CD Antigens(CD抗原)
Cell surface antigens of leukocytes are called CD antigens, and important for immune reactions of organisms. As lymphocytes mature, they express different protein receptors on the cell surface, which can aid in determining the type and maturation stage of the cells being examined. These proteins or antigen markers are called Clusters of Differentiation
The term CD means a cluster of differentiation OR a cluster of determinants which indicates the lineage or maturational stage of lymphocytes. During the course of development from precursor cells into functionally mature forms, lymphocytes display a complex pattern of surface antigens, some of which are acquired at certain stages while others are lost.
These surface antigens were identified initially by monoclonal antibodies and the designations of the antibodies were used often as synonyms for the cell surface proteins they detected, giving rise to a plethora of different names. CD antigens are present on some subpopulations and functional types of leukocytes. CD antigens participate in immune reaction as receptors for cell communication (e.g. adherence molecules, antigen recognizing receptors).
CD antigen nomenclature describes different monoclonal antibodies from different sources that recognize identical antigens. Numbers are assigned arbitrarily. A small letter w before the number designation stands for "workshop". It indicates that the CD designation is tentative.
CD antigens are found on practically all known cell types. In some cases CD antigens are expressed only at certain stages of development or under certain conditions, for example after cell activation or in certain disease conditions. In Hematology the morphological criteria is for the description of specific developmental stages of lymphocytes unlike in CD antigens which the use of monoclonal antibodies allows the objective and precise analysis and standardized typing of mature and immature normal and malignant cells of all hematopoietic cell lineages. The use antibodies also helps to delineate the biologic traits that distinguish normal immune and hematopoietic cells from their malignant counterparts, which is utmost important in the understanding of hematological malignancies.
The expression of CD antigens is influenced by cytokines, such as binding of ligands to CD antigens which has shown to modulate the expression of cytokines. CD antigens have been shown to be identical with receptors of cytokines such as CD25 (TAC antigen).
CD antigens appear to carry out cytokine receptor-like functions such as CD27, CD30 and CD40. CD antigens are involved in modulating the biological activities of cytokines such as CD4, CD28 and CD40. CD antigens exist also in soluble forms for example CD14, CD21, CD23, CD27, CD100 and CD137.
The CD Antigen’s designation isn’t related to the biological function, thus CD antigens include receptors, glycans, adhesion molecules, membrane-bound enzymes, etc.
The most commonly know CD antigens are CD4 and CD8 which are markers for T-helper and T-suppressor cells, respectively. CD4 binds to relatively invariant sites on class II major histocompatibility complex molecules outside the peptide-binding groove, which interacts with the T-cell receptor. CD4 is also the central docking receptor for human immunodeficiency virus. CD8 binds to relatively invariant sites on class I major histocompatibility complex molecules outside the peptide-binding groove. CD8 is also expressed on a subset of dendritic cells. Other more important CD antigens include the leukocytes integrins (CD11/CD18) and the hematopoietic stem cell marker CD34.
CD69 is homologous to members of a supergene family of type II integral membrane proteins having C-type lectin domains. Although the precise functions of the CD-69 antigen is not known, evidence suggests that these proteins transmit mitogenic signals across the plasma membrane and are up- regulated in response to lymphocyte activation
In the last decade the wide palette of monoclonal antibodies has been prepared which recognise of CD antigens on human cells. Much less monoclonal antibodies are available specific for typing of domestic animal cells. CD antigens have been characterized as both transmembrane proteins and cell surface proteins anchored to the plasma membrane via covalent attachment to fatty acid-containing glycolipids such as glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI).
Products for CD Antigens
- CD1(4)
- CD14(5)
- CD164(2)
- CD2(5)
- CD200(5)
- CD204(2)
- CD207(2)
- CD226(2)
- CD23(2)
- CD244(2)
- CD247(2)
- CD27(3)
- CD274(3)
- CD3(28)
- CD300(4)
- CD33(2)
- CD34(3)
- CD36(2)
- CD4(5)
- CD40(2)
- CD46(2)
- CD47(7)
- CD5(2)
- CD55(2)
- CD58(2)
- CD5L(3)
- CD68(3)
- CD7(2)
- CD73(12)
- CD74(2)
- CD79(3)
- CD80(1)
- CD84(2)
- CD8B(2)
- CD93(2)
- CD99(2)
- Fc Fragment of IgG Receptor(6)
- Other CD Antigens(46)
- sCD40L(5)
- LAG-3(3)
- Mucin(4)
- CD38(2)
- CD19(1)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
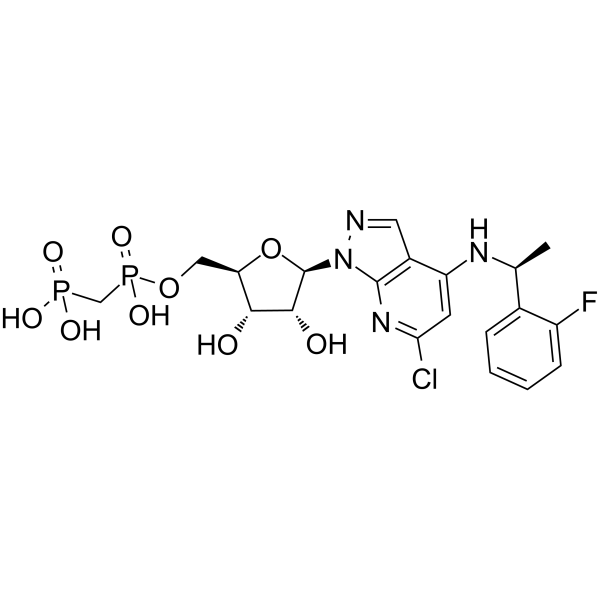
GC65293
AB-680
AB-680 是一种有效、可逆、选择性的 CD73 (胞外核苷酸酶) 抑制剂,对 hCD73 的 Ki 值为 4.9 pM,对其选择性是对相关胞外核苷酸酶 CD39 的 10000 多倍。具有抗肿瘤活性。
-
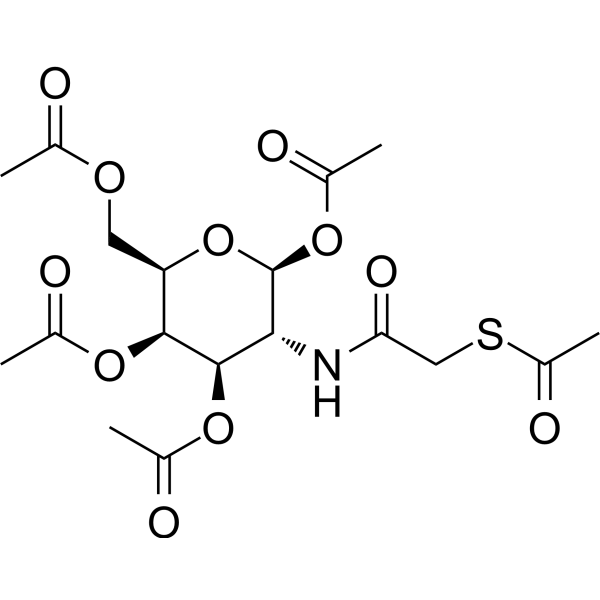
GC73849
Ac5GalNTGc
Ac5GalNTGc是己糖胺的类似物。
-
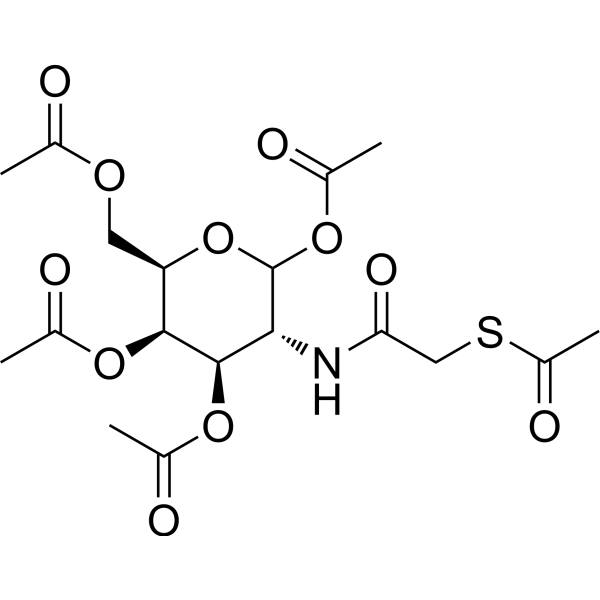
GC73850
Ac5GalNTGc epimer
Ac5GalNTGc epimer是己糖胺的类似物和Ac5GalNTGc的外消旋体。
-
GP22701
ALCAM (CD166) Human
Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule (CD166) Human Recombinant

-
GP26202
ALCAM (CD166) Mouse
ALCAM mouse produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 739 amino acids (28-527a

-
GC74428
Anzurstobart
CC-95251; BMS-986351
Anzurstobart (cc - 95251;BMS-986351)是一种高亲和力的全人源单克隆抗SIRPα抗体,可阻断CD47与SIRPα的结合。
-
GP22843
BCAM Human
Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule (CD239) Human Recombinant

-
GP22901
BSG Human
Basigin Human Recombinant

-
GC74531
Catumaxomab
卡妥索单抗
Catumaxomab是一种三功能IgG2抗体,由小鼠和大鼠的重链和轻链组成,与人EpCAM和人CD3受体结合。
-
GP23087
CD100 Human HEK
CD100 Human Recombinant HEK

-
GP22994
CD14 Human
CD14 Human Recombinant

-
GP22993
CD14 Human HEK
CD14 Human Recombinant HEK

-
GP22992
CD14 Human, CHO
CD14 Human Recombinant, CHO

-
GP22995
CD14 Mouse
CD14 Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22996
CD14 Mouse, Sf9
CD14 Mouse Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP23088
CD160 Human
CD160 Human Recombinant

-
GP24133
CD163 Human
CD163 Human Recombinant

-
GP24134
CD163 Porcine
CD163 Porcine Recombinant

-
GP23027
CD164 Human
CD164 Human Recombinant

-
GP23028
CD164L2 Human
CD164 Sialomucin-Like 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP22997
CD18 Human
CD18 Human Recombinant

-
GP23019
CD19 Human
CD19 Human Recombinant

-
GP22998
CD1A Human
CD1A Human Recombinant

-
GP22999
CD1B Human
CD1B Human Recombinant

-
GP23000
CD1D Human
CD1D Human Recombinant

-
GP23001
CD1E Human
CD1E Human Recombinant

-
GP23002
CD2 Human
CD2 Human Recombinant

-
GP23003
CD2 Human, GST
CD2 Human Recombinant, GST Tag

-
GP23004
CD2 Human, Sf9
CD2 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP23089
CD200 Human
CD200 Human Recombinant

-
GP23090
CD200 Human, Sf9
CD200 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP26244
CD200 Mouse
CD200 Mouse Recombinant produced in Baculovirus is a single, glycosylated, polypeptide chain containing 441 amino acids (31-232aa) and having a molecular mass of 49

-
GP23091
CD200R1 Human
CD200 Receptor 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP23092
CD200R1 Mouse
CD200 Receptor 1 Mouse Recombinant

-
GP23093
CD207 Human
CD207 Human Recombinant

-
GP23094
CD207 Human, sf9
CD207 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP26245
CD209 Human
CD209 Human Recombinant produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 587 amino acids (60-404 a

-
GP26237
CD21 Human
CD21 Human Recombinant produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 959 amino acids (21-971aa) and having a molecular mass of 105

-
GP23020
CD22 Human
CD22 Human Recombinant

-
GP23029
CD226 Human
CD226 Human Recombinant

-
GP23030
CD226 Human, Sf9
CD226 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP23022
CD23 Human, Sf9
CD23 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP23031
CD244 Human
CD244 Human Recombinant

-
GP23032
CD244 Human, Sf9
CD244 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP23033
CD247 Human
CD247 Human Recombinant

-
GP23034
CD247 Human, Sf9
CD247 Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP23035
CD27 Human
CD27 Human Recombinant

-
GP26238
CD27 Human, HEK
CD27 Human Recombinant produced in HEK cells is a single, glycosylated, polypeptide chain (20-191 a

-
GP23036
CD27 Human, sf9
CD27 Human Recombinant, sf9

-
GP23039
CD274 Human
CD274 Human Recombinant





