Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)

(Synonyms: S-(4-硝基苄基)-6-硫代肌苷,NBMPR) 目录号 : GC10835
Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)是一种平衡型核苷转运子亚型1(ENT1)转运蛋白抑制剂,以高亲和力与ENT1转运蛋白结合。
Cas No.:38048-32-7
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR) is an inhibitor of the equilibrative nucleoside transporter subtype 1 (ENT1) transporter, which binds to the ENT1 transporter with high affinity[1, 2]. Nitrobenzylthioinosine can inhibit adenosine reuptake by inhibiting the ENT1 transporter, and has anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, and neuroprotective effects[3]. Nitrobenzylthioinosine is a photoaffinity probe that can be used to track adenosine uptake sites in the brain and can cross the blood-brain barrier[4].
In vitro, treatment of HeLa cells with Nitrobenzylthioinosine (5μM) inhibited the uptake of uridine by the cells, but had no effect on uridine kinase in HeLa cell extracts or the relative proportions of uridine anabolic metabolites in intact cells[5].
In vivo, Nitrobenzylthioinosine (50, 100mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected into mice bearing B16 melanoma cells for 4 days, and combined with N-phosphonoacetyl-L-aspartic acid (PALA) was able to inhibit melanoma growth in mice[6].
References:
[1] Zhang Y W, Shepel P N, Peeling J, et al. Effects of nitrobenzylthioinosine on adenosine levels and neuronal injury in rat forebrain ischemia[J]. Neuroscience Research Communications, 2002, 30(2): 83-89.
[2] Rehan S, Shahid S, Salminen T A, et al. Current progress on equilibrative nucleoside transporter function and inhibitor design[J]. SLAS DISCOVERY: Advancing Life Sciences R&D, 2019, 24(10): 953-968.
[3] Li R W S, Yang C, Sit A S M, et al. Physiological and pharmacological roles of vascular nucleoside transporters[J]. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology, 2012, 59(1): 10-15.
[4] Kalaria R N, Harik S I. Nucleoside Transporter of Cerebral Micro vessels and Choroid Plexus[J]. Journal of neurochemistry, 1986, 47(6): 1849-1856.
[5] PATERSON A R P, NAIK S R, CASS C E. Inhibition of uridine uptake in HeLa cells by nitrobenzylthioinosine and related compounds[J]. Molecular Pharmacology, 1977, 13(6): 1014-1023.
[6] Erlichman C, Vidgen D. Antitumor activity of N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartic acid in combination with nitrobenzylthioinosine[J]. Biochemical pharmacology, 1984, 33(20): 3177-3181.
Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)是一种平衡型核苷转运子亚型1(ENT1)转运蛋白抑制剂,以高亲和力与ENT1转运蛋白结合[1, 2]。Nitrobenzylthioinosine能够通过抑制ENT1转运蛋白从而抑制腺苷再摄取,具有抗炎、心脏保护、神经保护作用[3]。Nitrobenzylthioinosine是一种光亲和探针,能够用于追踪大脑中腺苷的摄取位点,可以穿过血脑屏障[4]。
在体外,Nitrobenzylthioinosine(5μM)处理HeLa细胞,抑制了细胞对尿苷的摄取,对HeLa细胞提取物中的尿苷激酶或完整细胞中尿苷合成代谢物的相对比例没有影响[5]。
在体内,Nitrobenzylthioinosine(50, 100mg/kg)通过腹腔注射治疗B16黑色素瘤细胞异种移植小鼠4天,联合N-膦乙酰基-L-天冬氨酸(PALA)能够抑制小鼠体内黑色素瘤生长[6]。
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
Animal models | C57 black female mice |
Preparation Method | C57 black female mice were injected with 2×106 B16 melanoma cells intramuscularly in the hind leg. Eight or nine mice were allocated to each treatment group. Tumor weight doubling time for control animals was 2 days. Intraperitoneal injections daily for 4 consecutive days with N-Phosphonacetyl-L-aspartic acid (PALA) (300mg/kg), Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR) (100mg/kg) or PALA (150mg/kg) and NBMPR (50, 100mg/kg) together were started 6 days after tumor inoculation. i.e. when tumors were just detectable. Drug was administered in a total volume of 0.2mL. Tumors were measured by passing the hind leg through lucite with holes which had been calibrated previously to tumor weight. |
Dosage form | 50, 100mg/kg/day; 4 days; i.p. |
Applications | PALA, 300mg/kg daily×4, resulted in a 6-day tumor growth delay but Nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR), 100mg/kg daily×4, had no effect. PALA, 150mg/kg daily×4, plus NBMPR, 50 or 100mg/kg daily×4, resulted in a 6-day tumor growth delay also. |
References: | |
| Cas No. | 38048-32-7 | SDF | |
| 别名 | S-(4-硝基苄基)-6-硫代肌苷,NBMPR | ||
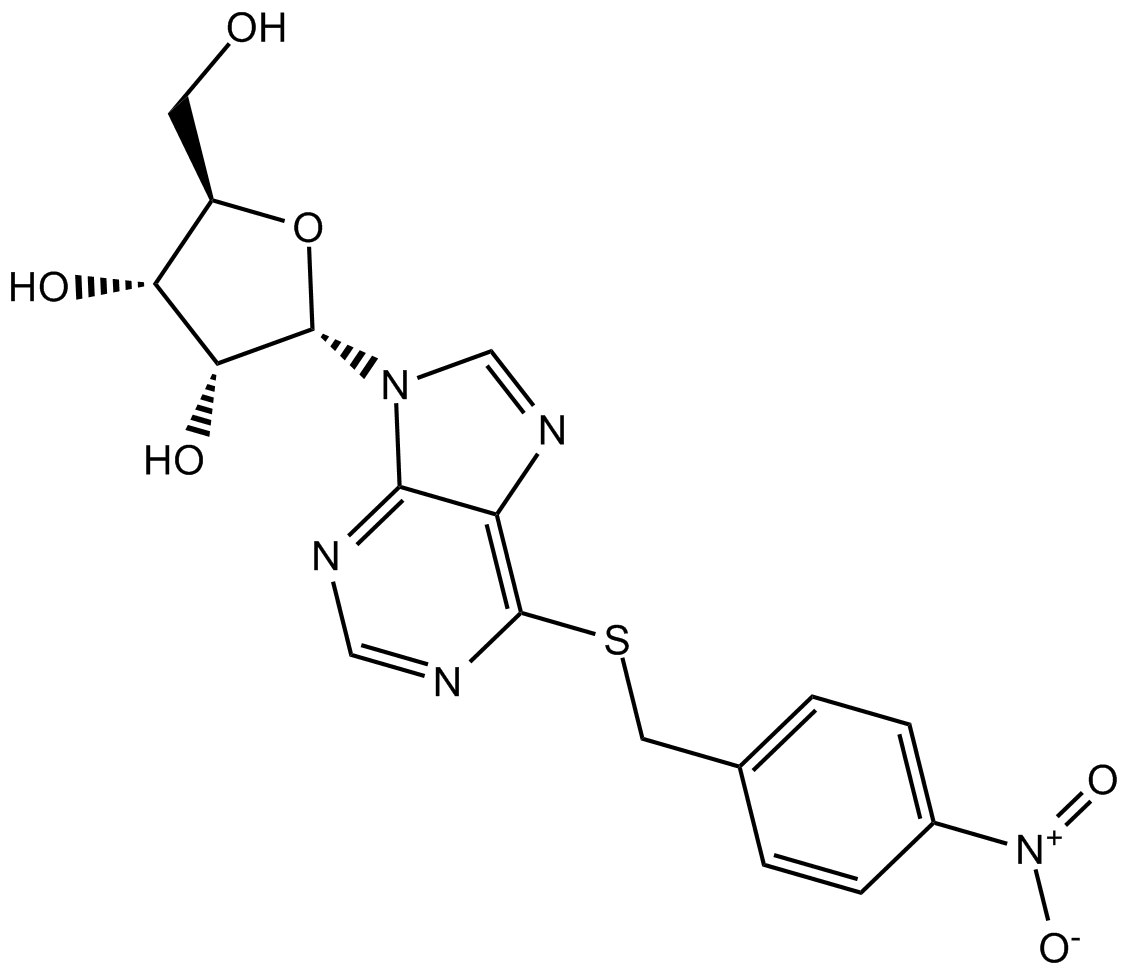
| 化学名 | (2R,3S,4R,5S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-5-(6-((4-nitrobenzyl)thio)-9H-purin-9-yl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol | ||
| Canonical SMILES | O[C@H]1[C@@H](N2C3=NC=NC(SCC(C=C4)=CC=C4[N+]([O-])=O)=C3N=C2)O[C@H](CO)[C@H]1O | ||
| 分子式 | C17H17N5O6S | 分子量 | 419.41 |
| 溶解度 | ≥ 16.9mg/mL in DMSO | 储存条件 | Store at -20°C, stored under nitrogen |
| General tips | 请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 储备液的保存方式和期限:-80°C 储存时,请在 6 个月内使用,-20°C 储存时,请在 1 个月内使用。 为了提高溶解度,请将管子加热至37℃,然后在超声波浴中震荡一段时间。 |
||
| Shipping Condition | 评估样品解决方案:配备蓝冰进行发货。所有其他可用尺寸:配备RT,或根据请求配备蓝冰。 | ||
| 制备储备液 | |||
 |
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 2.3843 mL | 11.9215 mL | 23.843 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4769 mL | 2.3843 mL | 4.7686 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2384 mL | 1.1922 mL | 2.3843 mL |
| 第一步:请输入基本实验信息(考虑到实验过程中的损耗,建议多配一只动物的药量) | ||||||||||
| 给药剂量 | mg/kg |  |
动物平均体重 | g |  |
每只动物给药体积 | ul |  |
动物数量 | 只 |
| 第二步:请输入动物体内配方组成(配方适用于不溶于水的药物;不同批次药物配方比例不同,请联系GLPBIO为您提供正确的澄清溶液配方) | ||||||||||
| % DMSO % % Tween 80 % saline | ||||||||||
| 计算重置 | ||||||||||
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/ml;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL,
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL saline,混匀澄清。
1. 首先保证母液是澄清的;
2.
一定要按照顺序依次将溶剂加入,进行下一步操作之前必须保证上一步操作得到的是澄清的溶液,可采用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等物理方法助溶。
3. 以上所有助溶剂都可在 GlpBio 网站选购。
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >99.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet