Viral Antigens(病毒抗原)
A viral Antigen is an antigen with multiple antigenicities that is protein in nature, strain-specific, and closely associated with the virus particle. A viral antigen is a protein encoded by the viral genome.A viral protein is an antigen specified by the viral genome that can be detected by a specific immunological response.
Viruses are infectious pathogens that cause serious diseases & major threats for global public health, such as influenza, hepatitis, & AIDS. Virus is a sub-micrometer particle that has DNA or RNA packed in a shell called capsid. Viral antigens protrude from the capsid and often fulfill important function in docking to the host cell, fusion, and injection of viral DNA/RNA. Antibody-based immune responses form a first layer of protection of the host from viral infection; however, in many cases a vigorous cellular immune response mediated by T-cells and NK-cells is required for effective viral clearance. When cellular immunity is unable to clear the virus, the infection can become chronic, and serum antibodies to the viral pathogen are used as first indicator for the diagnosis of the disease.
ELISAs provide a valuable tool in the detection and diagnosis of virus infection. The ability to produce recombinant viral proteins will ensure that future ELISAs are safe, specific and rapid. Even when a virus cannot be cultured, provided gene sequence is available, it is possible to rapidly respond to emerging viruses and new viral strains of existing pathogens.
Recombinant viral antigens contain part of viral sequence meaning that the recombinant antigen contains a region which can be recognized by different antibodies produced by different individuals. This reduces the risk of false negatives which can occur with synthetic peptides, which contain only a small portion of the entire protein. If an individual infected with a viral antigen makes antibodies to a part of the protein not included in the synthetic peptides, a false negative results.
Recombinant viral protein usually contains a fusion protein/partner which produces superior attachment to assay surfaces such as wells. For this reason, smaller amounts of recombinant protein will produce the same results as larger amounts of unfused protein. The choice of fusion partner prevents false positives, allowing superior adhesion without incorrect results.
Recombinant Viral proteins are expressed in bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, and viruses. E. Coli cells were first to be used for this purpose but the expressed proteins were not glycosylated, which was a major drawback since many of the immunogenic proteins of viruses such as the envelope glycoproteins, were glycosylated. Nevertheless, in many instances, it was demonstrated that the non-glycosylated protein backbone was just as immunogenic. The obvious advantage of recombinant viral antigens is that they are available in unlimited quantities and the production and quality control processes is simple.
Advantages of defined using recombinant viral antigens:
1. Production and quality control is simple.
2. No nucleic acids or other viral or external proteins, therefore less toxic.
3. Safer in cases where viruses are oncogenic or establish a persistent infection.
4. Feasible even if virus cannot be cultivated
Disadvantages:
1. May be less immunogenic than conventional inactivated whole-virus vaccines.
2. Requires adjuvant .
3. Fails to elicit CMI.
Facts about Viral Antigens:
1. A Viral Protein Mimics its Way into cells.
2. Viral Protein Helps Infected T Cells Stick To Uninfected Cells.
3. The Viral Protein A238L Inhibits Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression through a Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cell-dependent Trans-activation Pathway.
4. Viral Protein is an effective preventative against ear infection.
5. HIV-1 Viral Protein R Induces Apoptosis via a Direct Effect on the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore.
6. The Level of Viral Antigen Presented by Hepatocytes Influences CD8 T-Cell Function.
7. Antigen-presenting cells from calves persistently infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus, a member of the Flaviviridae, are not compromised in their ability to present viral antigen.
8. There is a difference in the distribution and spread of a viral antigen, development of lesions and correlation between presence of viral antigen and lesions.
9. The absence of viral antigens on the surface of equine herpesvirus-1-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells is a strategy to avoid complement-mediated lysis.
10. Viral Protein Influences Key Cell-signaling Pathway.
11. A viral protein produced by cancer-causing virus influences a key signaling pathway in the immune cells that the virus infects. This stimulates the cells to divide, helping the virus spread through the body.
12. Protection by recombinant viral proteins against a respiratory virulent avian metapneumovirus has been achieved.
13. Viral O-acetylesterases are found in influenza C viruses and Corona-viruses. Viral O-acetylesterases remove cellular receptors from the surface of target cells which destroys the receptor. Recombinant viral O-acetylesterases derived from Sf9 insect cells as chimeric proteins fused to eGFP specifically hydrolyze 9-O-acetylated sialic acids, while that of sialodacryoadenitis virus, a rat coronavirus related to mouse hepatitis virus, is specific for 4-O-acetylated sialic acid. The recombinant esterases were shown to specifically de-O-acetylate sialic acids on glycoconjugates. The recombinant viral proteins can be used to unambiguously identify O-acetylated acids.
Products for Viral Antigens
- Borrelia(28)
- Chagas(3)
- Chikungunya(7)
- Chlamydia(10)
- Cytomegalo(8)
- Dengue(50)
- Ebola(4)
- EBV(13)
- Encephalitis(8)
- Feline Leukemia Virus(1)
- Hantavirus(1)
- HBsAg(7)
- Helicobacter Pylori(3)
- Hepatitis A(15)
- Hepatitis B(10)
- Hepatitis C(85)
- Hepatitis D(1)
- Hepatitis E(5)
- Herpes(11)
- HERV-K(1)
- HIV(151)
- HTLV(6)
- Influenza(72)
- Lassa(2)
- Malaria(71)
- Mumps(1)
- Mycoplasma(4)
- Norovirus(4)
- Papillomavirus(5)
- Parvovirus(3)
- Rubella(3)
- S. Typhi(5)
- SARS(85)
- Shiga Like Toxin(2)
- Toxoplasma(9)
- Treponema(16)
- Varicella(3)
- West Nile(2)
- Zika(13)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP25461
Rubella E1
Rubella Virus E1 Mosaic Recombinant

-
GP25462
Rubella E2
Rubella Virus E2 Recombinant

-
GP25201
S.Typhi H
Salmonella Typhi H Antigen Recombinant

-
GP25204
S.Typhi HylE
Salmonella Typhi Haemolysin E Recombinant

-
GP25202
S.Typhi OMP
Salmonella Typhi Outer Membrane Protein Recombinant

-
GP25203
S.Typhi OMP 52kDa
Salmonella Typhi Outer Membrane Protein 52kDa Recombinant

-
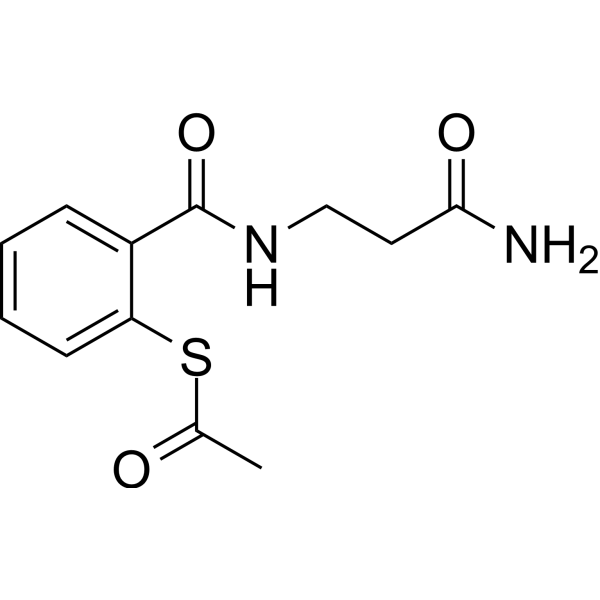
GC70228
SAMT-247
SAMT-247是一种杀微生物剂,可选择性地使病毒核衣壳蛋白NCp7失活,引起锌的排出并阻止RNA的衣壳化。
-
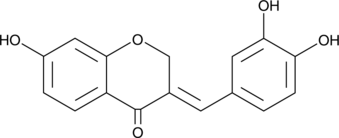
GC41626
Sappanone A
Sappanone A是一种具有较强抗氧化和抗炎活性的同型异黄酮。
-
GP25167
SARS Core (1-49)
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Core Recombinant, 1-49 a.a.

-
GP25168
SARS Core (1-49,192-220 a.a.)
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Core Recombinant

-
GP25166
SARS Core (340-390)
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Core Recombinant, (340-390 a.a)

-
GP25171
SARS Envelope
SARS相关冠状病毒包膜重组体

-
GP26377
SARS Envelope, His
The E

-
GP25170
SARS Matrix
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Matrix Recombinant

-
GP26380
SARS Membrane
The E

-
GP25173
SARS MERS
SARS MERS Spike S1 Recombinant

-
GP26374
SARS MERS RBD
SARS MERS RBD Recombinant produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 258 amino acids (358-606 aa) and having a molecular mass of 28

-
GP26373
SARS MERS S2
SARS MERS S2 Recombinant produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 554 amino acids (752-1296aa) and having a molecular mass of 60

-
GP26372
SARS MERS, (18-751)
SARS MERS Recombinant produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 740 amino acids (18-751aa) and having a molecular mass of 82

-
GP26370
SARS MERS, HEK
The HEK293 derived recombinant protein contains the SARS MERS Spike Glycoprotein S1, amino acids 18-725 fused to dimeric Fc tag at N-terminal having a total Mw of 215

-
GP26371
SARS MERS, Sf9
SARS MERS Recombinant produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 1285 amino acids (18-1296aa) and having a molecular mass of 141

-
GP25165
SARS Mosaic S(C)
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Spike Mosaic S(C) Recombinant

-
GP25164
SARS Mosaic S(M)
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Spike Mosaic S (M) Recombinant

-
GP25163
SARS Mosaic S(N)
SARS-Associated Coronavirus Spike Mosaic S (N) Recombinant

-
GP26379
SARS Nucleocapsid (340-390), His
The E

-
GP26378
SARS Nucleocapsid, 1-49 a.a.
The E

-
GP26369
SARS Nucleocaspid (2-422), HEK
The HEK293 derived recombinant protein contains the SARS Coronavirus Nucleoprotein, amino acids 2-422 fused to a 6 His tag at N-terminal

-
GP26381
SARS Spike (1-53, 90-115, 171-205)
The E

-
GP26384
SARS Spike (1-666)
The HEK293 derived recombinant protein contains the SARS Coronavirus Spike S1 Gycoprotein, amino acids 1-666 fused to His tag at C-terminal

-
GP26389
SARS Spike (14-1195)
SARS Spike produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 1188 amino acids (14-1195 aa) and having a molecular mass of 131

-
GP26385
SARS Spike (14-667)
The HEK293 derived recombinant protein contains the SARS Coronavirus Spike S1 Gycoprotein, amino acids 14-667 fused to His tag at C-terminal

-
GP26387
SARS Spike (306-515)
The recombinant SARS Spike containing a total of 220 amino acids (306-515) and having a calculated Mw of 24

-
GP26388
SARS Spike (306-515), Sf9
SARS Spike produced in Sf9 Baculovirus cells is a single, glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 219 amino acids (306-515 aa) and having a molecular mass of 24

-
GP26386
SARS Spike (306-527)
The HEK293 derived recombinant protein contains the SARS Coronavirus spike S glycoprotein Receptor Binding Domain, amino acids 306-527 fused to His tag at C-terminal

-
GP26382
SARS Spike (408-470, 540-573)
The E

-
GP26383
SARS Spike Mosaic
The E

-
GP25169
SARS-CoV
SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid (422a.a) Recombinant

-
GC39642
SARS-CoV-IN-2
SARS-CoV-IN-2 是一种有效的 SARS-CoV 复制抑制剂。在 Vero 细胞中,SARS-CoV-IN 1 抗冠状病毒,EC50 为 1.9 μM。SARS-CoV-IN-2 抑制 P. falciparum 3D7 和 W2 株,IC50 分别为 21.5 和 30 nM;IC90 分别为 51.0 和 99.9 nM。在 MT-4 细胞中,SARS-CoV-IN-2 降低 HIV-1 诱导的细胞病变,EC50 为 2.9 μM。具有抗疟和抗病毒活性。
-
GC39563
SARS-CoV-IN-3
SARS-CoV-IN-3 是一种有效的 SARS-CoV 复制抑制剂。在 Vero 细胞中,SARS-CoV-IN-3 抗冠状病毒,EC50 为 3.6 μM。SARS-CoV-IN-3 抑制 P. falciparum 3D7 和 W2 株,IC50 分别为 11.7 和 20.4 nM; IC90 分别为 29.19 和 56 nM。在 MT-4 细胞中,SARS-CoV-IN-3 降低 HIV-1 诱导的细胞病变,EC50 为 10 μM。具有抗疟和抗病毒活性。
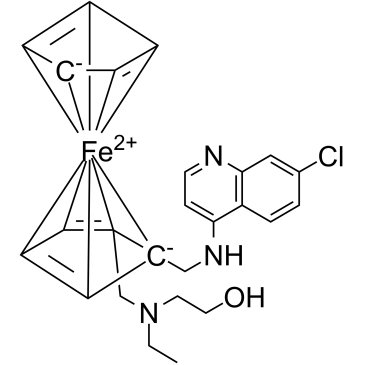
-
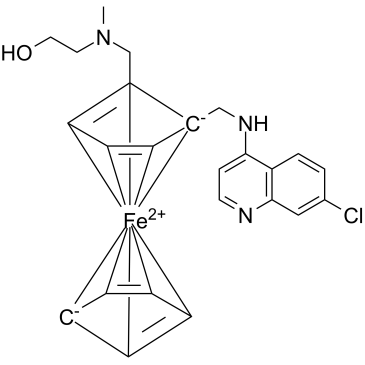
GC74628
Semzuvolimab
UB421
Semzuvolimab是一种小鼠IgG1κ抗体,靶向p55,T细胞表面抗原T4/Leu-3(CD4)。
-
GP25161
Shiga Like Toxin 1
Shiga Like Toxin-1 Subunit B Recombinant

-
GP25162
Shiga Like Toxin 2
志贺样毒素 2 亚基 B 重组体

-
GP26443
SIV GAG
SIV GAG Recombinant produced in E

-
GP25430
SIV p55
SIV p55 Recombinant

-
GC61284
Soyasaponin II
大豆皂苷II
SoyasaponinII是具有抗病毒活性的皂苷。SoyasaponinII抑制HSV-1,HCMV,流感病毒和HIV-1的复制。SoyasaponinII对HSV-1复制显示出有效的抑制作用。SoyasaponinII作为YB-1磷酸化和NLRP3炎性小体引发的抑制剂,可保护小鼠免受LPS/GalN诱导的急性肝衰竭。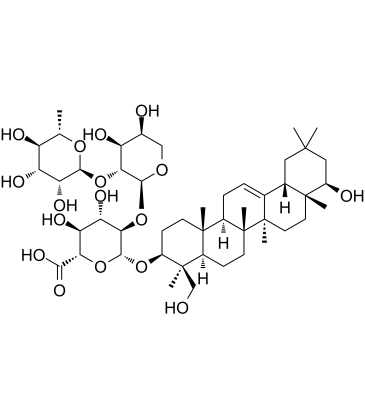
-
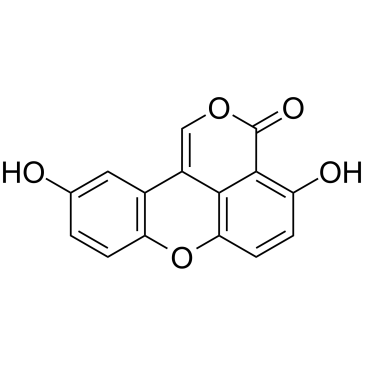
GC60344
Sparstolonin B
An isocoumarin with diverse biological activities
-
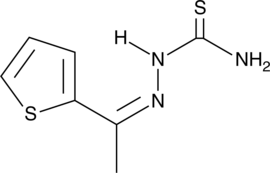
GC48101
SSAA09E1
A SARS-CoV entry inhibitor
-
GC40859
Steffimycin B
司替霉素B
An anthracycline bacterial metabolite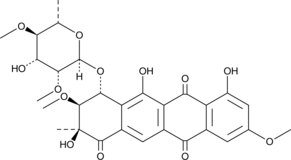
-
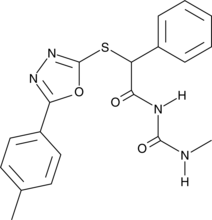
GC45570
STING Agonist C11
An agonist of the STING pathway
-
GC52174
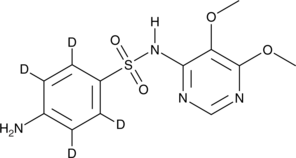
Sulfadoxin-d4
磺胺邻二甲氧嘧啶-D4,Sulphadoxine-d4
An internal standard for the quantification of sulfadoxin