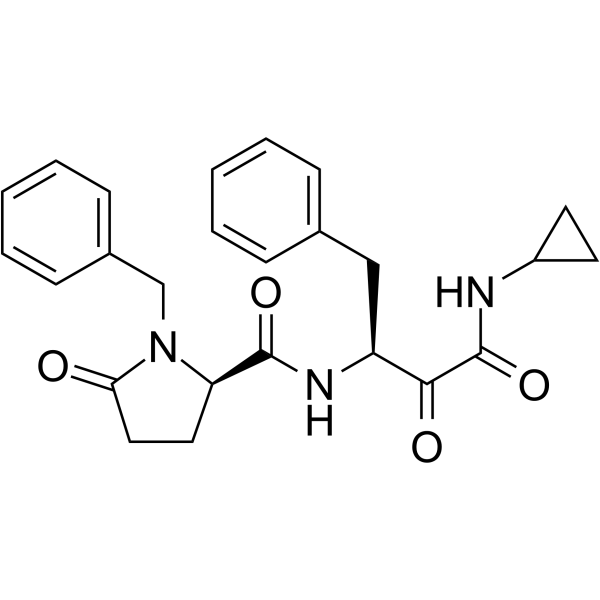
-
GC62193
(1S,2S)-Bortezomib
硼替佐米杂质E
(1S,2S)-Bortezomib 是 Bortezomib 的对映异构体。Bortezomib 是一种细胞渗透性、可逆性和选择性的蛋白酶体抑制剂,通过靶向苏氨酸残基有效抑制 20S 蛋白酶体 (Ki 为 0.6 nM)。Bortezomib 破坏细胞周期、诱导细胞凋亡以及抑制核因子 NF-κB。Bortezomib 是一种抗癌药物,也是第一种用于人类的蛋白酶体抑制剂。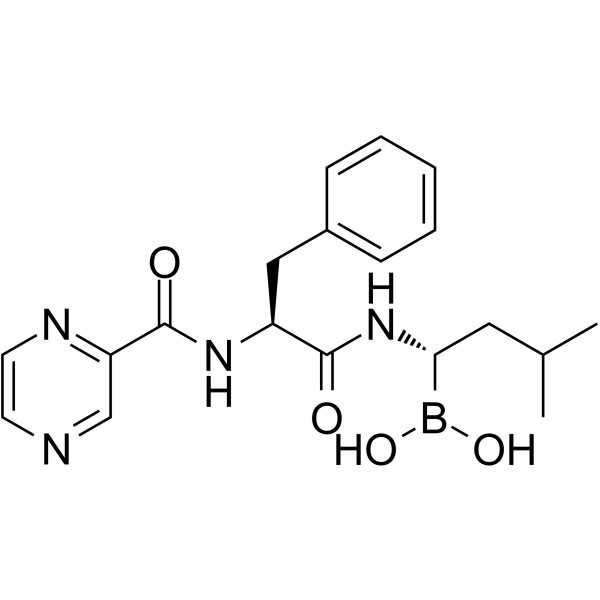
-
GC68525
(2α,3β,4α)-2,3,19-Trihydroxyurs-12-ene-23,28-dioic acid
(2α,3β,4α)-2,3,19-Trihydroxyurs-12-ene-23,28-dioic acid 是一种可从 Rubus ellipticus var. obcordatus 中分离得到的皂苷。(2α,3β,4α)-2,3,19-Trihydroxyurs-12-ene-23,28-dioic acid 抑制 α-Glucosidase,其 IC50 为 1.68 mM。
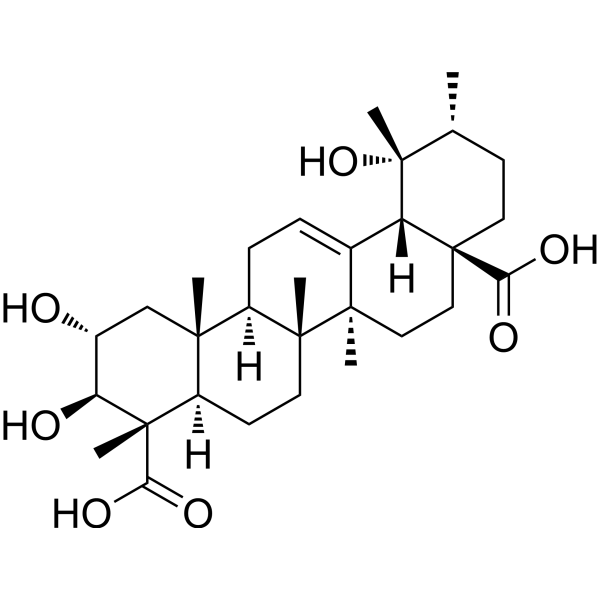
-
GC62735
(E/Z)-GO289
(E/Z)-GO289 potently and selectively inhibits casein kinase 2 (CK2) at an IC50 of 7 nM in vitro kinase assay.
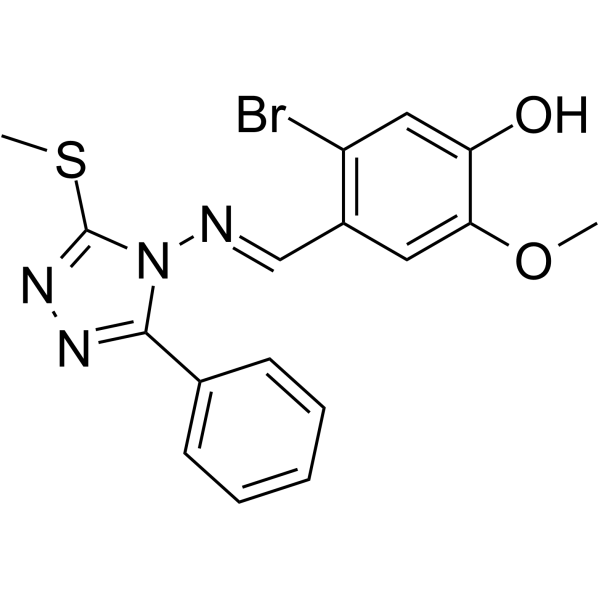
-
GC74184
(R)-Azasetron besylate
SENS-401
(R)-Azasetron besylateSENS-401是一种口服活性钙调神经磷酸酶抑制剂。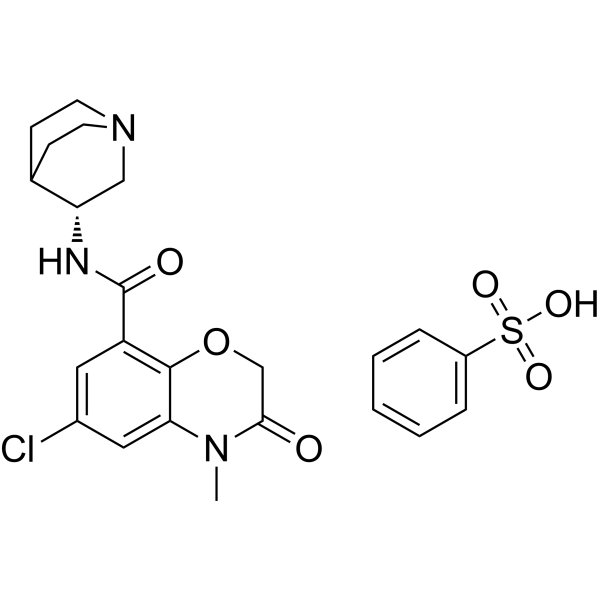
-
GC46351
(S)-CR8
An inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases
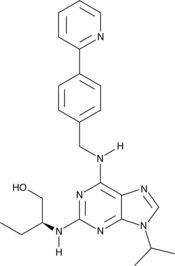
-
GC64535
(S,S)-TAPI-1
TAPI
A TACE inhibitor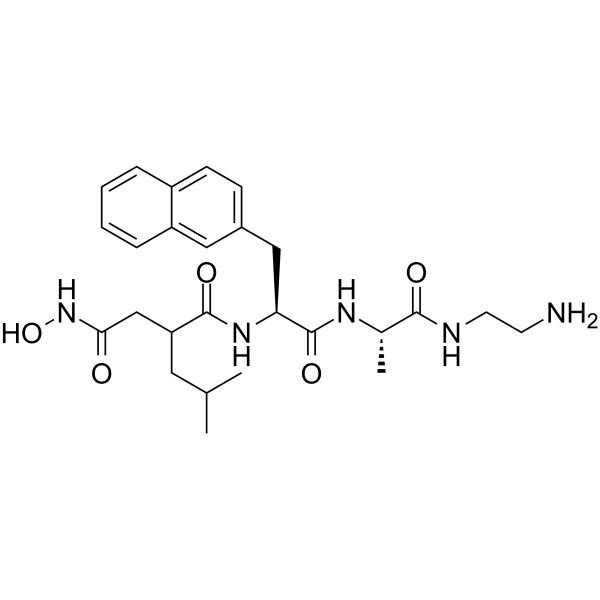
-
GC45978
1,10-Phenanthroline (hydrate)
邻菲罗啉,1,10-Phenanthroline monohydrate
A metal chelator and inhibitor of metalloproteases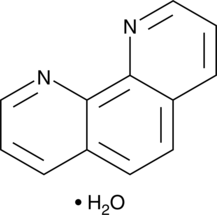
-
GC41774
1,2,3-Trimyristoyl-rac-glycerol
三肉豆蔻酸甘油酯
A triacylglycerol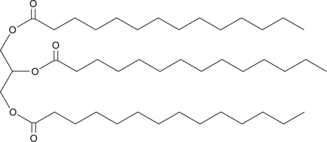
-
GC41992
1-Deoxynojirimycin (hydrochloride)
去氧野艽霉素盐酸盐,Duvoglustat hydrochloride
An iminosugar with diverse biological activities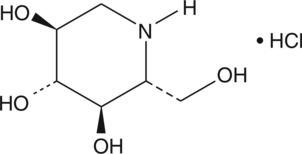
-
GC25005
1-Naphthyl phosphate potassium salt
α-Naphthyl acid phosphate monopotassium salt
1-Naphthyl phosphate potassium salt (α-Naphthyl acid phosphate monopotassium salt) is a non-specific phosphatase inhibitor which acts on acid, alkaline, and protein phosphatases.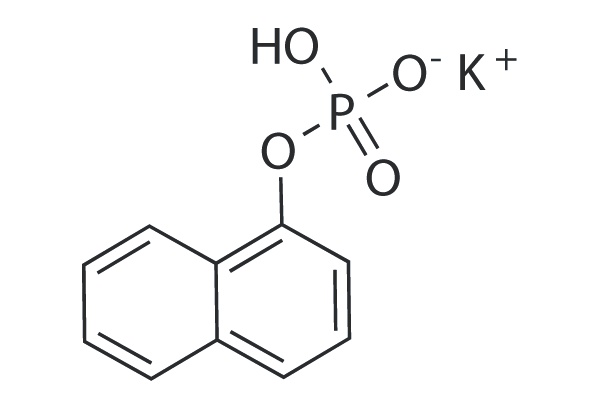
-
GC72952
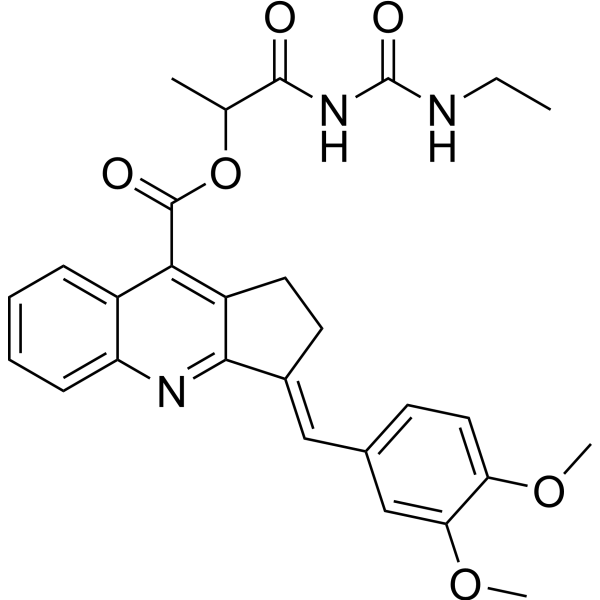
1E7-03
1E7-03是一种靶向蛋白磷酸酶-1的低分子量四喹啉衍生物,可以抑制HIV-1的转录。
-
GC71909
2,7"-Phloroglucinol-6,6'-bieckol
2,7"-Phloroglucinol-6,6'-bieckol是一种口服活性的双α-淀粉酶/α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂,IC50值分别为6.94μM和23.35μM。
-
GC72494
2-Hydroxyquinoline
2-Hydroxyquinoline是一种有效的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂,对α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的IC50值分别为64.4、130.5µg/mL。
-
GC68503
20S Proteasome activator 1
20S Proteasome activator 1 是一种有效的 20S 蛋白酶激活剂,对胰蛋白酶样位点、胰凝乳蛋白酶样位点和半胱天冬酶位点的 IC50 分别为 0.3 μM、0.7 μM 和 1.8 μM。20S Proteasome activator 1 能在细胞系统中翻译,防止致病性 α-synuclein A53T 突变体积累。20S Proteasome activator 1 可用于神经退行性疾病的研究。
-
GC64472
20S Proteasome-IN-1
20S Proteasome-IN-1 是一种 26S proteasome 抑制剂,详细信息请参考专利文献 WO2006128196A2 中的化合物 2。20S Proteasome-IN-1 具有用于癌症,免疫相关疾病,炎症,缺血性疾病,神经退行性疾病和其他疾病研究的潜力。
-
GC60019
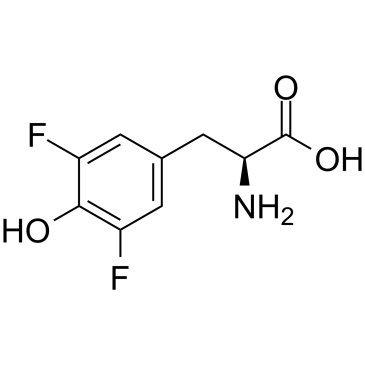
3,5-Difluoro-L-tyrosine
3,5-Difluoro-L-tyrosine是酪氨酸的一种功能性,耐酪氨酸酶的模拟物,可用于分析蛋白质酪氨酸磷酸酶(PTP)的底物特异性。
-
GC49337
4-Acetamidobenzenesulfonamide
对乙酰胺基苯磺酰胺
A metabolite of asulam and sulfanilamide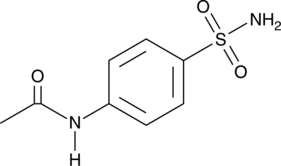
-
GC20095
5,7-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin
NSC 5302
A synthetic coumarin with diverse biological activities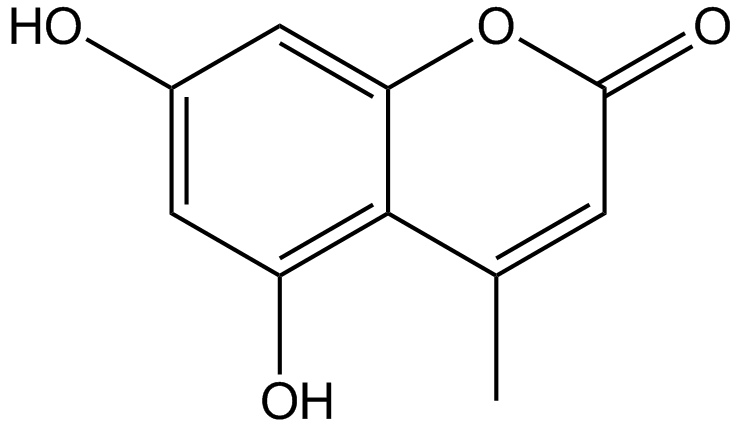
-
GC65668
5-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline
5A8HQ
5-氨基-8-羟基喹啉(5A8HQ)是一种潜在的抗癌候选药物,具有良好的蛋白酶体抑制活性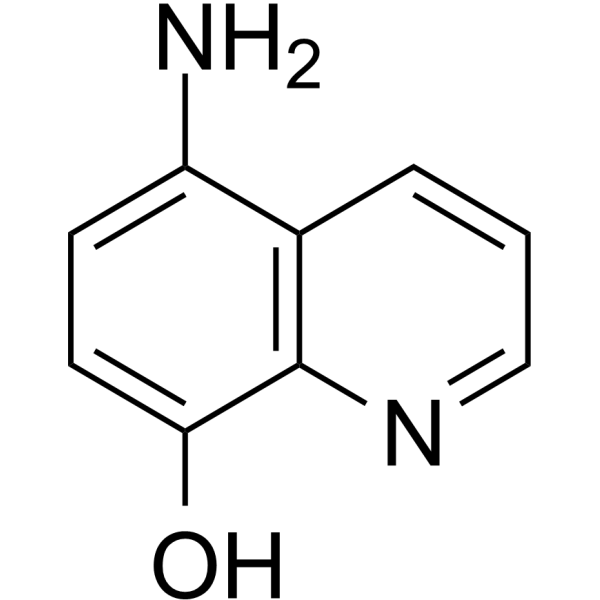
-
GC65394
7-BIA
7-BIA 是一种受体型蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶 D (PTPRD) 抑制剂,IC50 值约为 1-3 μM。
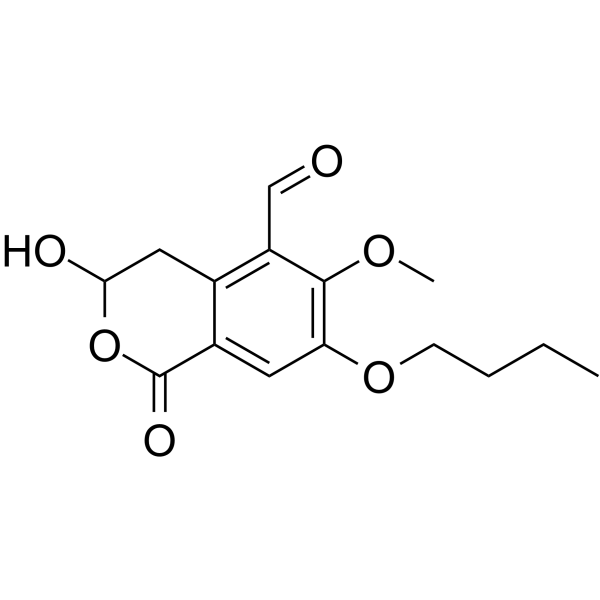
-
GC60037
A-3 hydrochloride
赤霉酸
A-3 hydrochloride, a potent, cell-permeable, reversible, ATP-competitive non-selective antagonist of various kinases, againsts cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) (Ki=4.3 ?M), casein kinase II (CK2) (Ki=5.1 ?M) and myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) (Ki=7.4 ?M), also inhibits Protein Kinase C (PKC) and casein kinase I (CK1) with Ki values of 47 ?M and 80 ?M, respectively.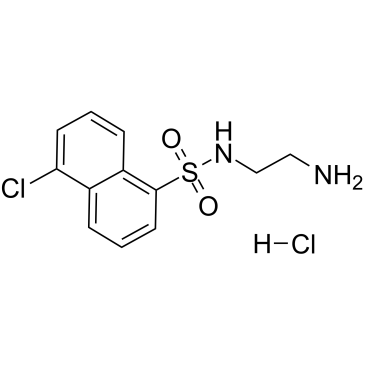
-
GP21322
AARS Human
Alanyl-tRNA Synthetase Human Recombinant

-
GP21321
AASDHPPT Human
Aminoadipate-Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase-Phosphopantetheinyl Transferase Human Recombinant

-
GC46769
Abametapir
55'-二甲基-2,2-联吡啶
A building block and an insecticide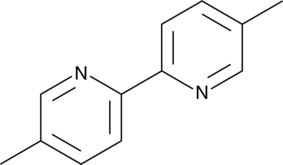
-
GC63921
ABBV-CLS-484
ABBV-CLS-484 is a potent PTPN1 or PTPN2 inhibitor with a sub-nanomolar activity.
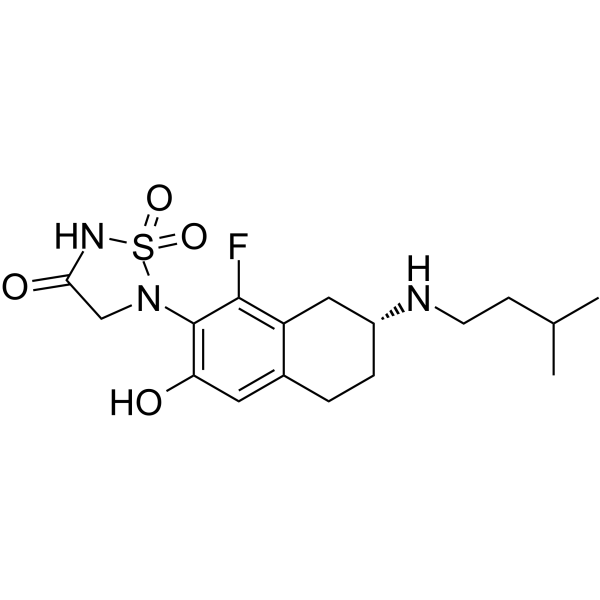
-
GP21323
ABHD10 Human
Abhydrolase Domain Containing 10 Human Recombinant

-
GP21324
ABHD14B Human
Abhydrolase Domain Containing 14B Human Recombinant

-
GP21325
ABO Human
ABO Blood Group Human Recombinant

-
GC68620
Ac-VLPE-FMK
Ac-Val-Leu-Pro-Glu(OMe)-CH2F
Ac-VLPE-FMK 是一种四肽基单氟甲基酮 (m-FMK),是一种 Cat-B 和 Cat-L 抑制剂。Ac-VLPE-FMK 可用于癌症侵袭性研究。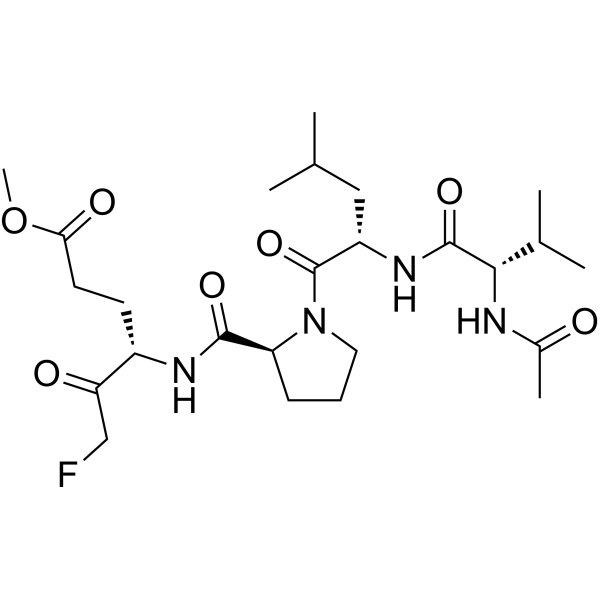
-
GP21326
ACAA1 Human
Acetyl-COA Acyltransferase Human Recombinant

-
GP21327
ACAA2 Human
Acetyl-COA Acyltransferase 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP21328
ACAD8 Human
Acyl-Coenzyme A Dehydrogenase 8 Human Recombinant

-
GP21329
ACADL Human
Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase, Long Chain, Human Recombinant

-
GP21330
ACADM Human
Acyl-Coenzyme A Dehydrogenase, C-4 to C-12 Human Recombinant

-
GP21331
ACADS Human
Acyl-Coenzyme A Dehydrogenase C-2 to C-3 Human Recombinant

-
GP21332
ACADSB Human
Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase, Short Chain Human Recombinant

-
GP21333
ACADVL Human
Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase, Very Long Chain Human Recombinant

-
GP21334
ACAT1 Human
Acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21335
ACAT2 Human
Acetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase 2 Human Recombinant

-
GC65612
Acetazolamide sodium
乙酰唑胺钠
An Analytical Reference Standard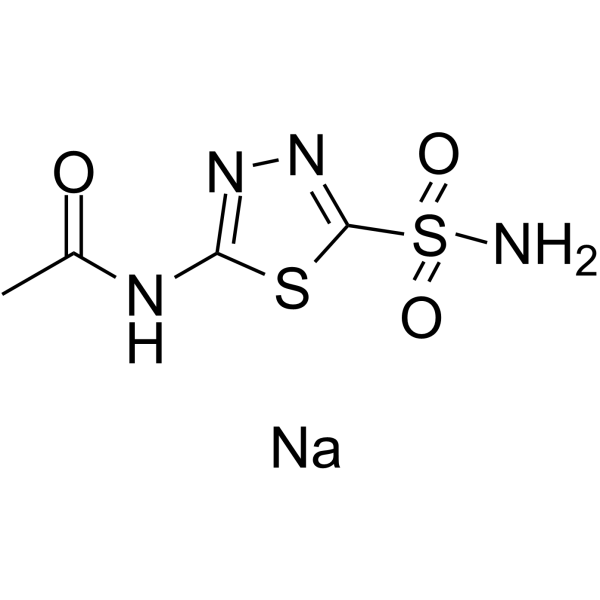
-
GP26121
ACHE Human
ACHE Human Recombinant produced in HEK cells is a single, glycosylated, polypeptide chain (32-614 a

-
GP22407
ACKA E.Coli
Acetate Kinase E.Coli Recombinant

-
GP21336
ACO1 Human
Aconitase-1 Human Recombinant

-
GP21338
ACOT11 Human
Acyl-CoA Thioesterase 11 Human Recombinant

-
GP21339
ACOT13 Human
Acyl-CoA Thioesterase 13 Human Recombinant





