Enzymes(酶)
Enzymes are very efficient and specific catalyst proteins which react with 1 or few types of substrates in biochemical reactions and are responsible for bringing about almost all of the chemical reactions in living organisms. Enzymes speed up reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Without enzymes, reactions take place at a rate far too slow for the pace of metabolism which means that they speed up the chemical reactions in living things.
There are 2 types of enzymes, ones that help join specific molecules together to form new molecules & others that help break specific molecules apart into separate molecules. Enzymes play many important roles ouside the cell as well. One of the best examples of this is the digestive system. For instance, it is enzymes in your digestive system that break food down in your digestive system break food down into small molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Some enzymes in your digestive system break down starch, some proteins and others break down fats. The enzymes used to digest our food are extra-cellular since they are located outside our cells & enzymes inside our cells are intra-cellular enzymes. Enzymes are used in ALL chemical reactions in living things; this includes respiration, photosynthesis, movement growth, getting rid of toxic chemicals in the liver and so on. Enzymes are proteins that must have the correct structure to be active. They are very easily affected by heat, pH and heavy metal ions.
Ribonucleoprotein enzyme catalytic activity is located in the protein part but for some the catalytic activity is in the RNA part. A catalyst is any substance which makes a chemical reaction go faster, without itself being changed. A catalyst can be used over and over again in a chemical reaction and does not get used up.
Enzymes lower the amount of activation energy needed by binding to the reactants of the reaction they catalyze, thus speed up the reaction and can process millions of molecules per second. Enzymes are typically large proteins with high molecular weight that permit reactions to go at conditions that the body can tolerate.
Enzyme nomenclature is based on what the enzyme reacts with & how it reacts along with the ending ase.
Enzymes must get over the activation energy hurdle.
Enzymes change how a reaction will proceed which reduces the activation energy and makes it faster. The more we increase the enzyme concentration the faster the reaction rate for non-catalyzed reactions. Enzymes that are catalyzed reactions also increase reaction rate at higher level of concentration but up to a certain point called Vmax which means that the enzyme has reached its maximum point. The reaction is limited by both the concentrations of the enzyme and substrate. Enzymes as catalysts take part in reactions which provide an alternative reaction pathway. Enzymes do not undergo permanent changes and remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. They only change the rate of reaction, not the position of the equilibrium.Enzymes as catalysts are highly selective by only catalysing specific reactions due to the shapes of the enzyme’s molecule.
Enzymes contain a globular protein part called apoenzyme and a non-protein part named cofactor or prosthetic group or metal-ion-activator. Changes in temperature and pH have great influence on the intra- and intermolecular bonds that hold the protein part in their secondary and tertiary structures.
Examples of cofactors are 1. Prosthetic group that are permanently bound to the enzyme. 2. Activator group which are cations (positively charged metal ions) & temporarily bind to the active site of the enzyme. 3.Coenzymes, usually vitamins or made from vitamins which are not permanently bound to the enzyme molecule, but combine with the enzyme-substrate complex temporarily. Enzymes require the presence cofactors before their catalytic activity can be exerted. This entire active complex is referred to as the holoenzyme.
Without enzymes, our guts would take weeks to digest our food, our muscles, nerves and bones would not work properly and so on…
Main Enzyme category groups:
Oxidoreductases:
All enzymes that catalyse oxido-reductions belong in this class. The substrate oxidized is regarded as a hydrogen or electron donor. The classification is based on 'donor:acceptor oxidoreductase'. The common name is 'dehydrogenase', wherever this is possible; as an alternative, 'acceptor reductase' can be used. 'Oxidase' is used only where O2 is an acceptor. Classification is difficult in some cases, because of the lack of specificity towards the acceptor.
Transferases:
Transferases are enzymes that transfer a group, for example, the methyl group or a glycosyl group, from one compound (generally regarded as donor) to another compound (generally regarded as acceptor). The classification is based on the scheme 'donor:acceptor grouptransferase'. The common names are normally formed as 'acceptor grouptransferase' or 'donor grouptransferase'. In many cases, the donor is a cofactor (coenzyme) that carries the group to be transferred. The aminotransferases constitute a special case.
Hydrolases:
These enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of various bonds. Some of these enzymes pose problems because they have a very wide specificity, and it is not easy to decide if two preparations described by different authors are the same, or if they should be listed under different entries. While the systematic name always includes 'hydrolase', the common name is, in most cases, formed by the name of the substrate with the suffix -ase. It is understood that the name of the substrate with this suffix, and no other indicator, means a hydrolytic enzyme. It should be noted that peptidases have recommended names rather than common names.
Lyases:
Lyases are enzymes that cleave C-C, C-O, C-N and other bonds by means other than by hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzymes in that two (or more) substrates are involved in one reaction direction, but there is one compound fewer in the other direction. When acting on the single substrate, a molecule is eliminated and this generates either a new double bond or a new ring. The systematic name is formed according to 'substrate group-lyase'. In common names, expressions like decarboxylase, aldolase, etc. are used. 'Dehydratase' is used for those enzymes that eliminate water. In cases where the reverse reaction is the more important, or the only one to be demonstrated, 'synthase' may be used in the name.
Ligases:
Ligases are enzymes that catalyse the joining of two molecules with concomitant hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond in ATP or a similar triphosphate. 'Ligase' is often used for the common name, but, in a few cases, 'synthase' or 'carboxylase' is used. 'Synthetase' may be used in place of 'synthase' for enzymes in this class.
Products for Enzymes
- 41701(11)
- Activating Transcription Factor(3)
- Adenylate Kinase(10)
- AHCY(3)
- Aldolase(9)
- Asparaginase(5)
- Aurora Kinase(18)
- Beta Lactamase(3)
- Calcium and Integrin Binding(2)
- Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase(4)
- Carbonic Anhydrase(49)
- Casein Kinase(36)
- Cathepsin(52)
- Chitinase(5)
- Creatin Kinases(9)
- Cyclin(7)
- Cyclin-Dependent Kinase(18)
- Cyclophilin(23)
- Deaminase(14)
- Decarboxylase(12)
- Dehydrogenase(96)
- Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase(2)
- DNA Polymerase(4)
- EGF Receptor(3)
- Endonuclease(6)
- Enolase(10)
- Enterokinase(5)
- Epimerase(3)
- Esterase(15)
- FGF Receptors(12)
- FK506 Binding Protein(10)
- Fructosamine 3 Kinase(2)
- Galactosidase(5)
- Glucosidase(32)
- Gluteradoxin(7)
- Glycogen synthase kinase(2)
- Glycosylase(10)
- Glyoxalase(3)
- Granzyme(7)
- Guanylate Kinase(2)
- Heparanase(2)
- Histone Deacetylase(3)
- Hydratase(10)
- Hydrolase(33)
- Hydroxylase(6)
- Isomerase(26)
- Jun N-terminal Kinase(1)
- Jun Proto-Oncogene(2)
- Kallikrein(26)
- Ligase(4)
- Lipase(14)
- Lipocalin(6)
- Lyase(9)
- LYVE1(3)
- Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase(16)
- MMP(68)
- Mutase(11)
- Natural Enzymes(4)
- Nuclease(18)
- Nucleotidase(4)
- Nudix Type Motif(11)
- Other Enzymes(63)
- Oxidase(23)
- Oxygenase(12)
- Paraoxonase(3)
- Peptidase(41)
- Peroxiredoxin(10)
- Phosphatase(150)
- Phosphorylase(9)
- PI3-kinase(5)
- Polymerase(13)
- PPARG(2)
- Protease(15)
- Proteasome(54)
- Protein Kinase Akt1/PKB alpha(4)
- Protein Kinase-A(7)
- Protein Kinase-C(3)
- Protein Kinases(86)
- Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase(10)
- Reductase(60)
- Secreted Phospholipase A2(10)
- Serine Threonine Kinase(4)
- Sulfatase(8)
- Synthase(23)
- Synthetase(33)
- TGFBR(3)
- TGM2(3)
- TIMP(10)
- TPA(4)
- Transferase(156)
- Tyrosine Kinase(9)
- Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme(39)
- Uromodulin(4)
- VEGF Receptors(14)
- Transaminase(19)
- Hexokinase(6)
- TIE1(6)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP22633
TEK Mouse
TEK Tyrosine Kinase Endothelial Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22635
TEK Mouse Fc
TEK Tyrosine Kinase Endothelial Fc Chimera Mouse Recombinant

-
GP24804
TEV
Tobacco Etch Virus Protease Recombinant

-
GP22636
TGFBR1 Human
Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor I Human Recombinant

-
GP22637
TGFBR2 Human
Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor II Human Recombinant

-
GP22638
TGFBR2 Human, His
Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor II, His Tag Human Recombinant

-
GP22290
TGM2 Human
Tissue Transglutaminase Human Recombinant

-
GP22291
TGM2 Human, Sf9
Tissue Transglutaminase Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP22292
TGM2 Mouse
Tissue Transglutaminase Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22293
TH Mouse
Tyrosine Hydroxylase Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22294
THG1L Human
tRNA-Histidine Guanylyltransferase 1-Like Human Recombinant

-
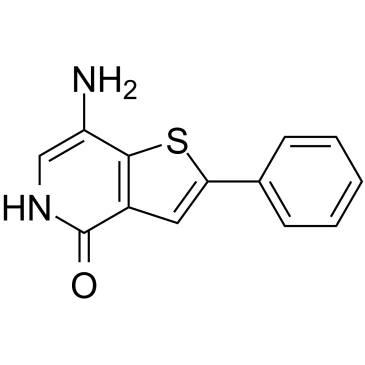
GC60364
Thienopyridone
Thienopyridone 是一种有效的选择性的肝再生磷酸酶 (PRL) 磷酸酶抑制剂,对于 PRL-1,PRL-2 和 PRL-3,IC50 值分别为 173 nM,277 nM 和 128 nM。Thienopyridone 对其他磷酸酶的影响很小。Thienopyridone 可诱导 p130Cas 裂解和细胞凋亡 (apoptosis),并具有抗癌作用。
-
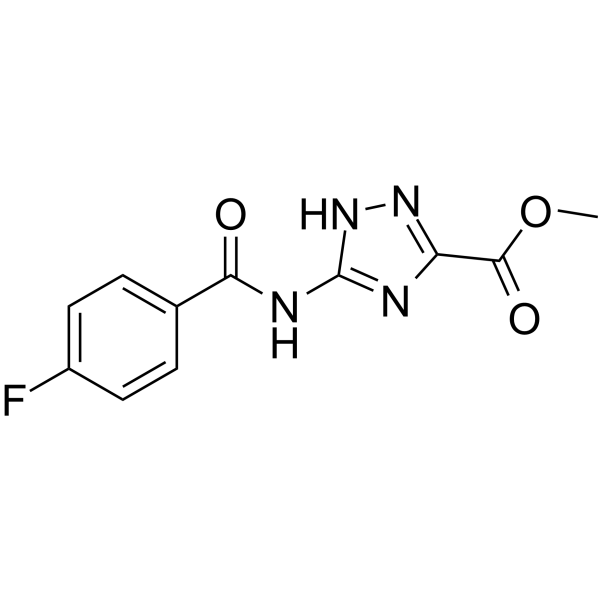
GC65938
Thrombin inhibitor 5
WAY-358871 is a bioactive compound.
-
GP22295
THTPA Human
Thiamine Triphosphatase Human Recombinant

-
GP22639
TIE1 Fc Human
TIE1 Fc Human Recombinant

-
GP22640
TIE1 Fc Mouse
TIE1 Fc Chimera Mouse Recombinant

-
GP26198
TIE1 Human
TIE1 Human Recombinant produced in HEK293 Cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 977 amino acids (22-759 a

-
GP22296
TIMP1 Human
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22297
TIMP1 Human, HEK
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 1 Human Recombinant, HEK

-
GP22298
TIMP1 Human, Sf9
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 1 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP22299
TIMP1 Mouse
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 1 Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22300
TIMP1 Rat
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 1 Rat Recombinant

-
GP22302
TIMP2 Human
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP22303
TIMP2 Human HEK
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 2 Human Recombinant, HEK

-
GP22301
TIMP2 Human, His
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 2 Human Recombinant, His Tag

-
GP22304
TIMP2 Human, Sf9
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 2 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP22305
TIMP4 Human
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloprotease 4 Human Recombinant

-
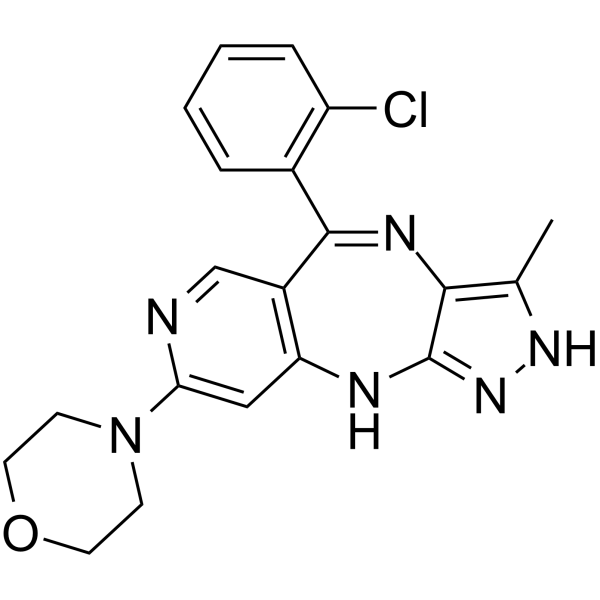
GC70030
Tinengotinib
Tinengotinib 是一种或多种蛋白激酶的调节剂,例如 Aurora 激酶和 VEGFR 激酶。Tinengotinib 具有研究这些激酶异常介导的疾病的潜力,尤其是癌症相关疾病 (摘自专利 WO2018108079A1)。
-
GP22641
TK1 Human
Thymidine Kinase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22642
TK2 Human
Thymidine Kinase 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP24843
TKT
Transketolase Streptococcus Pyogenes Recombinant

-
GP22306
TKT Human
Transketolase Human Recombinant

-
GC46026
TMI 1
WAY-171318
An ADAM and MMP inhibitor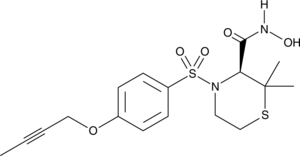
-
GC64131
TMX-4116
TMX-4116 是酪蛋白激酶 1α (CK1α) 降解剂。TMX-4116 在 MOLT4、Jurkat 和 MM.1S 细胞中显示出对 CK1α 的降解偏好,DC50 小于 200 nM。TMX-4116 可用于多发性骨髓瘤的研究。
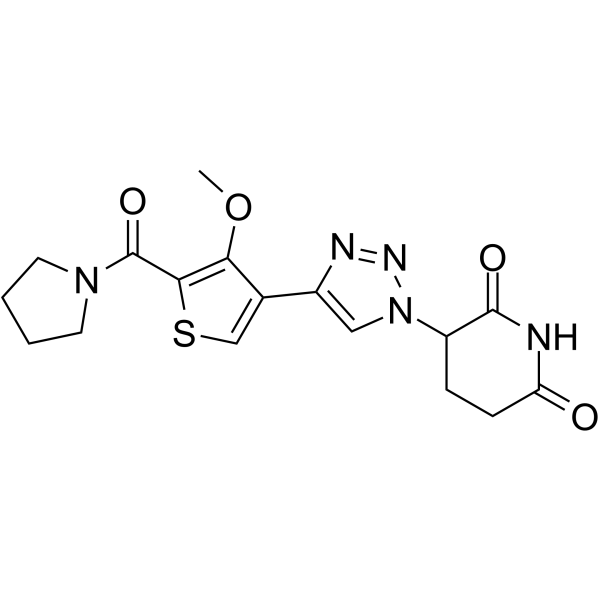
-
GP22307
TNAA E.Coli
Tryptophanase E.Coli Recombinant

-
GP22309
TOP1 70kDa Human
DNA Topoisomerase-I 70kDa Recombinant Human

-
GP22310
TOP1 Bovine
DNA Topoisomerase-I Bovine

-
GP22308
TOP1 Human
DNA Topoisomerase-I Human Recombinant

-
GC50198
Topiramate - d12
托吡酯-D12,McN 4853 D12 ; RWJ 17021 D12
An internal standard for the quantification of topiramate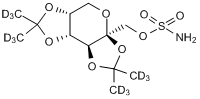
-
GC71038
TP0597850
TP0597850是MMP2的选择性抑制剂(IC50=0.22 nM)。
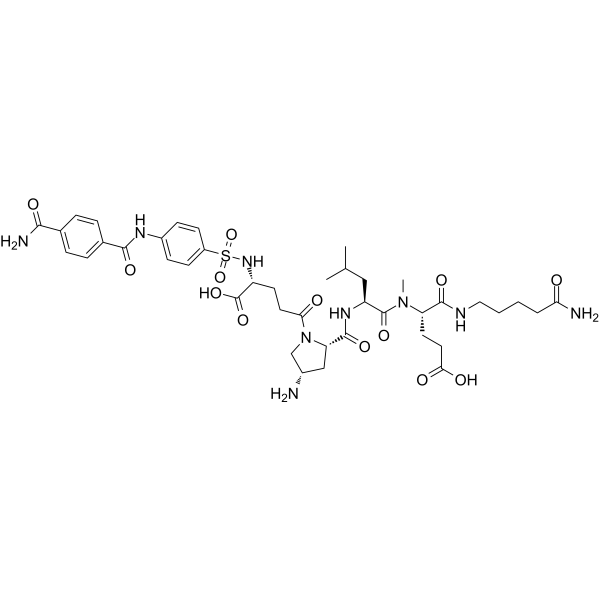
-
GP22311
TP53I3 Human
Tumor Protein p53 Inducible Protein 3 Human Recombinant

-
GP22314
TPA (311-562) Human
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (311-562 a.a.) Human Recombinant

-
GP22315
TPA (36-310) Human
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (36-310 a.a.) Human Recombinant

-
GP22312
tPA Human
组织纤溶酶原激活剂人类重组

-
GP22313
tPA Human, Sf9
Tissue Plasminogen Activator Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP22316
TPI1 Human
Triosephosphate Isomerase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22317
TPI1 Human, Active
Triosephosphate Isomerase 1 Human Recombinant, Active

-
GP22643
TPK1 Human
Thiamin Pyrophosphokinase 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22644
TPMT Human
Thiopurine S-methyltransferase Human Recombinant

-
GP22318
TPO Human
Thyroid Peroxidase Human Recombinant





