Recombinant Proteins(重组蛋白)
Recombinant proteins are a new combination of genes that forms DNA. Recombinant DNA technology allows for the production of wild type and modified human and mammalian proteins at bulk quantities. Recombinant proteins are made from cloned DNA sequences which usually encode an enzyme or protein with known function
Recombinant proteins are made through genetic engineering, also called gene splicing or recombinant DNA technology. By putting human, animal or plant genes into the genetic material of bacteria, mammalian or yeast cells, these microorganisms can be used as factories or producers to make proteins for medical, academic and research uses.
A vector is simply a tool for manipulating DNA and can be viewed as a "transport vehicle" for the production of proteins from specific DNA sequences cloned into them. Purification and expression of a protein can sometimes be quite complicated & time-consuming, therefore an additional tag is used in addition to the specific DNA sequence which will facilitate the purification & expresion of the recombinant protein.
Recombinant Proteins are proteins that their DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from 2 or more sources which is incorporated into a single recombinant molecule. The DNA is first treated with restriction endonuclease enzyme which the ends of the cut have an overhanging piece of single-stranded DNA. These are called "sticky ends" because they are able to base pair with any DNA molecule containing the complementary sticky end. DNA ligase covalently links the two strands into 1 recombinant DNA molecule.
Recombinant DNA molecule must be replicated many times to provide material for analysis & sequencing. Producing many identical copies of the same recombinant DNA molecule is called cloning. Cloning is done in vitro, by a process called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Cloning in vivo can be done in unicellular microbessuch as E. coli, unicellular eukaryotes like yeast and in mammalian cells grown in tissue culture.
Recombinant DNA must be taken up by the cell in a form in which it can be replicated and expressed. This is achieved by incorporating the DNA in a vector. A number of viruses (both bacterial and of mammalian cells) can serve as vectors.
Recombinant DNA is also sometimes referred to as chimera. When combining two or more different strands of DNA.There are 3 different methods by which Recombinant DNA is made. 1. Transformation, 2. Phage-Transfection 3.Yeast, Plant & Mammalian Transformation. When using the method of transformation one needs to select a piece of DNA to be inserted into a vector, cut a piece of DNA with a restriction enzyme and ligate the DNA insert into the vector with DNA Ligase. The insert contains a selectable marker which allows for identification of recombinant molecules. An antibiotic marker is used in order to cause death for a host cell which does not contain the vector when exposed to a certain antibiotic.
Trasnformation is the insertion of the vector into the host cell. The host cells are prepared to take up the foreign DNA. Selectable markers are used for antibiotic resistance, color changes, or any other characteristic which can distinguish transformed hosts from untransformed hosts. Yeast, Plant & Mammalian Transformation is done by micro-injecting the DNA into the nucleus of the cell being transformed. Phage-Transfection process, is equivalent to transformation except for the fact that phage lambda or MI3 is used instead of bacteria.
These phages produce plaques which contain recombinant proteins which can be easily distinguished from the non-recombinant proteins by various selection methods.
Significant amounts of recombinant protein are produced by the host only when expression genes are added. The Protein’s expression depends on the genes which surround the DNA of interest, this collection of genes act as signals which provide instructions for the transcription and translation of the DNA of interest by the cell. These signals include the promoter, ribosome binding site, and terminator.
The recombinant DNA is inserted into expression vectors which contain the promoter, ribosome binding site, and terminator.
In prokaryotic systems, the promoter, ribosome binding site, and terminator have to be from the same host since the bacteria is unlikely to understand the signals of human promoters and terminators. The designated gene must not contain human introns since the bacteria does not recognize it and this results in premature termination, and the recombinant protein may not be processed correctly, be folded correctly, or may even be degraded.
The peptide sequence can be added as an extension at the N-terminal. Researchers can select the specific purification system which they would like to use. The unique vectors available contain several features needed for the production of bulk quantities of the target protein. The peptide sequence is usually placed in the vector so that it is designed to be a point of attack for a specific protease. Thus, after the recombinant protein is expressed and extracted from bacteria, specific peptide extension can be used to purify the protein and subsequently removed from the target protein to generate a nearly natural sequence on the final product.
6 or more consistent Histidine residues act as a metal binding site for recombinant protein purification and expression. The hexa-His sequence is called a His-Tag sequence which can be placed on the N-terminal of a target protein by using vectors from various commercial molecular biology companies. The His-Tag contains a cleavage site for a specific protease. His-Tag recombinant proteins are purified by Metal Chelate Affinity Chromatography such as nickel ion columns that are used as the heavy metal ion and the His-Tag protein is eluted from the metal-chelate column with Histidine or imidazole. Then the purified His-Tag protein is treated with the specific protease to cleave off the His-Tag or not if the tag doesn’t affect the active site of the protein.
Proteins have metal binding sites which can be used for the purification of recombinant and natural proteins. This type of purification is rather simple when using a gel bead which is covalently modified so that it displays a chelator group for binding a heavy metal ion like Ni2+ or Zn2+. The chelating group on the gel bead contains a small amount of the ligands needed to hold the metal ion. So when the protein’s metal binding site finds the heavy metal, it will bind by providing the ligands from its metal binding site to attach to the metal ion displayed on the chelator location of the gel bead. This purification method is quite identical to affinity chromatography when purifying metal-binding class of proteins.
Products for Recombinant Proteins
- Actin(7)
- ADAM(3)
- Adaptor-Related Protein Complex(3)
- ADP-Ribosylation Factor(21)
- Ag85(2)
- Albumin(7)
- Allergy(156)
- Alpha-2-HS-Glycoprotein(4)
- Anaplasma(3)
- Angiogenin(2)
- Ankyrin Repeat Domain(5)
- Annexin(20)
- Anterior Gradient Protein(3)
- ASF1 Anti-Silencing Function 1(2)
- ATP Synthase Mitochondrial(3)
- ATPase(9)
- Autophagy Related(4)
- B Cell Lymphoma(24)
- B9 Protein(2)
- Babesia Microti(3)
- Baculoviral IAP Repeat-Containing(3)
- Bartonella H.(3)
- Basic Transcription Factor(2)
- BATF(2)
- Bax(2)
- Beta 2 Microglobulin(3)
- BID(4)
- Biglycan(3)
- Bridging Integrator(2)
- Bromodomain Containing(3)
- Cadherin(8)
- Calbindin(4)
- Calcium Binding Protein(30)
- Calmodulin(4)
- Calpain(2)
- Calponin(2)
- Calreticulin(2)
- Calumenin(2)
- Candida Albicans(4)
- Canopy FGF Signaling Regulator(3)
- Capping Protein(2)
- Caspase Recruitment Domain Family(2)
- CCR4-NOT Transcription Complex(2)
- CEA(9)
- CEBP(2)
- Cell Division Cycle(5)
- Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein(2)
- Centrin(3)
- Centromere Protein(7)
- Charged Multivesicular Body Protein(3)
- Chloride Intracellular Channel(2)
- Chromatin Modifying Protein(4)
- Chromobox(3)
- Chromogranin(6)
- Chromosome Open Reading Frame(17)
- Clathrin(2)
- Coagulation Factors(7)
- Cofilin(2)
- Coiled-Coil Domain(9)
- Collagen(16)
- COMM Domain Containing(4)
- Complement Component(55)
- COP9 Signalosome(3)
- C-Reactive Protein(6)
- Crystallin(13)
- C-type Lectin Domain(11)
- CUE Domain Containing(2)
- Cystatin(25)
- Cysteine-Rich(2)
- Cysteine-Rich Secretory Protein(3)
- Cytochrome(9)
- Cytohesin(4)
- Cytokeratin(14)
- DCUN1D(3)
- DEAD Box Protein(2)
- Decorin(3)
- Density Lipoprotein(8)
- Developmental Pluripotency Associated(3)
- Dickkopf-Related Protein(7)
- DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region(2)
- DNA-Damage Protein(7)
- Dynactin(4)
- Dynein Light Chain(7)
- Dysbindin(2)
- Ectodysplasin(4)
- Elongator Acetyltransferase Complex(2)
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein(3)
- Endothelial Cell-Specific Molecule 1(4)
- EPH Receptor(6)
- Ephrin(13)
- ERCC(1)
- Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor(21)
- Exosome Component(6)
- FABP(28)
- Family with Sequence Similarity(8)
- F-Box Protein(1)
- Ferritin(3)
- Fibrinogen(3)
- Fibronectin Type III Domain Containing(2)
- Four And A Half LIM(2)
- Fragile Histidine Triad(2)
- G Antigen(3)
- GABA(A) Receptor-Associated Protein(3)
- Gastrokine(3)
- GDP Dissociation Inhibitor(2)
- General Transcription Factor(6)
- GIPC PDZ Domain(2)
- Gliadin(3)
- Glycophorin(3)
- Glycoprotein Nmb(3)
- Glypican(3)
- Gremlin(2)
- GTPase IMAP Family(2)
- GTP-Binding Protein(2)
- Guanine Nucleotide Binding Protein(11)
- Hairy and Enhancer of Split(2)
- Haptoglobin(5)
- Heat Shock Protein(66)
- Hematological And Neurological Expressed(2)
- Hemoglobin(8)
- Hemopexin(3)
- High-Mobility Group(8)
- HINT(2)
- HLA(8)
- HNRNP(3)
- Hypoxia-Inducible Factor(3)
- IMPAD1(4)
- Ig Heavy Chain Constant Region(7)
- Inhibitor of DNA Binding(2)
- Inhibitor of Growth Family(2)
- Integrin(52)
- Intercellular Adhesion Molecule(9)
- Junctional Adhesion Molecule(3)
- Karyopherin(2)
- KCTD(4)
- Killer Cell(8)
- Killer Cell Lectin-like Receptor(9)
- Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene(2)
- Kruppel-Like Factor(6)
- Lactoferrin(3)
- LBP(3)
- Leukocyte Cell Derived Chemotaxin(3)
- Leukocyte-Associated Ig-Like Receptor(3)
- LIN Protein(5)
- Listeriolysin(2)
- LRG1(3)
- Lymphocyte Antigen(3)
- Lysosomal-Associated Membrane Protein(3)
- MAD2(2)
- MAF(3)
- Mago-Nashi Homolog(2)
- Maltose Binding Protein(3)
- Mediator Complex(5)
- Melanoma Antigen Family A(8)
- Member RAS Oncogene Family(40)
- Mesoderm Development Candidate(2)
- Methylmalonic Aciduria(2)
- MHC class I chain-related gene(3)
- Microfibrillar Associated Protein(4)
- Microtubule-Associated Protein(8)
- Mitochondrial Ribosomal Protein(8)
- Mitochondrial Transcription Factor(2)
- Mortality Factor(2)
- Myelin Basic Protein(1)
- Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein(4)
- Myoglobin(4)
- Myosin Light Chain(12)
- Myxovirus(3)
- NANOG(4)
- NCK Adaptor Protein(2)
- NECTIN(3)
- Nescient Helix Loop Helix(2)
- Neuronal Calcium Sensor(2)
- Neutrophil Cytosolic Factor(2)
- NFKB Inhibitor(5)
- NHP2(2)
- N-Myc Downstream Regulated(3)
- Non-Metastatic Cells(7)
- NPM(2)
- NTF2-like Export Factor(1)
- Nucleobindin(2)
- Nucleopurin(2)
- Nucleosome Assembly Protein(2)
- Orosomucoid(5)
- Other(755)
- Outer Membrane Protein(1)
- p53(20)
- Paired Box(2)
- Parkinson Disease Protein(3)
- Parvalbumin(2)
- PCNA(2)
- PDZ Domain Containing(2)
- Pentraxin(3)
- Peroxisomal Biogenesis Factor(2)
- PHD Finger Protein(2)
- Phosducin-Like(2)
- Phosphatase and Tensin(1)
- Phospholipid Scramblase(2)
- PIH1 Domain Containing(2)
- Pim Oncogene(2)
- PITPN(2)
- Polymerase (RNA) (DNA directed) Polypeptide(7)
- Prefoldin(5)
- Pregnancy Specific Beta-1-Glycoprotein(4)
- Prion Protein(2)
- Processing Of Precursor(2)
- Profilin(4)
- Programmed Cell Death(8)
- Prohibitin(2)
- Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin(1)
- Protein C-Ets(2)
- Protein Phosphatase(2)
- Prothymosin(2)
- RAD51(9)
- RAN Binding Protein(2)
- Ras-Related C3 Botulinum Toxin Substrate(5)
- RASSF(2)
- Receptor Activity-Modifying Protein(2)
- Regenerating Islet-Derived(4)
- Regulator of Calcineurin(3)
- Regulator of G-Protein Signaling(9)
- Related RAS Viral (r-ras) Oncogene(2)
- Relaxin(3)
- Renin(5)
- Reticulocalbin(2)
- Retinoblastoma(3)
- Retinoic Acid Early Transcript(6)
- Retinoic Acid Receptor Responder(4)
- Rho Family GTPase(2)
- Rho GDP Dissociation Inhibitor(2)
- Ribosomal Protein(30)
- Ring Finger Protein(5)
- RNA Binding Motif Protein(3)
- R-Spondin(4)
- RWD Domain Containing(2)
- Sclerostin(3)
- SDHAF(2)
- Secretagogin(2)
- Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein(6)
- Secretoglobin(4)
- Secretogranin(2)
- Selectin(7)
- Selenoprotein(2)
- Septin(3)
- Serglycin(2)
- Serine Peptidase Inhibitor(3)
- Serpin(27)
- SERTA Domain Containing(2)
- SH2 Domain(2)
- SH3 Domain(6)
- SIGLEC(5)
- Signal Recognition Particle(2)
- Signal Sequence Receptor(3)
- Signal-Regulatory Protein(6)
- Single-Stranded DNA Binding Protein(2)
- Sirtuin(35)
- SLAM Family(5)
- SMAD(3)
- SNRP(15)
- Solute Carrier Family(3)
- Sorting Nexin(2)
- SPSB(1)
- sRAGE(3)
- SRY (Sex Determining Region Y)-Box(3)
- Stathmin(4)
- STIP(3)
- Streptavidin Proteins(5)
- Superoxide Dismutase(36)
- Surfeit(2)
- Synaptobrevin(11)
- Synaptosomal Associated Protein(5)
- Synaptotagmin(5)
- Syndecan(5)
- Syntaxin(10)
- Synuclein(7)
- Tachykinin(2)
- TAR DNA(4)
- TBC1 Domain Family(2)
- TCL(2)
- THAP Domain(4)
- Thioredoxin(15)
- TIGAR(3)
- Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor(3)
- TNF receptor-Associated Factor(2)
- Toll Like Receptor(1)
- Trafficking Protein Particle Complex(4)
- Transcription Elongation Factor(9)
- Transferrin(3)
- Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced(5)
- Transgelin(2)
- Translocase Of Outer Mitochondrial Membrane(2)
- Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells(2)
- Tripartite Motif(4)
- Tropomyosin(3)
- Troponin(16)
- TROVE Domain Family(3)
- Trypsin(4)
- TTC(3)
- Tubulin Folding Cofactor(5)
- Tubulin Gamma(2)
- U6 Small Nuclear RNA(5)
- Ubiquinol-Cytochrome C Reductase(3)
- Ubiquitin(16)
- UCHL1(4)
- UL16 binding protein(7)
- Uroplakin(2)
- Vacuolar Protein Sorting(7)
- Vascular cell adhesion molecule(5)
- V-crk Sarcoma Virus CT10(2)
- Vimentin(3)
- Visinin-Like Protein(2)
- V-ral Simian Leukemia Viral Oncogene(3)
- WAP Four-Disulfide Core Domain(2)
- Y. Enterocolitica(8)
- Zinc Finger(16)
- Default Categoryobox(9)
- Default Categoryr Homolog(3)
- MOB1(2)
- POU Class(4)
- Protein-A(24)
- SIX Default Categoryobox(2)
- Synovial Sarcoma(2)
- Mps One Binder Kinase Activator(2)
- X Breakpoint(2)
- p62(3)
- Cat.No. 产品名称 Information
-
GP25137
BETV6.0102
Allergenic Isoflavone Reductase-Like Protein Bet v 6.0102 Recombinant

-
GP22872
BEX1 Human
Brain Expressed X-Linked 1 Human Recombinant

-
GC65909
Bexotegrast
Bexotegrast 是 αΝβ6 整合素的有效抑制剂。Bexotegrast 可用于研究特发性肺纤维化 (IPF) 和非特异性间质性肺炎 (NSIP) 等纤维化 (信息摘自专利 WO2020210404A1,compound 5)。
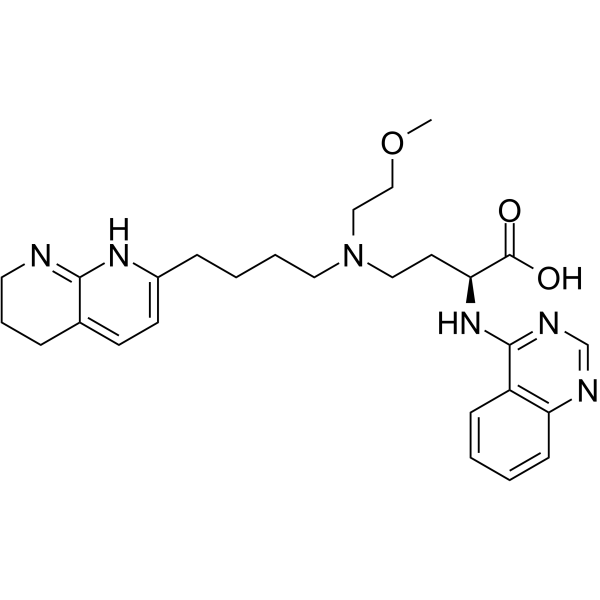
-
GP22873
BGN Human
Biglycan Human Recombinant

-
GP22874
BGN Human, Sf9
Biglycan Human Recombinant, Sf9

-
GP22875
BGN Mouse
Biglycan Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22876
BID Human
BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist Human Recombinant

-
GP22877
BID Mouse
BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist Mouse Recombinant

-
GP22878
BID Mouse, GST
BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist Mouse Recombinant, GST

-
GP22880
BIN1 Human
Bridging Integrator 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22881
BIN2 Human
Bridging Integrator 2 Human Recombinant

-
GC49724
BIO-1211 (trifluoroacetate salt)
A peptide inhibitor of α4β1 integrin
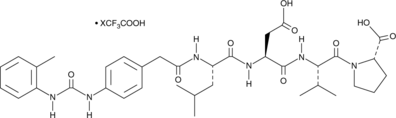
-
GC60077
BIO5192 hydrate
BIO5192hydrate是一种选择性强的整合素α4β1(VLA-4)抑制剂(Kd<10pM)。BIO5192hydrate选择性地与α4β1(IC50=1.8nM)结合,选择性高过其他一系列整合素。BIO5192hydrate导致小鼠造血干细胞和祖细胞(HSPCs)的动员比基础水平增加30倍。
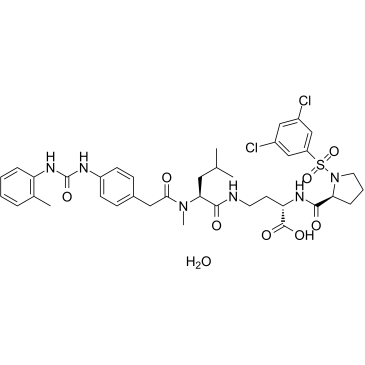
-
GP22882
BIRC5 Human
Baculoviral IAP Repeat-Containing 5 Human Recombinant

-
GP22883
BIRC7 Human
Baculoviral IAP Repeat-Containing 7 Human Recombinant

-
GP22884
BIRC7 Human, (1-280 a.a.)
Baculoviral IAP Repeat-Containing 7 (1-280 a.a.) Human Recombinant

-
GC50078
BIRT 377
BIRT 377 是一种有效的口服生物利用度抑制剂,可抑制细胞间粘附分子-1 (ICAM-1) 和淋巴细胞功能相关抗原-1 (LFA-1) 之间的相互作用,Ki 为 25.8 nM。
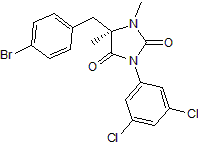
-
GP22886
BLOC1S2 Human
Biogenesis of Lysosomal Organelles Complex-1, Subunit 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP23974
BLOC1S5 Human
Biogenesis of Lysosomal Organelles Complex-1, Subunit 5 Human Recombinant

-
GP22887
BMF Human
Bcl2 Modifying Factor, Isoform 3 Human Recombinant

-
GC61783
BMS-309403 sodium
A cell-
permeable, potent, and selective inhibitor of FABP4 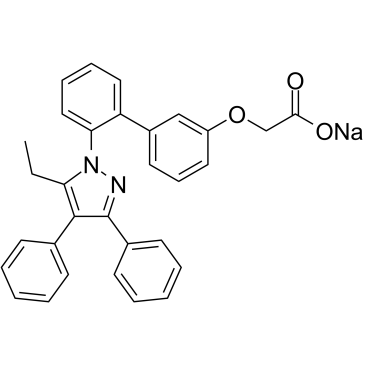
-
GC62872
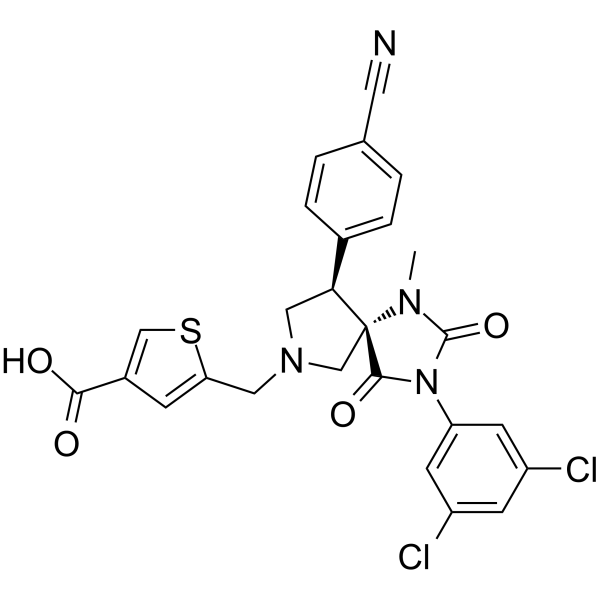
BMS-587101
BMS-587101 是一种有效的具有口服活性的 leukocyte function associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) 拮抗剂。BMS-587101 具有抗炎作用,可用于类风湿关节炎的研究。
-
GP22889
BNIP1 Human
BCL2/Adenovirus E1B 19kDa Interacting Protein 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22890
BOLA1 Human
BolA Homolog 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22891
BOLA3 Human
BolA Homolog 3 Human Recombinant

-
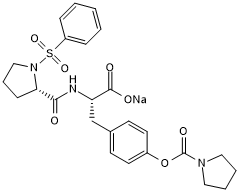
GC50325
BOP
BOP 是一种有效和选择性的双重 α9β1/α4β1 整合素抑制剂,Kd 值在皮摩尔范围内。
-
GP22892
BP-1 Human
BP-1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22893
BPI Human
Bactericidal/Permeability-Increasing Protein Human

-
GP22894
BPIFA1 Human
BPI fold containing family A Member 1 Human Recombinant

-
GC62128
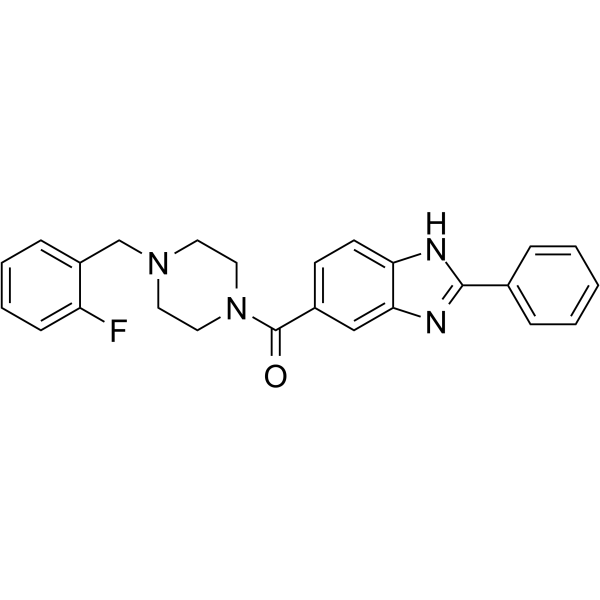
Bractoppin
Bractoppin 是一种串联 BRCT(串联 BRCT,BRCA1),由人乳腺癌和卵巢癌抑制蛋白 (BRCA1) tBRCT 结构域识别磷酸肽的药物样抑制剂,在体外选择性抑制底物结合的纳摩尔活性,IC50 为0.074 77777#181;M。
-
GP22895
BRD1 Human
Bromodomain Containing 1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22896
BRD2 Human
Bromodomain Containing 2 Human Recombinant

-
GP22897
BRD3 Human
Bromodomain Containing 3 Human Recombinant

-
GP22899
BRK1 Human
BRK1 Human Recombinant

-
GP22898
BRMS1 Human
Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor 1 Human Recombinant

-
GC46024
Bromodiphenhydramine (hydrochloride)
Ambodryl hydrochloride
A histamine H1 receptor antagonist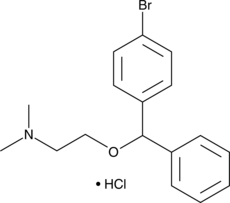
-
GP22902
BSND Human
Bartter Syndrome Infantile with Sensorineural Deafness Human Recombinant

-
GC73519
BT200 sodium
BT200 sodium,适配体BT100的聚乙二醇化形式,抑制von Willebrand因子(VWF)与血小板糖蛋白GPIb的结合,预防动脉血栓形成。
-
GP22903
BTF3 Human
Basic Transcription Factor 3 Human Recombinant

-
GP22904
BTF3L4 Human
Basic Transcription Factor 3-Like 4 Human Recombinant

-
GP22905
BTLA Human
B And T Lymphocyte Associated Human Recombinant

-
GP22906
BTN3A1 Human
Butyrophilin Subfamily 3 Member A1 Human Recombinant

-
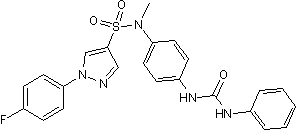
GC50075
BTT 3033
BTT 3033 是一种口服活性的 α2β1 (EC50: 130 nM) 构象选择性抑制剂,通过与 α2I 结构域结合。
-
GP22907
BUB3 Human
BUB3 Human Recombinant

-
GP22908
BUD31 Human
BUD31 Human Recombinant

-
GC46956
Budesonide-d8
布地奈德 d8
An internal standard for the quantification of budesonide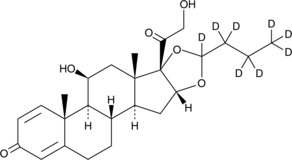
-
GC19432
BXL-628
艾洛骨化醇,BXL-628; Ro-26-9228
A vitamin D3 analog with diverse biological activities
-
GC65455
c(phg-isoDGR-(NMe)k)
c(phg-isoDGR-(NMe)k) 是有效选择性的 α5β1 整合素 配体,IC50 为 2.9 nM。
-
GP22974
c-Actin
Cardiac Actin

-
GP22910
C.Albicans Bgl2
Candida Albicans Bgl2 Recombinant





