Viral Antigens(病毒抗原)
A viral Antigen is an antigen with multiple antigenicities that is protein in nature, strain-specific, and closely associated with the virus particle. A viral antigen is a protein encoded by the viral genome.A viral protein is an antigen specified by the viral genome that can be detected by a specific immunological response.
Viruses are infectious pathogens that cause serious diseases & major threats for global public health, such as influenza, hepatitis, & AIDS. Virus is a sub-micrometer particle that has DNA or RNA packed in a shell called capsid. Viral antigens protrude from the capsid and often fulfill important function in docking to the host cell, fusion, and injection of viral DNA/RNA. Antibody-based immune responses form a first layer of protection of the host from viral infection; however, in many cases a vigorous cellular immune response mediated by T-cells and NK-cells is required for effective viral clearance. When cellular immunity is unable to clear the virus, the infection can become chronic, and serum antibodies to the viral pathogen are used as first indicator for the diagnosis of the disease.
ELISAs provide a valuable tool in the detection and diagnosis of virus infection. The ability to produce recombinant viral proteins will ensure that future ELISAs are safe, specific and rapid. Even when a virus cannot be cultured, provided gene sequence is available, it is possible to rapidly respond to emerging viruses and new viral strains of existing pathogens.
Recombinant viral antigens contain part of viral sequence meaning that the recombinant antigen contains a region which can be recognized by different antibodies produced by different individuals. This reduces the risk of false negatives which can occur with synthetic peptides, which contain only a small portion of the entire protein. If an individual infected with a viral antigen makes antibodies to a part of the protein not included in the synthetic peptides, a false negative results.
Recombinant viral protein usually contains a fusion protein/partner which produces superior attachment to assay surfaces such as wells. For this reason, smaller amounts of recombinant protein will produce the same results as larger amounts of unfused protein. The choice of fusion partner prevents false positives, allowing superior adhesion without incorrect results.
Recombinant Viral proteins are expressed in bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, and viruses. E. Coli cells were first to be used for this purpose but the expressed proteins were not glycosylated, which was a major drawback since many of the immunogenic proteins of viruses such as the envelope glycoproteins, were glycosylated. Nevertheless, in many instances, it was demonstrated that the non-glycosylated protein backbone was just as immunogenic. The obvious advantage of recombinant viral antigens is that they are available in unlimited quantities and the production and quality control processes is simple.
Advantages of defined using recombinant viral antigens:
1. Production and quality control is simple.
2. No nucleic acids or other viral or external proteins, therefore less toxic.
3. Safer in cases where viruses are oncogenic or establish a persistent infection.
4. Feasible even if virus cannot be cultivated
Disadvantages:
1. May be less immunogenic than conventional inactivated whole-virus vaccines.
2. Requires adjuvant .
3. Fails to elicit CMI.
Facts about Viral Antigens:
1. A Viral Protein Mimics its Way into cells.
2. Viral Protein Helps Infected T Cells Stick To Uninfected Cells.
3. The Viral Protein A238L Inhibits Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression through a Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cell-dependent Trans-activation Pathway.
4. Viral Protein is an effective preventative against ear infection.
5. HIV-1 Viral Protein R Induces Apoptosis via a Direct Effect on the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore.
6. The Level of Viral Antigen Presented by Hepatocytes Influences CD8 T-Cell Function.
7. Antigen-presenting cells from calves persistently infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus, a member of the Flaviviridae, are not compromised in their ability to present viral antigen.
8. There is a difference in the distribution and spread of a viral antigen, development of lesions and correlation between presence of viral antigen and lesions.
9. The absence of viral antigens on the surface of equine herpesvirus-1-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells is a strategy to avoid complement-mediated lysis.
10. Viral Protein Influences Key Cell-signaling Pathway.
11. A viral protein produced by cancer-causing virus influences a key signaling pathway in the immune cells that the virus infects. This stimulates the cells to divide, helping the virus spread through the body.
12. Protection by recombinant viral proteins against a respiratory virulent avian metapneumovirus has been achieved.
13. Viral O-acetylesterases are found in influenza C viruses and Corona-viruses. Viral O-acetylesterases remove cellular receptors from the surface of target cells which destroys the receptor. Recombinant viral O-acetylesterases derived from Sf9 insect cells as chimeric proteins fused to eGFP specifically hydrolyze 9-O-acetylated sialic acids, while that of sialodacryoadenitis virus, a rat coronavirus related to mouse hepatitis virus, is specific for 4-O-acetylated sialic acid. The recombinant esterases were shown to specifically de-O-acetylate sialic acids on glycoconjugates. The recombinant viral proteins can be used to unambiguously identify O-acetylated acids.
Products for Viral Antigens
- Borrelia(28)
- Chagas(3)
- Chikungunya(7)
- Chlamydia(10)
- Cytomegalo(8)
- Dengue(50)
- Ebola(4)
- EBV(13)
- Encephalitis(8)
- Feline Leukemia Virus(1)
- Hantavirus(1)
- HBsAg(7)
- Helicobacter Pylori(3)
- Hepatitis A(15)
- Hepatitis B(10)
- Hepatitis C(85)
- Hepatitis D(1)
- Hepatitis E(5)
- Herpes(11)
- HERV-K(1)
- HIV(151)
- HTLV(6)
- Influenza(72)
- Lassa(2)
- Malaria(71)
- Mumps(1)
- Mycoplasma(4)
- Norovirus(4)
- Papillomavirus(5)
- Parvovirus(3)
- Rubella(3)
- S. Typhi(5)
- SARS(85)
- Shiga Like Toxin(2)
- Toxoplasma(9)
- Treponema(16)
- Varicella(3)
- West Nile(2)
- Zika(13)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GC68449
CA inhibitor 1
GS-6207 analog
CA inhibitor 1 (GS-6207 analog) 是一种有效的 HIV 衣壳抑制剂,可用于抑制 HIV。
-
GC66051
Cabotegravir sodium
卡博特韦钠; GSK-1265744 sodium; S/GSK1265744 sodium
An HIV-1 integrase inhibitor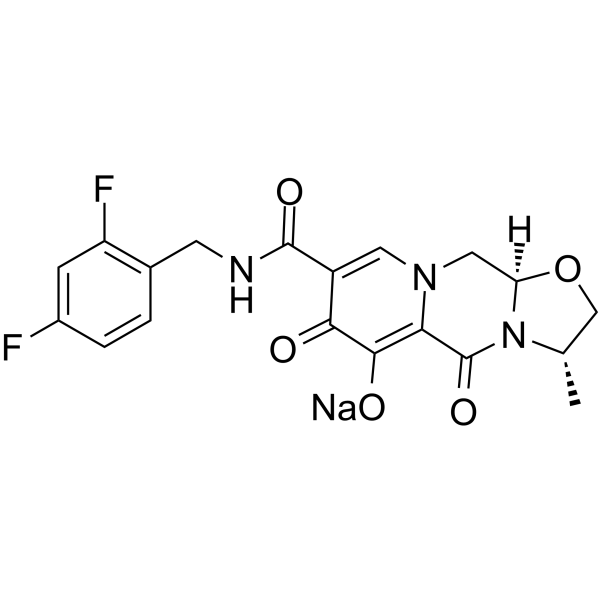
-
GP24098
CagA Pylori
Helicobacter Pylori Cytotoxin-Associated Gene A Recombinant

-
GC48893
Carbazomycin B
A bacterial metabolite with diverse biological activities
-
GC48850
Carbazomycin C
A bacterial metabolite with diverse biological activities
-
GC47062
CAY10766
An antiviral compound
-
GC64261
Censavudine
OBP-601; BMS-986001
Censavudine (OBP-601; BMS-986001),一种核苷类似物,是一种核苷逆转录酶 (nucleoside reverse transcriptase) 抑制剂。Censavudine 是一种有效的 HIV 抑制剂,对 HIV-2 和 HIV-1 的 EC50 范围分别为 30-81 nM 和 450-890 nM。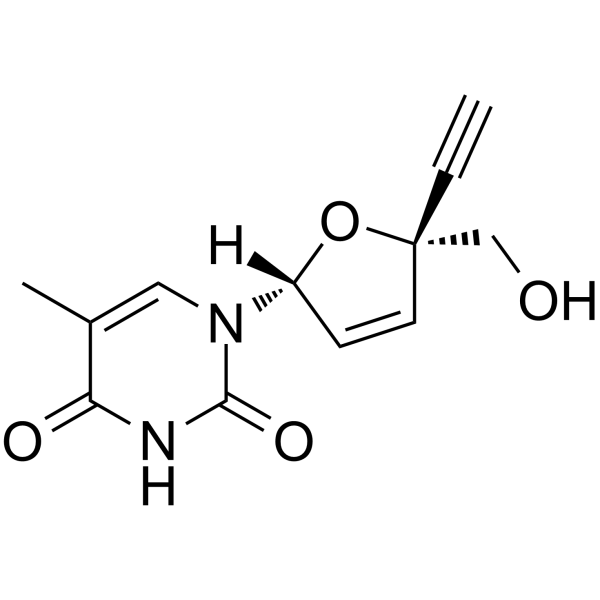
-
GP25472
Chikungunya E1
Chikungunya Wild Type E1 Recombinant

-
GP25474
CHIKV E1
Chikungunya E1 Recombinant

-
GP25475
CHIKV E2
Chikungunya E2 Recombinant

-
GP25473
CHIKV Mutant
Chikungunya Mutant (A226V) E1 Recombinant

-
GP25205
Chimeric Chagas
Chimeric Chagas Multiantigen Recombinant

-
GP25226
Chlamydia HSP70 (462-503 a.a.)
Chlamydia Trachomatis HSP70 (462-503 a.a.) Recombinant

-
GP25227
Chlamydia HSP70 (549-660a.a.)
Chlamydia Trachomatis HSP70 (549-660 a.a.) Recombinant

-
GP25225
Chlamydia PGP-3D
Chlamidia Trachomatis PGP-3D Recombinant

-
GP25228
Chlamydia Pneumonia
Chlamydia Pneumonia Recombinant

-
GP25219
Chlamydia W2
Chlamydia Trachomatis W2 Recombinant

-
GP25224
Chlamydia W3-W6
Chlamidia Trachomatis W3-W6 Recombinant

-
GP25220
Chlamydia W4
Chlamydia Trachomatis W4 Recombinant

-
GP25222
Chlamydia W4-W5
Chlamydia Trachomatis W4-W5 Recombinant

-
GP25221
Chlamydia W5
Chlamydia Trachomatis W5 Recombinant

-
GP25223
Chlamydia W5-W6
Chlamydia Trachomatis W5-W6 Recombinant

-
GC60700
Chloroquine D5
氯喹 d5
An internal standard for the quantification of chloroquine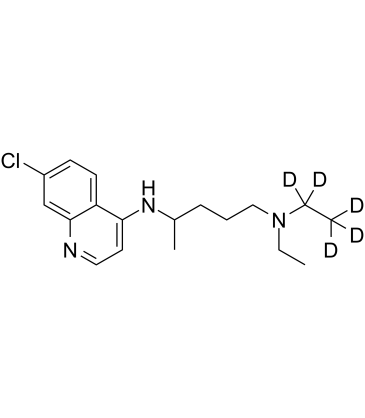
-
GC45885
Chloroquine-d5 (phosphate)
磷酸氯喹 d5 (二磷酸盐)
An internal standard for the quantification of chloroquine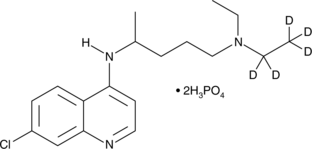
-
GC66467
Claficapavir
A1752
Claficapavir (A1752) 是一种特异的核衣壳蛋白 (nucleocapsid protein) 抑制剂,IC50 约为1μM。Claficapavir 与 HIV-1 NC(Kd=20 nM) 强烈结合,从而抑制 NC 的伴侣特性,并导致对 HIV-1 具有良好的抗病毒活性。
-
GC70227
Clathrin-IN-1
Clathrin-IN-1是一种选择性网格蛋白介导的内吞作用(CME)抑制剂。
-
GC49852
Clindamycin (hydrochloride hydrate)
盐酸克林霉素
Clindamycin (hydrochloride hydrate)是一种林可酰胺类抗生素,用于治疗由敏感厌氧菌、链球菌、葡萄球菌和肺炎球菌引起的严重感染,主要用于骨髓炎、呼吸系统感染、胆道感染、心内膜炎、中耳炎、皮肤软组织感染及败血症等。
-
GC43278
Clindamycin Sulfoxide
克林霉素亚砜
An active metabolite of clindamycin
-
GC52171
Clindamycin-d3 (hydrochloride)
克林霉素-D3盐酸盐
An internal standard for the quantification of clindamycin
-
GP25351
CMV gB
Cytomegalo Virus gB Recombinant

-
GP25356
CMV Mosaic
Cytomegalo Virus Mosaic Recombinant

-
GP25355
CMV Pp150
Cytomegalo Virus Pp150 (UL32) Recombinant

-
GP25352
CMV Pp28
Cytomegalo Virus Pp28 (UL99) Recombinant

-
GP26433
CMV Pp38
The E

-
GP25353
CMV Pp52
Cytomegalo Virus Pp52 (UL44) Recombinant

-
GP25354
CMV Pp65
巨细胞病毒 Pp65 (UL83) 重组体

-
GP26434
CMV Pp65, 561 a.a.
The E

-
GC47119
Colletodiol
(+)-Colletodiol
A fungal metabolite with immunosuppressive and antiviral activities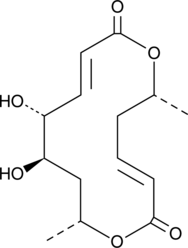
-
GP26375
CoV HKU1 Human
Recombinant Human Coronavirus HKU1 Nucleoprotein is full length protein except the predicted signal peptide of the first 30 aa produced in E

-
GP26376
CoV OC43 Human
Recombinant Human Coronavirus OC43 Nucleoprotein is full length protein except the predicted signal peptide of the first 30 aa produced in E

-
GP26423
CoV-2 3CL
Recombinant Coronavirus 2019 3CL Protease having a Mw of approximately 33

-
GP26411
CoV-2 Envelope (1-75)
The E

-
GP26412
CoV-2 Membrane Env.
The E

-
GP26417
CoV-2 N (1-419)
The E

-
GP26416
CoV-2 N (1-419), Biotin
TheHEK293 derived recombinant biotinylated protein contains the Coronavirus 2019 CoV-2 Nucleocapsid, Wuhan-Hu-1 strain, amino acids 1-419 fused toHis-Avi tag at C-terminal

-
GP26415
CoV-2 N (1-419), HEK
The HEK293 derived recombinant protein contains the Coronavirus 2019 CoV-2 Nucleocapsid, Wuhan-Hu-1 strain, amino acids 1-419 fused to His tag at C-terminal having a calculated Mw of 47

-
GP26421
CoV-2 N (127 a.a.)
The E

-
GP26420
CoV-2 N (196 a.a.)
The E

-
GP26419
CoV-2 N (201-419)
The E

-
GP26422
CoV-2 N (329 a.a.)
The E





