CD Antigens(CD抗原)
Cell surface antigens of leukocytes are called CD antigens, and important for immune reactions of organisms. As lymphocytes mature, they express different protein receptors on the cell surface, which can aid in determining the type and maturation stage of the cells being examined. These proteins or antigen markers are called Clusters of Differentiation
The term CD means a cluster of differentiation OR a cluster of determinants which indicates the lineage or maturational stage of lymphocytes. During the course of development from precursor cells into functionally mature forms, lymphocytes display a complex pattern of surface antigens, some of which are acquired at certain stages while others are lost.
These surface antigens were identified initially by monoclonal antibodies and the designations of the antibodies were used often as synonyms for the cell surface proteins they detected, giving rise to a plethora of different names. CD antigens are present on some subpopulations and functional types of leukocytes. CD antigens participate in immune reaction as receptors for cell communication (e.g. adherence molecules, antigen recognizing receptors).
CD antigen nomenclature describes different monoclonal antibodies from different sources that recognize identical antigens. Numbers are assigned arbitrarily. A small letter w before the number designation stands for "workshop". It indicates that the CD designation is tentative.
CD antigens are found on practically all known cell types. In some cases CD antigens are expressed only at certain stages of development or under certain conditions, for example after cell activation or in certain disease conditions. In Hematology the morphological criteria is for the description of specific developmental stages of lymphocytes unlike in CD antigens which the use of monoclonal antibodies allows the objective and precise analysis and standardized typing of mature and immature normal and malignant cells of all hematopoietic cell lineages. The use antibodies also helps to delineate the biologic traits that distinguish normal immune and hematopoietic cells from their malignant counterparts, which is utmost important in the understanding of hematological malignancies.
The expression of CD antigens is influenced by cytokines, such as binding of ligands to CD antigens which has shown to modulate the expression of cytokines. CD antigens have been shown to be identical with receptors of cytokines such as CD25 (TAC antigen).
CD antigens appear to carry out cytokine receptor-like functions such as CD27, CD30 and CD40. CD antigens are involved in modulating the biological activities of cytokines such as CD4, CD28 and CD40. CD antigens exist also in soluble forms for example CD14, CD21, CD23, CD27, CD100 and CD137.
The CD Antigen’s designation isn’t related to the biological function, thus CD antigens include receptors, glycans, adhesion molecules, membrane-bound enzymes, etc.
The most commonly know CD antigens are CD4 and CD8 which are markers for T-helper and T-suppressor cells, respectively. CD4 binds to relatively invariant sites on class II major histocompatibility complex molecules outside the peptide-binding groove, which interacts with the T-cell receptor. CD4 is also the central docking receptor for human immunodeficiency virus. CD8 binds to relatively invariant sites on class I major histocompatibility complex molecules outside the peptide-binding groove. CD8 is also expressed on a subset of dendritic cells. Other more important CD antigens include the leukocytes integrins (CD11/CD18) and the hematopoietic stem cell marker CD34.
CD69 is homologous to members of a supergene family of type II integral membrane proteins having C-type lectin domains. Although the precise functions of the CD-69 antigen is not known, evidence suggests that these proteins transmit mitogenic signals across the plasma membrane and are up- regulated in response to lymphocyte activation
In the last decade the wide palette of monoclonal antibodies has been prepared which recognise of CD antigens on human cells. Much less monoclonal antibodies are available specific for typing of domestic animal cells. CD antigens have been characterized as both transmembrane proteins and cell surface proteins anchored to the plasma membrane via covalent attachment to fatty acid-containing glycolipids such as glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI).
Products for CD Antigens
- CD1(4)
- CD14(5)
- CD164(2)
- CD2(5)
- CD200(5)
- CD204(2)
- CD207(2)
- CD226(2)
- CD23(2)
- CD244(2)
- CD247(2)
- CD27(3)
- CD274(3)
- CD3(28)
- CD300(4)
- CD33(2)
- CD34(3)
- CD36(2)
- CD4(5)
- CD40(2)
- CD46(2)
- CD47(7)
- CD5(2)
- CD55(2)
- CD58(2)
- CD5L(3)
- CD68(3)
- CD7(2)
- CD73(12)
- CD74(2)
- CD79(3)
- CD80(1)
- CD84(2)
- CD8B(2)
- CD93(2)
- CD99(2)
- Fc Fragment of IgG Receptor(6)
- Other CD Antigens(46)
- sCD40L(5)
- LAG-3(3)
- Mucin(4)
- CD38(2)
- CD19(1)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GC74548
Flotetuzumab
伏妥珠单抗; MGD006; S80880
Flotetuzumab(MGD006;S80880)是一种正在研究的CD123/CD3双特异性双亲和力再靶向抗体(DART)分子。
-
GC69127
Foralumab
NI-0401
Foralumab (NI-0401) 是一种口服有效的人源化单克隆抗体,靶向 CD3。Foralumab 可调节 NSG 小鼠中由人类造血干细胞重建的人类细胞的免疫反应。
-
GC73334
Glutaminyl cyclases-IN-1
IsoQC-IN-1
Glutaminyl cyclases-IN-1(IsoQC-IN-1)是一种强效的谷氨酰胺环化酶(QC)抑制剂,对人类QC和IsoQC的IC50值分别为12 nM和73 nM。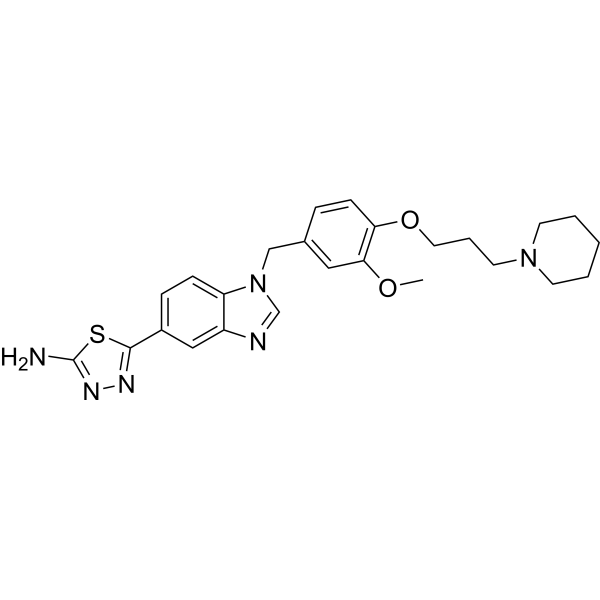
-
GC74494
Gresonitamab
AMG 910; Anti-Human CD3xClaudin18 2
Gresonitamab(AMG 910)是一种半衰期延长(HLE)双特异性T细胞接合剂(BiTE)抗体,靶向CD3阳性T细胞和CLDN18.2表达的肿瘤细胞。
-
GP23696
IGLL1 Human
Immunoglobulin Lambda-Like Polypeptide 1 Human Recombinant

-
GC74571
Ligufalimab
莱法利单抗; AK 117
Ligufalimab(AK 117)是一种人源化IgG4抗CD47单克隆抗体。
-
GC74604
Linvoseltamab
利伏赛坦单抗; REGN5458
Linvoseltamab是一种针对BCMA (TNFRSF17)和CD3 epsilon的双特异性抗体。
-
GC73846
MA3 aptamer sodium
MA3 aptamer sodium是一个86碱基长的DNA适体,靶向粘蛋白MUC1。

-
GC69453
MethADP triammonium
Adenosine 5'-(α,β-methylene)diphosphate triammonium
MethADP (Adenosine 5'-(α,β-methylene)diphosphate) triammonium 是一种 CD73 抑制剂。MethADP 可用于 ATP-腺苷通路的研究。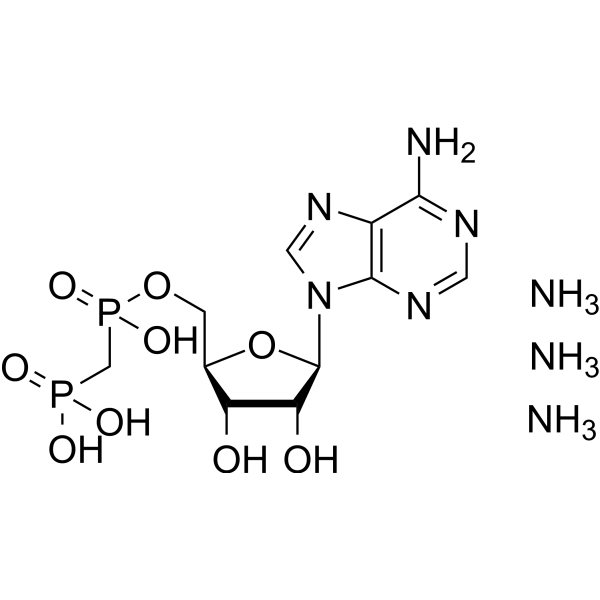
-
GC74576
Mezagitamab
迈泽妥单抗; TAK-079
Mezagitamab(TAK-079)是一种IgG1λ抗CD38单克隆抗体。
-
GC74581
Modakafusp alfa
TAK-573
Modakafusp alfa (TAK-573)是一种人源化的抗cd38 IgG4单克隆抗体,与2个减毒的IFNα2b分子融合,将干扰素- α传递到表达cd38的细胞。
-
GP23966
MS4A1 Human
Membrane Spanning 4-Domains A1 Human Recombinant

-
GP23964
MSR1 Human
Macrophage Scavenger Receptor 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP23965
MSR1 Human, sf9
Macrophage Scavenger Receptor 1, sf9 Human Recombinant

-
GC68344
Mupadolimab
CPI-006
Mupadolimab (CPI-006) 是一种 IgG1κ 人源化的 FcγR 结合缺陷抗 CD73 单抗,激活 CD73POS B 细胞。
-
GC69512
Muromonab
Muromonab 是一种靶向 CD3 受体的单克隆抗体。Muromonab 可以阻断所有细胞毒性 T 细胞功能。Muromonab 也作为一种免疫抑制剂用于减少急性实体器官移植排斥反应。

-
GC74582
Nivatrotamab
Hu3F8-BsAb
Nivatrotamab (Hu3F8-BsAb)是人源抗gd2 /CD3双特异性抗体。
-
GP24069
NT5E (CD73) Human
5'-Nucleotidase Ecto (CD73) Human Recombinant

-
GP24070
NT5E (CD73) Mouse
5'-Nucleotidase Ecto (CD73) Mouse Recombinant

-
GC74585
Obexelimab
奥贝利单抗; XmAb5871
Obexelimab(XmAb5871)是一种人源化抗CD19抗体。
-
GC74586
Obrindatamab
MGD009
Obrindatamab是一种人源化抗B7-H3/CD3双特异性抗体。
-
GC65470
Oleclumab
奥来鲁单抗,MEDI9447
Oleclumab (MEDI9447) 是一种人 IgG1Λ 抗 CD73 单克隆抗体,可抑制 CD73 功能。Oleclumab 具有抗肿瘤活性。
-
GC74589
Ontorpacept
TTI-621
Ontorpacept (TTI-621)是一种可溶性融合蛋白,由与人IgG1 Fc区连接的人SIRPα n端(1-118)组成。
-
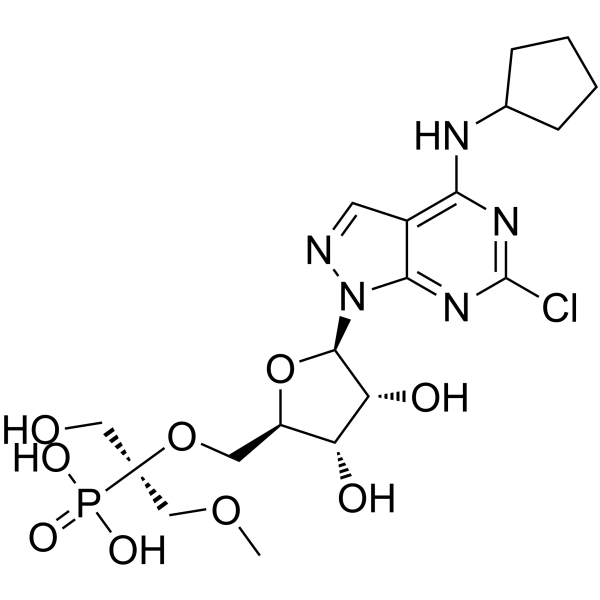
GC62694
OP-5244
OP-5244 是一种有效和具有口服活性的 CD73 抑制剂,IC50 值为 0.25 nM。OP-5244 通过阻断腺苷的产生来逆转免疫抑制作用,具有进行癌症研究的潜力。
-
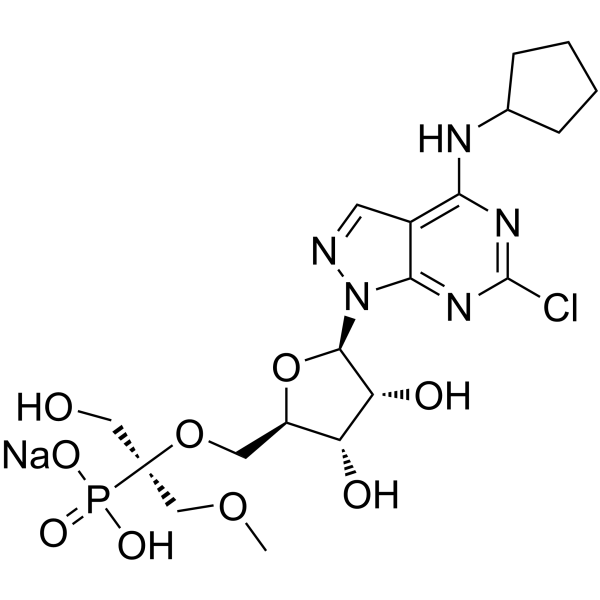
GC62695
OP-5244 sodium
OP-5244 sodium 是一种有效和具有口服活性的 CD73 抑制剂,IC50 值为 0.25 nM。OP-5244 sodium 通过阻断腺苷的产生来逆转免疫抑制作用,具有进行癌症研究的潜力。
-
GC72342
Otelixizumab
Otelixizumab(ChAglyCD3)是一种抗人CD3单克隆抗体,可用于1型糖尿病的研究。
-
GC74591
Pacanalotamab
AMG 420; BI-836909
Pacanalotamab (amg 420;BI-836909)是一种靶向BCMA和CD3E的双特异性t细胞接合剂(BiTE)。
-
GC74593
Pasotuxizumab
帕妥昔珠单抗; BAY 2010112; AMG 212
Pasotuxizumab (BAY 2010112)是一种PSMA和CD3双特异性t细胞接合器(BiTE)。
-
GC72443
Pavurutamab
Pavurutamab (AMG-701)是一种抗cd3和抗b细胞成熟抗原(BCMA)的双特异性T细胞接合分子。
-
GC74588
Plamotamab
帕拉莫妥单抗; XmAb-13676
Plamotamab(XmAb-13676)是一种结合CD3和CD20的人双特异性抗体(bsAb)。
-
GP23021
sCD23 Human
Soluble CD23 Human Recombinant

-
GP20872
sCD40L Human
Soluble CD-40 Ligand/TRAP Human Recombinant

-
GP20873
sCD40L Human, His
可溶性 CD40 配体/TRAP 人类重组体,His 标签

-
GP26070
sCD40L Human, His Active
sCD40L Human Recombinant produced in E

-
GP20874
sCD40L Mouse
Soluble CD-40 Ligand/TRAP Mouse Recombinant

-
GP20875
sCD40L Mouse, sf9
soluble CD40 Ligand/TRAPMouse Recombinant, sf9

-
GC69894
Siplizumab
MEDI-507
Siplizumab (MEDI-507) 是一种抗 CD2 的人源化 IgG1 单克隆抗体。Siplizumab 可耗尽 T 细胞、降低 T 细胞活化、抑制 T 细胞增殖并富集 naÏve 和 bona fide 调节性 T 细胞。
-
GC74539
Solitomab
索利托单抗; AMG 110; MT110
Solitomab(AMG 110)是一种双特异性抗CD3和抗上皮细胞粘附分子(EpCAM)抗体。
-
GC74624
Surzebiclimab
BGB-A425
Surzebiclimab (BGB-A425)是一种人源化igg1变异单克隆抗体,抗t细胞免疫球蛋白和粘蛋白结构域-3 (TIM-3)。
-
GC69985
Talquetamab
JNJ-64407564
Talquetamab(JNJ-64407564)是一种人源化的双特异性抗体,可与 GPRC5D (G 蛋白偶联受体家族C5组成员 D) 和 CD3 结合,通过T 细胞的募集和活化诱导 T 细胞介导的杀死表达 GPRC5 的 MM 细胞。Talquetamab(JNJ-64407564)具有抗肿瘤活性。
-
GC74498
Teclistamab
特立妥单抗
Teclistamab是一种针对BCMA和CD3的人双特异性抗体,其识别靶细胞上的BCMA和T细胞上的CD3,并诱导T细胞介导的细胞毒性,导致T细胞活化和随后的靶细胞裂解。
-
GC70011
Teplizumab
MGA-031; PRV-031
Teplizumab (MGA-031) 是一种 Fc 受体型、非结合类型的抗-人 CD3 的单克隆抗体。Teplizumab 可缓解 β 细胞的功能丧失。Teplizumab 可用于 type 1 型糖尿病的研究。
-
GC74497
Tepoditamab
MCLA 117
Tepoditamab (MCLA-117)是一种双特异性单克隆抗体,可结合骨髓细胞的clecl12a和细胞毒性T细胞的CD3。
-
GC74530
Ubamatamab
乌巴妥单抗; REGN4018
Ubamatamab(REGN4018)是一种针对粘蛋白16(MUC16)和CD3的人源化双特异性抗体。
-
GC68346
Uliledlimab
TJ004309
Uliledlimab 是一种有效的抗 CD73 人源单克隆抗体。Uliledlimab 抑制胞外单磷酸腺苷 (AMP) 向腺苷的转化。Uliledlimab 可用于癌症的研究。
-
GC74528
Urabrelimab
SRF-231; SRF231
Urabrelimab(SRF231)是一种阻断CD47-SIRP相互作用的全人源性抗CD47单克隆抗体。
-
GC74526
Vepsitamab
维斯妥单抗; AMG 199
Vepsitamab(AMG 199)是一种抗MUC17/CD3 BiTE抗体,与T细胞上的CD3和肿瘤细胞上表达的MUC17结合,介导重定向的肿瘤细胞裂解,并诱导T细胞活化和增殖。
-
GC74525
Vibecotamab
维克妥单抗; XmAb14045
Vibecotamab (XmAb14045)是一种有效的针对CD123和CD3的双特异性抗体,可刺激T细胞介导的靶向杀伤表达CD123的细胞。
-
GC74449
Vonsetamig
Vonsetamig是一种人源免疫球蛋白G4-kappa,抗tnfrsf17和CD3E单克隆抗体。

-
GC74524
Voxalatamab
沃昔莱妥单抗; JNJ-63898081
Voxalatamab(JNJ-63898081)是一种结合PSMA和CD3的双特异性IgG4抗体,具有抗癌活性,用于癌症研究。




