D-+-Galactosamine

(Synonyms: D-氨基半乳糖盐酸盐; D-Galactosamine hydrochloride) 目录号 : GC11746
D-+-Galactosamine是一种高度选择性的肝毒素,主要通过产生自由基和尿嘧啶核苷酸的消耗引起肝损伤。
Cas No.:1772-03-8
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
D-+-Galactosamine is a highly selective hepatotoxin that causes liver damage primarily through the production of free radicals and the consumption of uracil nucleotides[1]. D-+-Galactosamine is a 6-carbon amino sugar derived from galactose that is used to induce hepatitis in the liver of rodents[2]. D-+-Galactosamine poisoning can also lead to renal insufficiency, so renal failure is often associated with end-stage liver damage[3].
In vitro, D-+-Galactosamine (5mM) treatment of mouse primary hepatocytes for 24h significantly induced apoptosis 2h after hepatotoxin administration, significantly increased cell necrosis 24h after administration, induced caspase-3 activation and DNA fragmentation in hepatocytes, but did not change the activity of caspase-6, -8, -9, SMases or cytochrome c release [4]. Treatment of rat primary hepatocytes with D-+-Galactosamine (1-40 mM) for 24 h reduced mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity and glutathione content in a dose-dependent manner, and increased the concentration of lipid peroxide MDA[5].
In vivo, a single intraperitoneal injection of D-+-Galactosamine (500 mg/kg) in Sprague-Dawley rats caused significant damage to liver tissue, increased serum aspartate and alanine aminotransferase, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, sialic acid and uric acid levels, increased serum superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, catalase activities and lipid peroxidation values, and reduced serum and liver glutathione levels[6]. A single intraperitoneal injection of D-+-Galactosamine (1400 mg/kg) in Wistar rats induced acute liver failure with severe parenchymal necrosis and severe lobular and periportal inflammatory infiltration in the liver[7].
References:
[1] Endo Y, Shibazaki M, Yamaguchi K, et al. Enhancement by galactosamine of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‐induced tumour necrosis factor production and lethality: its suppression by LPS pretreatment[J]. British journal of pharmacology, 1999, 128(1): 5-12.
[2] Saracyn M, Zdanowski R, Brytan M, et al. D-Galactosamine intoxication in experimental animals: is it only an experimental model of acute liver failure?[J]. Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, 2015, 21: 1469.
[3] Sinha M, Manna P, Sil P C. Amelioration of galactosamine-induced nephrotoxicity by a protein isolated from the leaves of the herb, Cajanus indicus L[J]. BMC complementary and alternative medicine, 2007, 7: 1-18.
[4] Siendones E, JIMÉNEZ‐GÓMEZ Y, Montero J L, et al. PGE1 abolishes the mitochondrial‐independent cell death pathway induced by D‐galactosamine in primary culture of rat hepatocytes[J]. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 2005, 20(1): 108-116.
[5] Kučera O, Lotková H, Kanďár R, et al. The model of D-galactosamine-induced injury of rat hepatocytes in primary culture[J]. Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the human bone marrow: Cultivation, phenotypic and changes, 2006, 49(1): 59-65.
[6] Catal T, Tunali S, Bolkent S, et al. An antioxidant combination improves histopathological alterations and biochemical parameters in D-galactosamine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats[J]. European Journal of Biology, 2017, 76(1): 14-19.
[7] Éboli L P C B, Netto A A S, Azevedo R A, et al. Evaluating the best time to intervene acute liver failure in rat models induced by d-galactosamine[J]. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira, 2016, 31(12): 783-792.
D-+-Galactosamine是一种高度选择性的肝毒素,主要通过产生自由基和尿嘧啶核苷酸的消耗引起肝损伤[1]。D-+-Galactosamine是一种从半乳糖衍生的6碳氨基糖,用于在啮齿动物肝脏中诱导肝炎[2]。D-+-Galactosamine中毒也会导致肾功能不全,所以肾功能衰竭通常和终末期肝损伤有关[3]。
在体外,D-+-Galactosamine(5mM)处理小鼠原代肝细胞24h,在肝毒素给药2小时后显著诱导细胞凋亡,给药24小时后显著增加细胞坏死,诱导了肝细胞中caspase-3活化和DNA碎片化,但不改变caspase-6、-8、-9、SMases或细胞色素c释放的活性[4]。D-+-Galactosamine(1-40mM)处理大鼠原代肝细胞24h,以剂量依赖性方式降低线粒体脱氢酶活性和谷胱甘肽含量,增加脂质过氧化物MDA的浓度[5]。
在体内,D-+-Galactosamine(500mg/kg)通过单剂量腹腔注射处理Sprague-Dawley大鼠,对肝组织造成显著损伤,升高了血清天冬氨酸和丙氨酸转氨酶、γ-谷氨酰转肽酶、碱性磷酸酶、乳酸脱氢酶、唾液酸和尿酸水平,升高了血清超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶、过氧化氢酶活性以及脂质过氧化值,降低了血清和肝脏谷胱甘肽水平[6]。D-+-Galactosamine(1400mg/kg)通过单剂量腹腔注射处理Wistar大鼠,引起了急性肝衰竭,肝脏出现严重的实质坏死以及严重的小叶和门静脉周围炎症浸润[7]。
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
Cell lines | Hepatocytes |
Preparation Method | Cells were treated with PGE1 (1mM) 2 h before D-+-Galactosamine (5mM) and then cultured for 24 h. Apoptosis was determined by DNA fragmentation and caspase-3, -6, -8, and -9 activation in hepatocytes. Necrosis was determined by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in the culture medium. |
Reaction Conditions | 5mM; 0-24h |
Applications | D-+-Galactosamine significantly induced cell apoptosis 2 hours after hepatotoxin administration and significantly increased cell necrosis 24 hours after administration. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
Animal models | Sprague-Dawley rats |
Preparation Method | The rats were separated into four groups of 10 rats each: (1) control animals (0.9% NaCl i.p.); (2) control animals given antioxidants (100 mg/kg/day ascorbic acid,100 mg/kg/day alpha tocopherol, 15 mg/kg/day beta carotene, and 0.2 mg/kg/day sodium selenate, p.o.); (3)animals given only a single dose of D-+-Galactosamine (500mg/kg, i.p.) (dissolved in 0.9% NaCl); (4)animals given D-+-Galactosamine and antioxidants. D-+-Galactosamine was administered on day 3, and rats were sacrificed 7 hours after the last antioxidant administration. Blood samples were collected and liver tissue samples were obtained for biochemical and histological analyses. |
Dosage form | 500mg/kg; i.p. |
Applications | D-+-Galactosamine administration caused significant damage to liver tissue. Serum aspartate and alanine aminotransferase, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, sialic acid, and uric acid levels were increased. Serum and liver glutathione levels were decreased, and serum superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, catalase activities, and lipid peroxidation values were increased in the D-+-Galactosamine group. |
References: [1]Siendones E, JIMÉNEZ‐GÓMEZ Y, Montero J L, et al. PGE1 abolishes the mitochondrial‐independent cell death pathway induced by D‐galactosamine in primary culture of rat hepatocytes[J]. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 2005, 20(1): 108-116. [2]Catal T, Tunali S, Bolkent S, et al. An antioxidant combination improves histopathological alterations and biochemical parameters in D-galactosamine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats[J]. European Journal of Biology, 2017, 76(1): 14-19. | |
| Cas No. | 1772-03-8 | SDF | |
| 别名 | D-氨基半乳糖盐酸盐; D-Galactosamine hydrochloride | ||
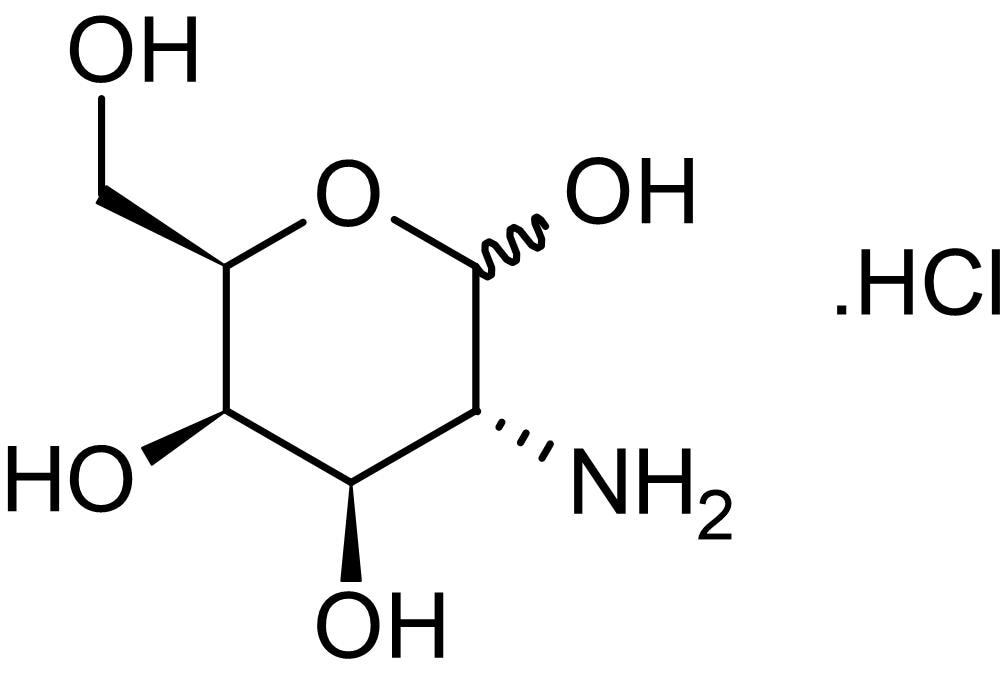
| 化学名 | (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-amino-3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyhexanal hydrochloride | ||
| Canonical SMILES | N[C@@]([C@](O)([H])[C@](O)([H])[C@@](O)([H])CO)([H])C=O.Cl | ||
| 分子式 | C6H13NO5.HCl | 分子量 | 215.63 |
| 溶解度 | ≥ 21.6mg/mL in Water | 储存条件 | Store at RT |
| General tips | 请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 储备液的保存方式和期限:-80°C 储存时,请在 6 个月内使用,-20°C 储存时,请在 1 个月内使用。 为了提高溶解度,请将管子加热至37℃,然后在超声波浴中震荡一段时间。 |
||
| Shipping Condition | 评估样品解决方案:配备蓝冰进行发货。所有其他可用尺寸:配备RT,或根据请求配备蓝冰。 | ||
| 制备储备液 | |||
 |
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 4.6376 mL | 23.1879 mL | 46.3757 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9275 mL | 4.6376 mL | 9.2751 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4638 mL | 2.3188 mL | 4.6376 mL |
| 第一步:请输入基本实验信息(考虑到实验过程中的损耗,建议多配一只动物的药量) | ||||||||||
| 给药剂量 | mg/kg |  |
动物平均体重 | g |  |
每只动物给药体积 | ul |  |
动物数量 | 只 |
| 第二步:请输入动物体内配方组成(配方适用于不溶于水的药物;不同批次药物配方比例不同,请联系GLPBIO为您提供正确的澄清溶液配方) | ||||||||||
| % DMSO % % Tween 80 % saline | ||||||||||
| 计算重置 | ||||||||||
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/ml;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL,
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL saline,混匀澄清。
1. 首先保证母液是澄清的;
2.
一定要按照顺序依次将溶剂加入,进行下一步操作之前必须保证上一步操作得到的是澄清的溶液,可采用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等物理方法助溶。
3. 以上所有助溶剂都可在 GlpBio 网站选购。
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet