Viral Antigens(病毒抗原)
A viral Antigen is an antigen with multiple antigenicities that is protein in nature, strain-specific, and closely associated with the virus particle. A viral antigen is a protein encoded by the viral genome.A viral protein is an antigen specified by the viral genome that can be detected by a specific immunological response.
Viruses are infectious pathogens that cause serious diseases & major threats for global public health, such as influenza, hepatitis, & AIDS. Virus is a sub-micrometer particle that has DNA or RNA packed in a shell called capsid. Viral antigens protrude from the capsid and often fulfill important function in docking to the host cell, fusion, and injection of viral DNA/RNA. Antibody-based immune responses form a first layer of protection of the host from viral infection; however, in many cases a vigorous cellular immune response mediated by T-cells and NK-cells is required for effective viral clearance. When cellular immunity is unable to clear the virus, the infection can become chronic, and serum antibodies to the viral pathogen are used as first indicator for the diagnosis of the disease.
ELISAs provide a valuable tool in the detection and diagnosis of virus infection. The ability to produce recombinant viral proteins will ensure that future ELISAs are safe, specific and rapid. Even when a virus cannot be cultured, provided gene sequence is available, it is possible to rapidly respond to emerging viruses and new viral strains of existing pathogens.
Recombinant viral antigens contain part of viral sequence meaning that the recombinant antigen contains a region which can be recognized by different antibodies produced by different individuals. This reduces the risk of false negatives which can occur with synthetic peptides, which contain only a small portion of the entire protein. If an individual infected with a viral antigen makes antibodies to a part of the protein not included in the synthetic peptides, a false negative results.
Recombinant viral protein usually contains a fusion protein/partner which produces superior attachment to assay surfaces such as wells. For this reason, smaller amounts of recombinant protein will produce the same results as larger amounts of unfused protein. The choice of fusion partner prevents false positives, allowing superior adhesion without incorrect results.
Recombinant Viral proteins are expressed in bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, and viruses. E. Coli cells were first to be used for this purpose but the expressed proteins were not glycosylated, which was a major drawback since many of the immunogenic proteins of viruses such as the envelope glycoproteins, were glycosylated. Nevertheless, in many instances, it was demonstrated that the non-glycosylated protein backbone was just as immunogenic. The obvious advantage of recombinant viral antigens is that they are available in unlimited quantities and the production and quality control processes is simple.
Advantages of defined using recombinant viral antigens:
1. Production and quality control is simple.
2. No nucleic acids or other viral or external proteins, therefore less toxic.
3. Safer in cases where viruses are oncogenic or establish a persistent infection.
4. Feasible even if virus cannot be cultivated
Disadvantages:
1. May be less immunogenic than conventional inactivated whole-virus vaccines.
2. Requires adjuvant .
3. Fails to elicit CMI.
Facts about Viral Antigens:
1. A Viral Protein Mimics its Way into cells.
2. Viral Protein Helps Infected T Cells Stick To Uninfected Cells.
3. The Viral Protein A238L Inhibits Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression through a Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cell-dependent Trans-activation Pathway.
4. Viral Protein is an effective preventative against ear infection.
5. HIV-1 Viral Protein R Induces Apoptosis via a Direct Effect on the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore.
6. The Level of Viral Antigen Presented by Hepatocytes Influences CD8 T-Cell Function.
7. Antigen-presenting cells from calves persistently infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus, a member of the Flaviviridae, are not compromised in their ability to present viral antigen.
8. There is a difference in the distribution and spread of a viral antigen, development of lesions and correlation between presence of viral antigen and lesions.
9. The absence of viral antigens on the surface of equine herpesvirus-1-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells is a strategy to avoid complement-mediated lysis.
10. Viral Protein Influences Key Cell-signaling Pathway.
11. A viral protein produced by cancer-causing virus influences a key signaling pathway in the immune cells that the virus infects. This stimulates the cells to divide, helping the virus spread through the body.
12. Protection by recombinant viral proteins against a respiratory virulent avian metapneumovirus has been achieved.
13. Viral O-acetylesterases are found in influenza C viruses and Corona-viruses. Viral O-acetylesterases remove cellular receptors from the surface of target cells which destroys the receptor. Recombinant viral O-acetylesterases derived from Sf9 insect cells as chimeric proteins fused to eGFP specifically hydrolyze 9-O-acetylated sialic acids, while that of sialodacryoadenitis virus, a rat coronavirus related to mouse hepatitis virus, is specific for 4-O-acetylated sialic acid. The recombinant esterases were shown to specifically de-O-acetylate sialic acids on glycoconjugates. The recombinant viral proteins can be used to unambiguously identify O-acetylated acids.
Products for Viral Antigens
- Borrelia(28)
- Chagas(3)
- Chikungunya(7)
- Chlamydia(10)
- Cytomegalo(8)
- Dengue(50)
- Ebola(4)
- EBV(13)
- Encephalitis(8)
- Feline Leukemia Virus(1)
- Hantavirus(1)
- HBsAg(7)
- Helicobacter Pylori(3)
- Hepatitis A(15)
- Hepatitis B(10)
- Hepatitis C(85)
- Hepatitis D(1)
- Hepatitis E(5)
- Herpes(11)
- HERV-K(1)
- HIV(151)
- HTLV(6)
- Influenza(72)
- Lassa(2)
- Malaria(71)
- Mumps(1)
- Mycoplasma(4)
- Norovirus(4)
- Papillomavirus(5)
- Parvovirus(3)
- Rubella(3)
- S. Typhi(5)
- SARS(85)
- Shiga Like Toxin(2)
- Toxoplasma(9)
- Treponema(16)
- Varicella(3)
- West Nile(2)
- Zika(13)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GC18516
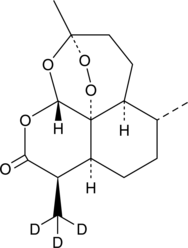
(+)-Aeroplysinin-1
(+)-Aeroplysinin-1
A sea sponge metabolite with diverse biological activities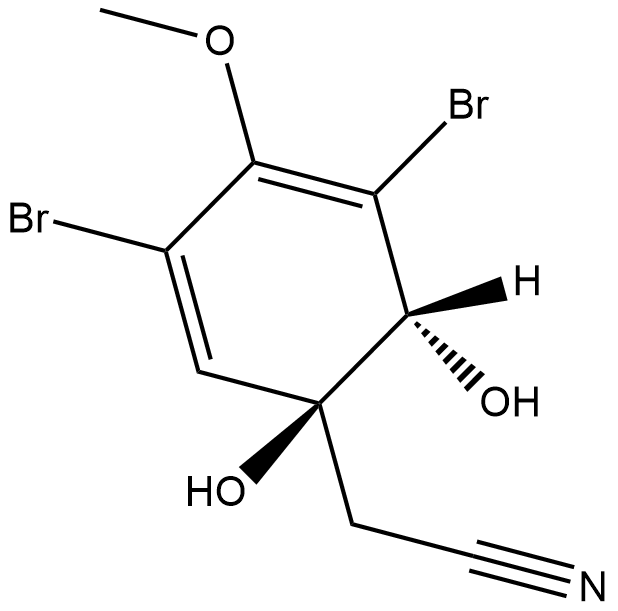
-
GC18749
(+)-Rugulosin
细皱青霉素+FORM,(+)-Rugulosin
A mycotoxin
-
GC65363
(1R)-Tenofovir amibufenamide
(1R)-HS-10234
(1R)-Tenofovir amibufenamide ((1R)-HS-10234) 是 Tenofovir amibufenamide 的异构体,是一种口服活性抗病毒药物。(1R)-Tenofovir amibufenamide ((1R)-HS-10234) 是一个 HIV 病毒感染的抑制剂和乙型肝炎病毒的抑制剂 ( HBV )。(1R)-Tenofovir amibufenamide ((1R)-HS-10234) 可用于 HIV 感染、乙肝研究。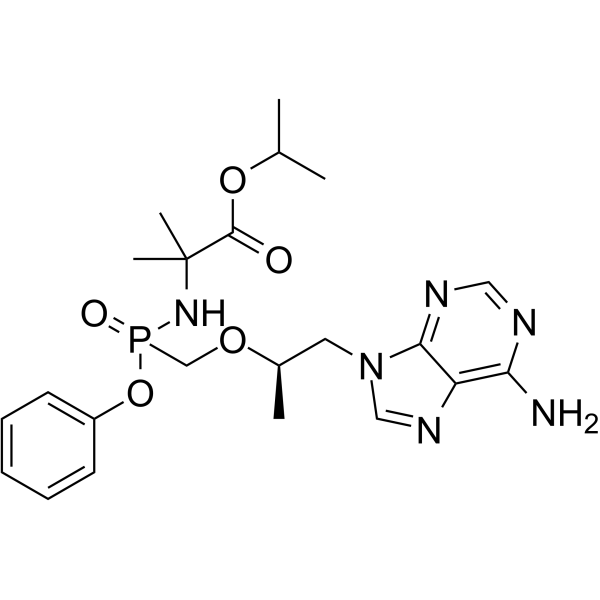
-
GC64260
(2S,5S)-Censavudine
(2S,5S)-OBP-601; (2S,5S)-BMS-986001
(2S,5S)-Censavudine ((2S,5S)-OBP-601) 是 Censavudine 的 (2S,5S)-对映异构体。Censavudine 是一种核苷类逆转录酶抑制剂,是一种有效的 HIV 抑制剂。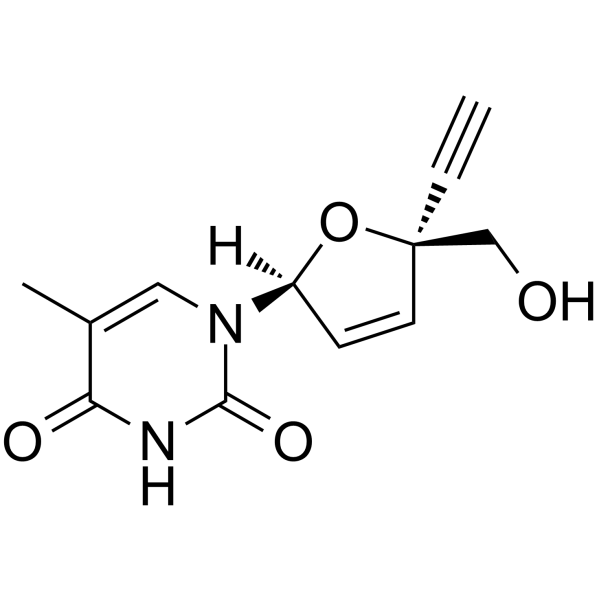
-
GC49167
(R)-(+)-Trityl glycidyl ether
三苯甲基-(R)-缩水甘油醚
A synthetic precursor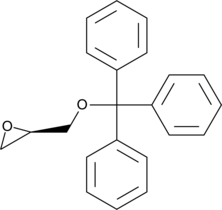
-
GC41620
(R)-(-)-Mellein
(R)-蜂蜜曲菌素,以及(S)-蜂蜜曲菌素,(R)-Mellein
A dihydroisocoumarin compound with antibacterial, antimalarial, antifungal , and anticancer effects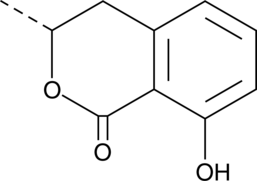
-
GC90744
1,2-Dioleoyl-3(R)-trimethylammoniumpropane (chloride)
R-DOTAP
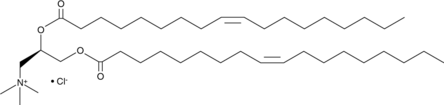
一个阳离子脂质
-
GC46404
10-Norparvulenone
(±)-10-Norparvulenone
A fungal metabolite
-
GC41942
16,16-dimethyl Prostaglandin A2
16,16dimethyl PGA2
A metabolism resistant analog of PGA2
-
GC41982
19,20-Epoxycytochalasin C
19,20-环氧细胞松弛素C
A fungal metabolite
-
GC41983
19,20-Epoxycytochalasin D
19,20-环氧细胞松弛素D
A fungal metabolite
-
GC72952
1E7-03
1E7-03是一种靶向蛋白磷酸酶-1的低分子量四喹啉衍生物,可以抑制HIV-1的转录。
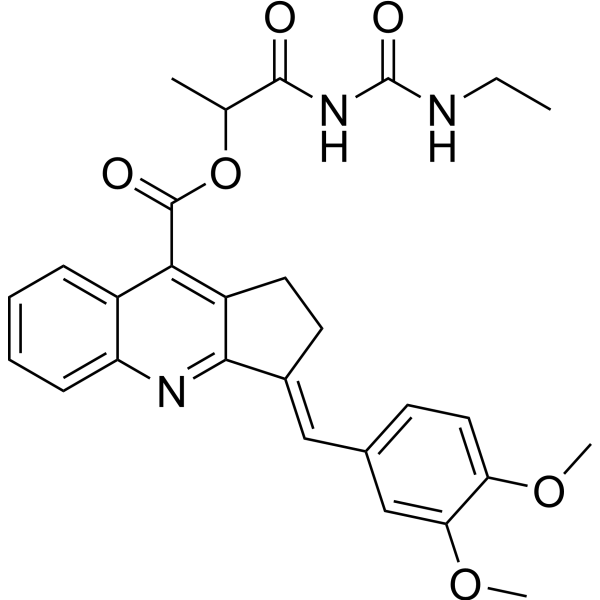
-
GP25206
1F8 Chagas
1F8 Chagas Recombinant

-
GC49823
2′-C-β-Methylguanosine
2'-C-甲基鸟苷
An active nucleoside metabolite of BMS-986094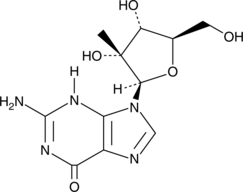
-
GC40675
2-deoxy-Artemisinin
脱氧青蒿素
An inactive metabolite of artemisinin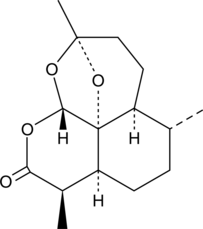
-
GC40634
2-epi-Abamectin
epi-Avermectin B1a
A degradation product of abamectin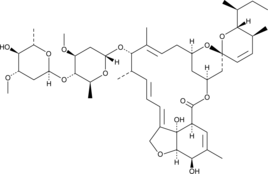
-
GC61674
2-Hydroxyacetophenone
2-羟基苯乙酮
2-Hydroxyacetophenone是Carissaedulis的主要根挥发物。2-Hydroxyacetophenone对HIV/SARS-CoVS假病毒的感染具有抑制作用,IC50为1.8mM。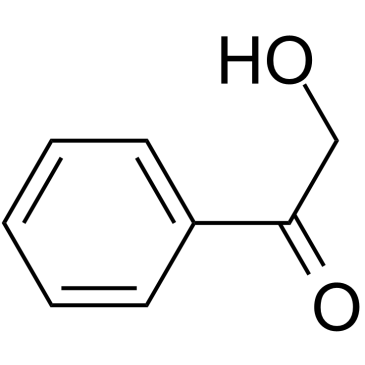
-
GC61753
2-Hydroxycinnamic acid
(E)-3-(2-羟基苯基)丙烯酸
2-Hydroxycinnamicacid是从肉桂的甲醇提取物中分离出的。2-Hydroxycinnamicacid对HIV/SARS-CoVS假病毒的感染具有抑制作用,IC50为0.3mM。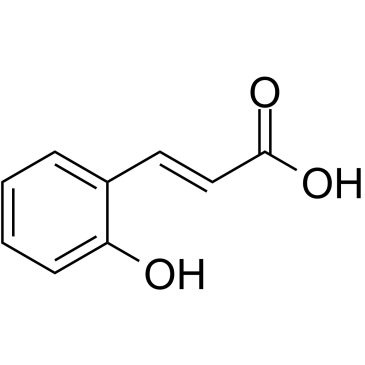
-
GC65085
3'-Azido-3'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine
3'-Azido-3'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine (CS-92) 是一种有效的异嗜性小鼠白血病相关逆转录病毒 (XMRV) 抑制剂,作用于 MCF-7 细胞,CC50 为 43.5 μM。3'-Azido-3'-deoxy-5-methylcytidine (CS-92) 作用于外周血单核细胞 (PBM),抑制 HIV-1 逆转录酶,EC50 为 0.06 μM。
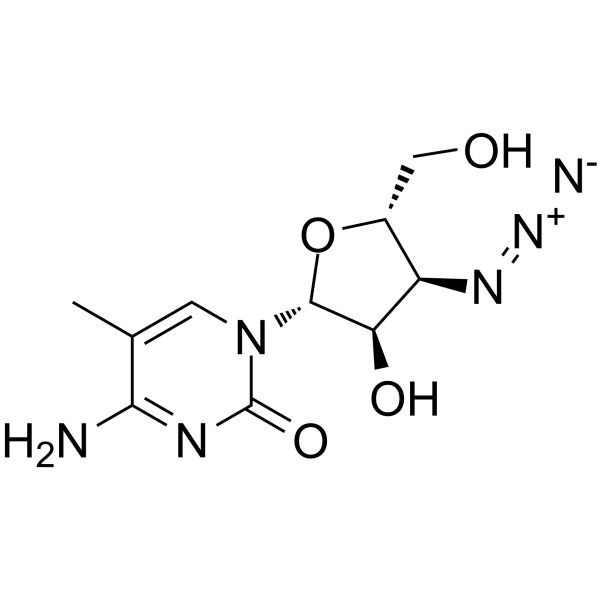
-
GC42312
3'-Sialyllactose (sodium salt)
3'-唾液乳糖钠盐
An abundant oligosaccharide in milk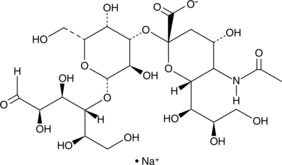
-
GC42448
4-MUNANA (sodium salt)
N-乙酰基-2-O-(4-甲基-2-氧代-2H-1-苯并吡喃-7-基)-ALPHA-神经氨酸一钠盐, 4-Methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-α-D-Neuraminic Acid
4-MUNANA (sodium salt)是一种用于神经氨酸酶活性测定的荧光底物。4-MUNANA被酶水解时,会释放出荧光团4-甲基伞形酮(4-MU),4-MU的最大激发波长为365nm,最大发射波长为450nm。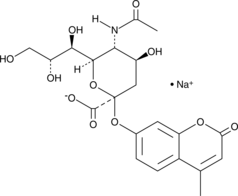
-
GC92085
4-O10b1
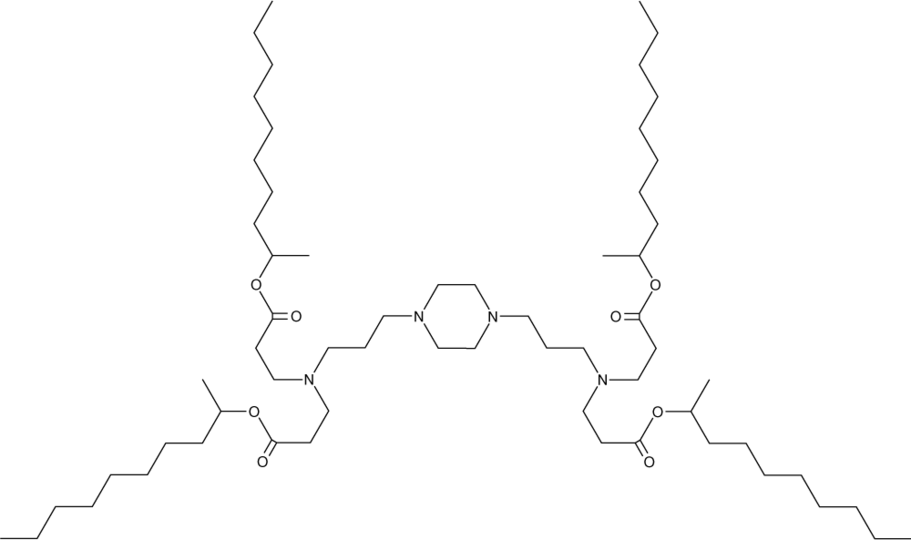
4-O10b1是一种可电离的阳离子脂质(pKa = 5.148),已被用于生成脂质纳米颗粒(LNPs),用于体外和体内递送siRNA。
-
GC48815
5,7,8-Trimethoxydictamnine
Acronycidine, NSC 30619
A quinoline alkaloid with antimalarial activity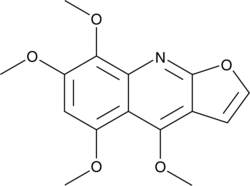
-
GC46705
5-Methoxycanthinone
5-甲氧基铁屎米酮
An alkaloid with anticancer properties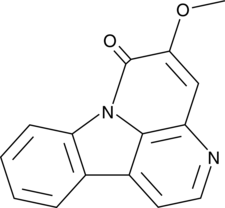
-
GC19536
6'-Sialyllactose Sodium Salt
6'-唾液乳糖钠盐,6'-N-Acetylneuraminyl-D-lactose
A major milk oligosaccharide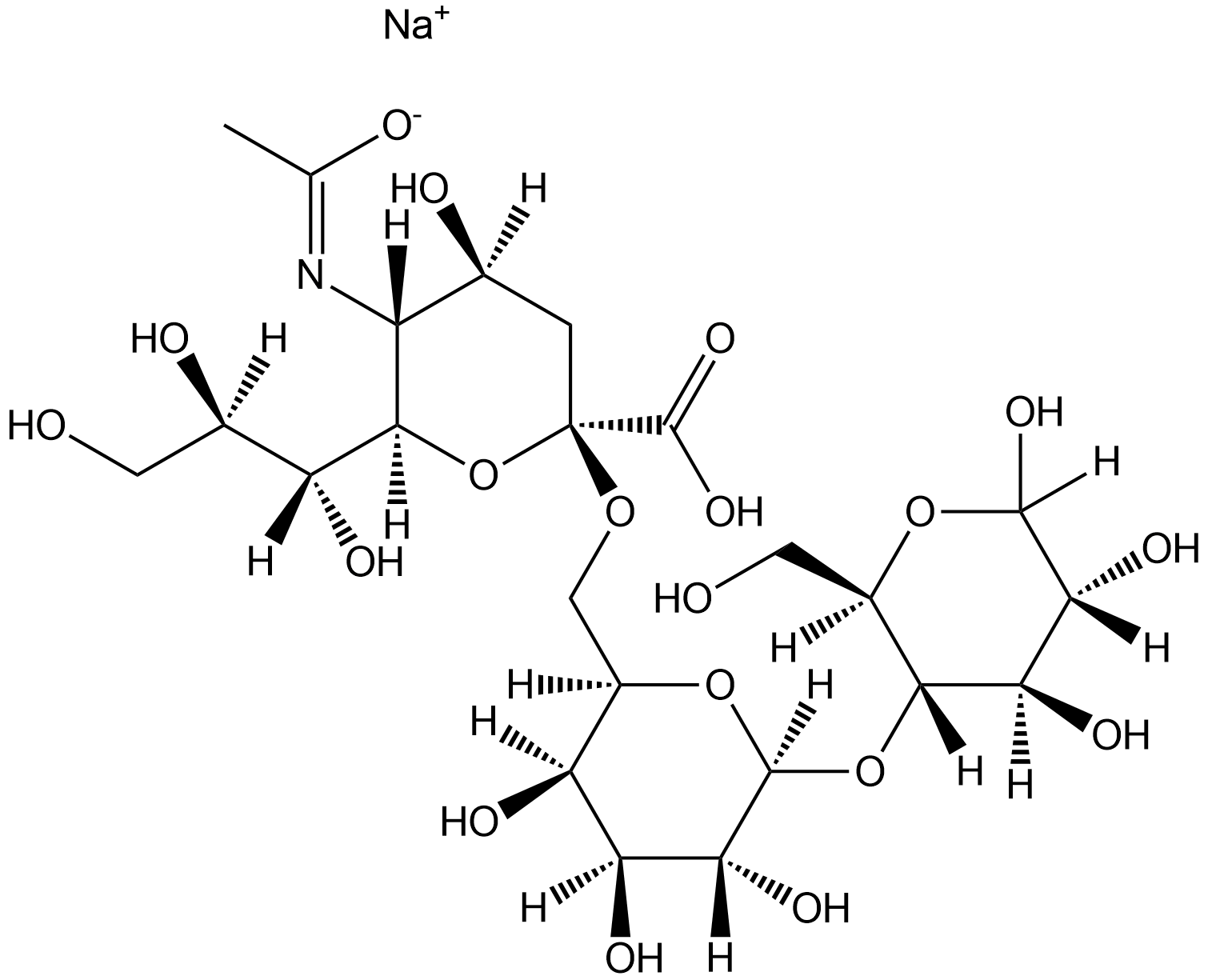
-
GC92071
6,6′-Trehalose Dioleate
6,6′-TDO
6,6′-Trehalose Dioleate(6,6′-TDO)是一种糖脂,已被用于制备脂质纳米粒(LNPs),用于在体外和体内递送mRNA。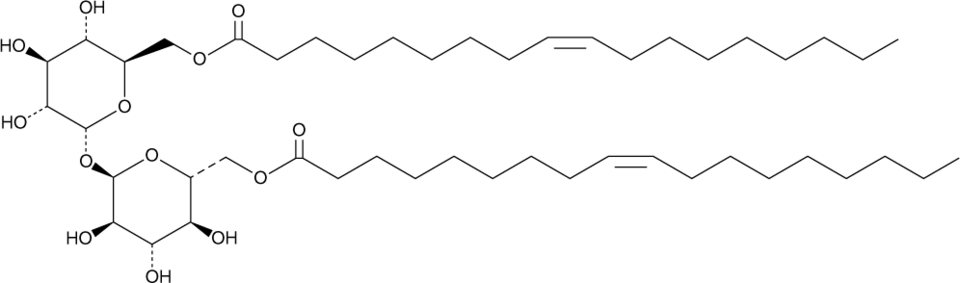
-
GC45715
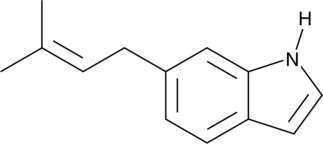
6-Prenylindole
A bacterial metabolite
-
GC18426
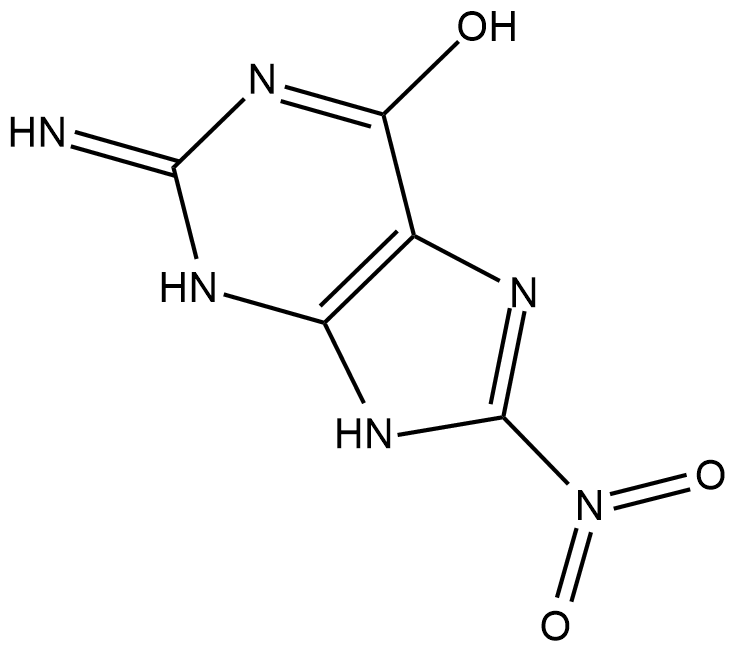
8-Nitroguanine
A mutagenic nitrative guanine derivative
-
GC46753
9(S),12(S),13(S)-TriHOME
(-)-Pinellic Acid, 9S,12S,13S-Pinellic Acid
An oxylipin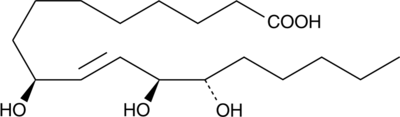
-
GC42648
9-Methylstreptimidone
9一甲基链霉戊二酰亚胺
A microbial metabolite with antifungal and antiviral activities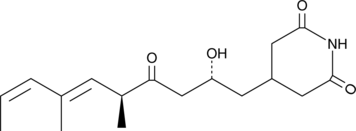
-
GC49745
ABT-263-d8
生根粉263 d8
An internal standard for the quantification of ABT-263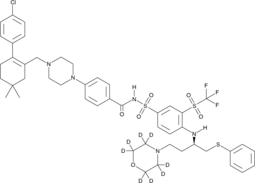
-
GP26113
ACE Human
ACE Human produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 1235 amino acids (30-1256 a

-
GP26114
ACE2 (18-615) Human
The CHO derived ACE2 Human recombinant protein contains the extracellular domain amino acids 18- 615 fused to Fc tag at C-terminal and has a molecular weight of ~130 kDa

-
GP26116
ACE2 (18-740) Human
The HEK293 derived ACE2 Human recombinant protein contains the amino acids 18-740 fused to IgG-His tag ( 242 a

-
GP26118
ACE2 (18-740) Human, Biotin
The HEK293 derived ACE2 Human recombinant biotinylated protein contains the amino acids Gln 18-Ser 740 fused to His-AVI tag at C-terminal having a predicted Mw of 87

-
GP26117
ACE2 (18-740) Human, Fc
The HEK293 derived ACE2 Human recombinant protein contains the amino acids 18-740 fused to Fc tag at C-terminal

-
GP26115
ACE2 (19-740) Human
TheCHOderived ACE2 Human recombinant protein contains theextracellular domain amino acids 19-740 fused to Fc tag at C-terminal

-
GA20545
Acetyl-Pepstatin
醋酸胃酶抑素,Pepstatin A acetate
Acetyl-pepstatin 是一种有效的经典天冬氨酸蛋白酶 (PRs) 抑制剂,XMRV PR 和 HIV-1 PR Ki 值分别为 712 nM 和 13 nM。
-
GC49804
Acridine
吖啶
An azaarene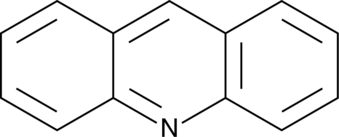
-
GC48842
Actiphenol
放线菌酚
A bacterial metabolite with antiviral activity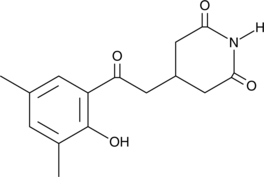
-
GC18274
Amiprofos-methyl
甲基胺草磷,BAY-NTN 6867
An herbicide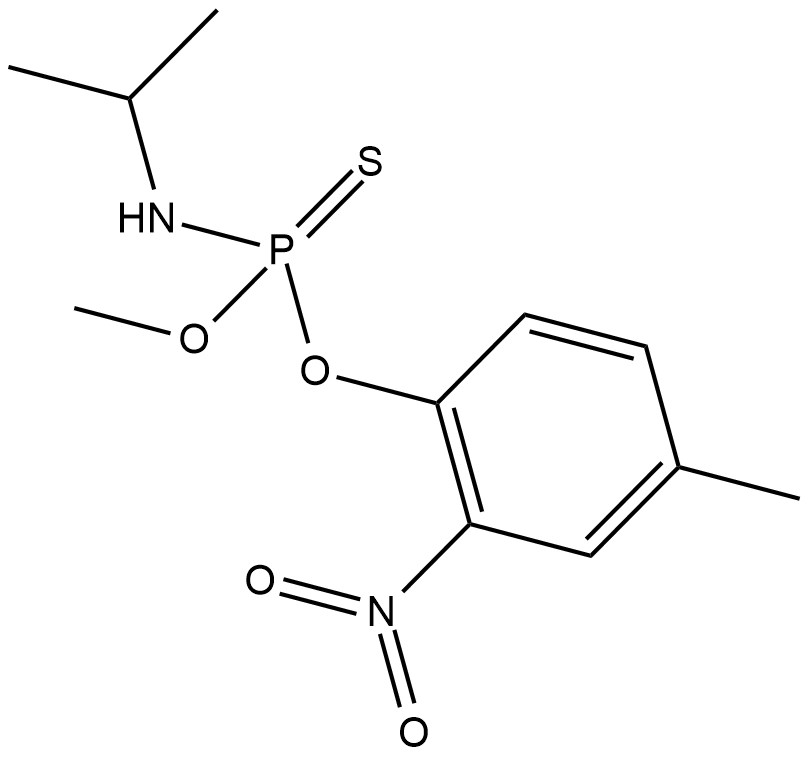
-
GC45725
Amodiaquine-d10
Camoquine-d10, Flavoquine-d10
An internal standard for the quantification of amodiaquine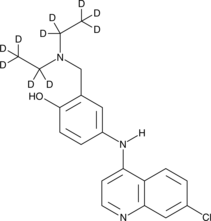
-
GC60047
Amphotericin B methyl ester
两性霉素B甲酯
A polyene antiviral and antifungal agent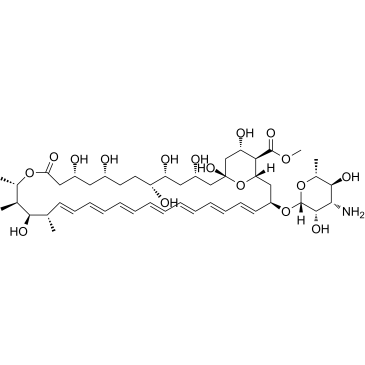
-
GC62842
Amylmetacresol
戊甲酚
Amylmetacresol is an antiseptic used to treat infections of the mouth and throat.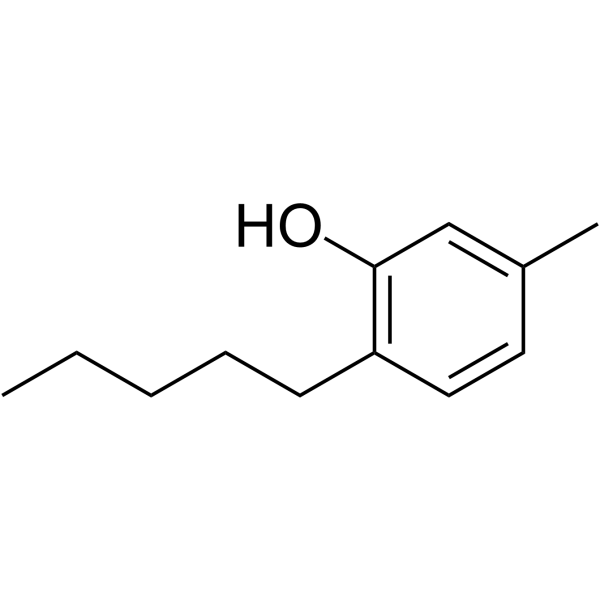
-
GP26444
Anhui H7N9
Anhui H7N9 produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 330 amino acids (19-339 aa) and having a molecular mass of 36 kDa

-
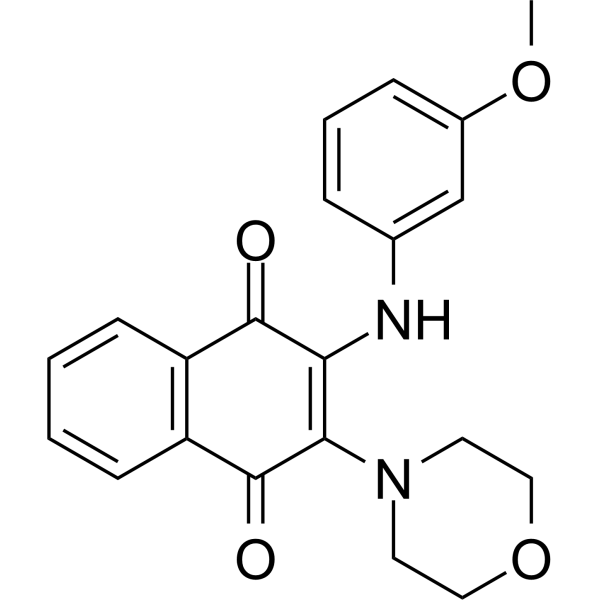
GC73805
Antiviral agent 55
Antiviral agent 55(化合物95)是人类免疫缺陷病毒1和2 (HIV 1和HIV 2)的抑制剂,具有抗病毒活性。
-
GC62610
Aplaviroc hydrochloride
AK602 hydrochloride; GSK-873140 hydrochloride; GW-873140 hydrochloride
Aplaviroc (AK 602) hydrochloride,SDP的一个衍生物,是 CCR5 的拮抗剂,其对 HIV-1Ba-L, HIV-1JRFL 和 HIV-1MOKW 的 IC50 值为 0.1-0.4 nM。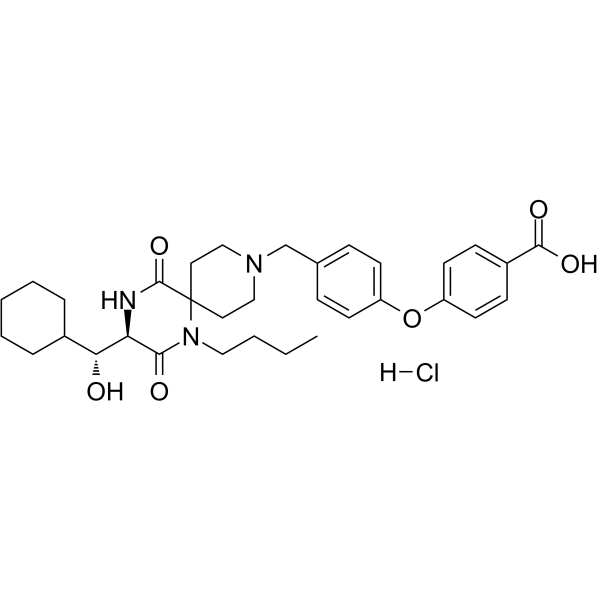
-
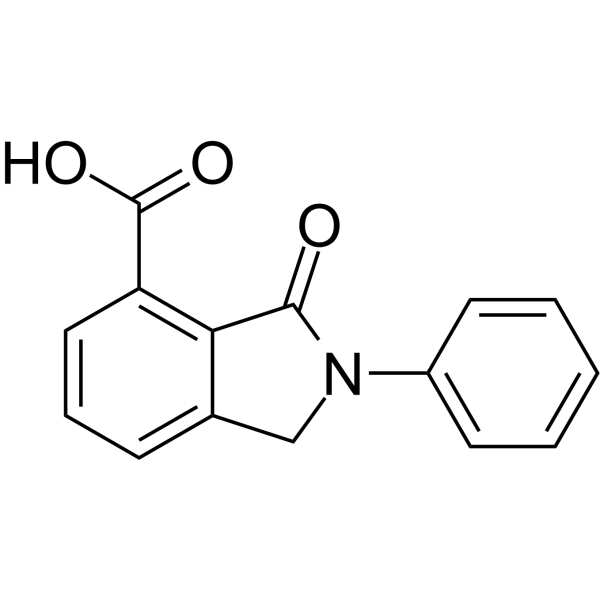
GC68678
APOBEC3G-IN-1
APOBEC3G-IN-1 (MN136.0185) 是一种强效的 HIV 抑制剂,靶向 APOBEC3G。
-
GC46881
Artemether-d3
蒿甲醚-D3,Dihydroqinghaosu methyl ether-d3; Dihydroartemisinin methyl ether-d3; SM224-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of artemether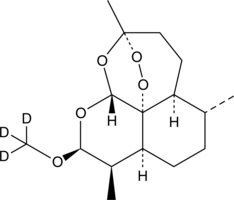
-
GC46882
Artemisinin-d3
Qinghaosu-d3; NSC 369397-d3
An internal standard for the quantification of artemisinin