Nile Red

(Synonyms: 尼罗红; Nile Blue A oxazone; Phenoxazone 9) 目录号 : GC15539
尼罗红是一种常见的脂质染料。
Cas No.:7385-67-3
Sample solution is provided at 25 µL, 10mM.
Nile red is a common lipid dye. Nile red is a hydrophobic and metachromatic dye with poor solubility and fluorescence in water, with colour emission varying from deep red to strong yellow gold in hydrophobic environments [1].
Nile red can dye the cholesterol in the human plasma through staining of lipid vesicles in smooth muscle cells and in cultured macrophages incubated at low density, using the excitation/emission wavelengths 450 to 500/>528 [2]. Nile red was also used to study membrane heterogeneity [3] and ligand-hydrophobic protein surface interactions with the alternative wavelengths 570/610 [4] and to study enzyme mechanism by using the wavelengths 550/640 to 660 [5]. Nile red has also been successfully used to stain intracellular neutral lipids that is, TAG and cholesterol esters in yeast, fungi with coupled wavelengths 488/565 to 585 [6] and also in microalgae, with wavelengths set to 488 to 525/570 to 600 [7] or to stain total lipids with wavelengths set to 490/585 [8].
References:
[1]. Rumin J, Bonnefond H, Saint-Jean B, et al. The use of fluorescent Nile red and BODIPY for lipid measurement in microalgae[J]. Biotechnology for biofuels, 2015, 8(1): 1-16.
[2]. Greenspan P, Mayer E P, Fowler S D. Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets[J]. The Journal of cell biology, 1985, 100(3): 965-973.
[3]. Ira and, Krishnamoorthy G. Probing the link between proton transport and water content in lipid membranes[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2001, 105(7): 1484-1488.
[4]. Sackett D L, Wolff J. Nile red as a polarity-sensitive fluorescent probe of hydrophobic protein surfaces[J]. Analytical biochemistry, 1987, 167(2): 228-234.
[5]. Ruvinov S B, Yang X J, Parris K D, et al. Ligand-mediated Changes in the Tryptophan Synthase Indole Tunnel Probed by Nile Red Fluorescence with Wild Type, Mutant, and Chemically Modified Enzymes (∗)[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1995, 270(11): 6357-6369.
[6]. Kimura K, Yamaoka M, Kamisaka Y. Rapid estimation of lipids in oleaginous fungi and yeasts using Nile red fluorescence[J]. Journal of microbiological methods, 2004, 56(3): 331-338.
[7]. Cooksey K E, Guckert J B, Williams S A, et al. Fluorometric determination of the neutral lipid content of microalgal cells using Nile Red[J]. Journal of microbiological methods, 1987, 6(6): 333-345.
[8]. Lee S J, Yoon B D, Oh H M. Rapid method for the determination of lipid from the green alga Botryococcus braunii[J]. Biotechnology techniques, 1998, 12(7): 553-556.
尼罗红是一种常见的脂质染料。尼罗红是一种疏水性异染性染料,在水中溶解度差且发荧光,在疏水环境中发射的颜色从深红色到强黄色不等[1]。
使用激发/发射波长 450 至 500/>528,尼罗红可以通过染色平滑肌细胞和培养的低密度巨噬细胞中的脂质囊泡来染色人血浆中的胆固醇 [2] 。尼罗红还用于研究膜异质性 [3] 和配体疏水蛋白表面与替代波长 570/610 [4] 的相互作用,并通过使用研究酶机制波长 550/640 至 660 [5]。尼罗红也已成功用于染色细胞内中性脂质,即酵母中的 TAG 和胆固醇酯,耦合波长为 488/565 至 585 的真菌 [6] 以及微藻,波长设置为488 至 525/570 至 600 [7] 或将波长设置为 490/585 [8] 对总脂质进行染色。
本方案仅提供一个指导,请根据您的具体需要进行修改。
1. 制备染色液
(1)配置储存液:使用DMSO溶解Nile Red,配置浓度为1mM的储存液。
注意:未使用的储存液分装后在-20℃或-80°C避光保存,避免反复冻融。
(2)配置工作液:用合适的缓冲液(如:无血清培养基或PBS)稀释储存液,配制浓度为0.2-1μM的工作液。
注意:请根据实际情况调整工作液浓度,现用现配。
2.细胞悬浮染色
(1)悬浮细胞:经1000g离心3-5分钟,弃去上清液,用PBS清洗两次,每次5分钟。
(2)贴壁细胞:使用PBS清洗两次,加入胰酶消化细胞,消化完成后经1000g离心3-5min。
(3)加入1mL的Nile Red工作溶液重悬细胞,室温避光孵育5-30分钟。不同细胞最佳孵育时间不同,请根据具体实验需求自行摸索。
(4)孵育结束后,经1000g离心5分钟,去除上清液,加入PBS清洗2-3次,每次5分钟。
(5)用预温的无血清细胞培养基或PBS重悬细胞,通过荧光显微镜或流式细胞术观察。
3.细胞贴壁染色
(1)在无菌盖玻片上培养贴壁细胞。
(2)从培养基中移走盖玻片,吸出过量的培养基,将盖玻片放在潮湿的环境中。
(3)从盖玻片的一角加入100μL的染料工作液,轻轻晃动使染料均匀覆盖所有细胞。
(4) 室温避光孵育5-30分钟。不同细胞最佳孵育时间不同,请根据具体实验需求自行摸索。
(5)孵育结束后吸弃染料工作液,使用预温的培养液清洗盖玻片2~3次。
4.显微镜检测。在甘油三酯(中性脂质)中,Nile Red的最大激发光/发射光为515/585nm;在磷脂(极性脂质)中的最大激发光/发射光为554nm/638 nm。
注意事项:
1)荧光染料均存在淬灭问题,请尽量注意避光,以减缓荧光淬灭。
2)为了您的安全和健康,请穿实验服并戴一次性手套操作。
| Cas No. | 7385-67-3 | SDF | |
| 别名 | 尼罗红; Nile Blue A oxazone; Phenoxazone 9 | ||
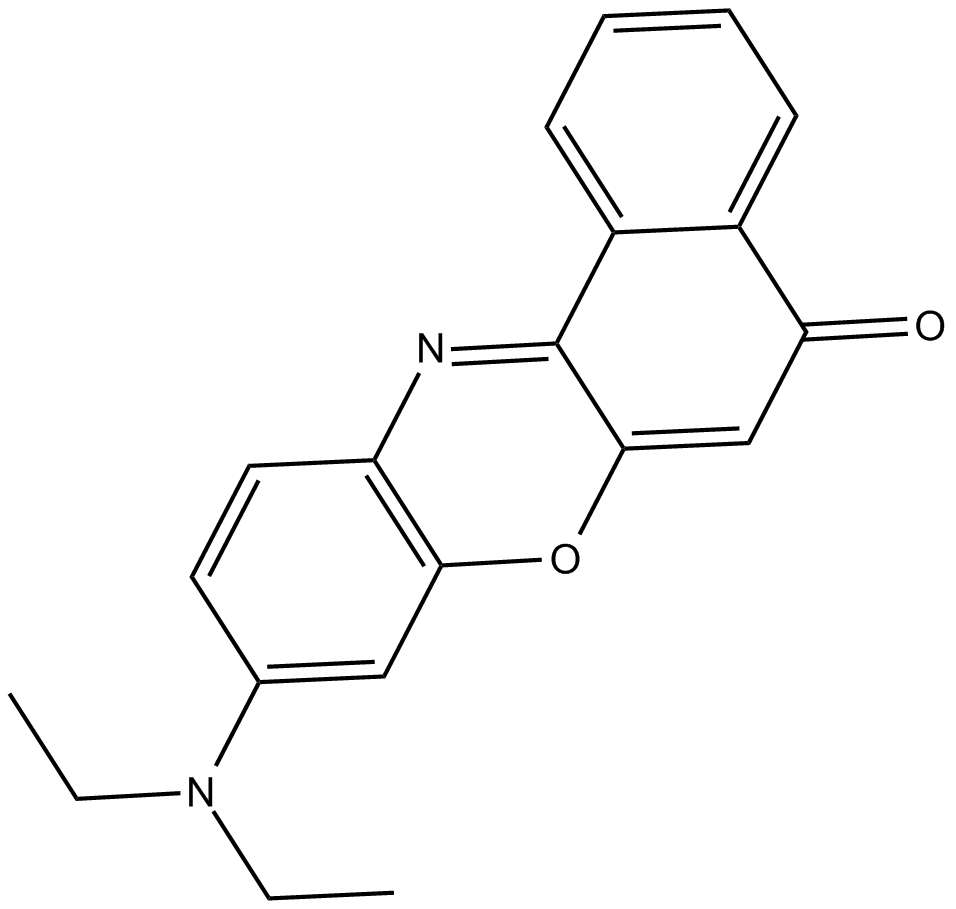
| 化学名 | 9-(diethylamino)-5H-benzo[a]phenoxazin-5-one | ||
| Canonical SMILES | CCN(C1=CC2=C(N=C3C4=CC=CC=C4C(C=C3O2)=O)C=C1)CC | ||
| 分子式 | C20H18N2O2 | 分子量 | 318.37 |
| 溶解度 | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (157.05 mM) | 储存条件 | Store at 4°C, protect from light |
| General tips | 请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 储备液的保存方式和期限:-80°C 储存时,请在 6 个月内使用,-20°C 储存时,请在 1 个月内使用。 为了提高溶解度,请将管子加热至37℃,然后在超声波浴中震荡一段时间。 |
||
| Shipping Condition | 评估样品解决方案:配备蓝冰进行发货。所有其他可用尺寸:配备RT,或根据请求配备蓝冰。 | ||
| 制备储备液 | |||
 |
1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg |
| 1 mM | 3.141 mL | 15.705 mL | 31.41 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6282 mL | 3.141 mL | 6.282 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3141 mL | 1.5705 mL | 3.141 mL |
| 第一步:请输入基本实验信息(考虑到实验过程中的损耗,建议多配一只动物的药量) | ||||||||||
| 给药剂量 | mg/kg |  |
动物平均体重 | g |  |
每只动物给药体积 | ul |  |
动物数量 | 只 |
| 第二步:请输入动物体内配方组成(配方适用于不溶于水的药物;不同批次药物配方比例不同,请联系GLPBIO为您提供正确的澄清溶液配方) | ||||||||||
| % DMSO % % Tween 80 % saline | ||||||||||
| 计算重置 | ||||||||||
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/ml;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL,
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL saline,混匀澄清。
1. 首先保证母液是澄清的;
2.
一定要按照顺序依次将溶剂加入,进行下一步操作之前必须保证上一步操作得到的是澄清的溶液,可采用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等物理方法助溶。
3. 以上所有助溶剂都可在 GlpBio 网站选购。
Quality Control & SDS
- View current batch:
- Purity: >98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- SDS (Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
-
Related Biological Data
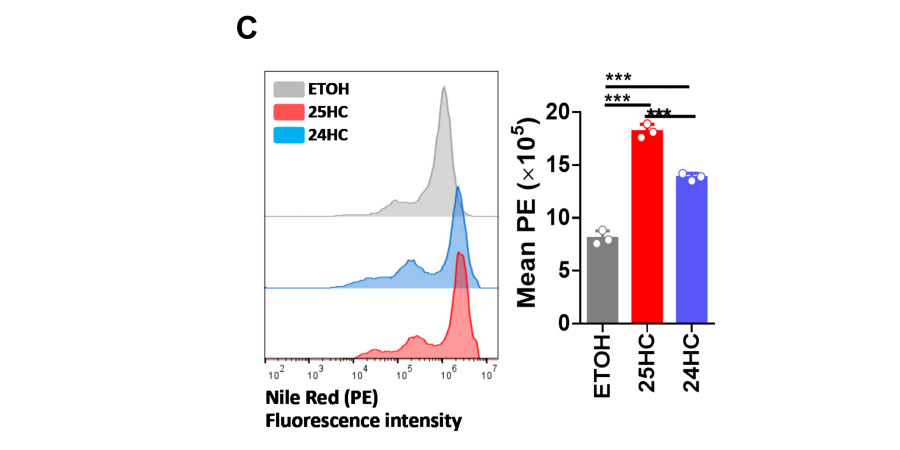
24HC induces cholesterol accumulation in multivesicular bodies or late endosomes.C. N2a cells were treated with ETOH, 24HC (5 µM), or 25HC (5 µM) for 24 h, then fixed and stained with Nile red. The cells were then analyzed for PE fluorescence intensity by flow cytometr.
N2a cells were treated with ETOH, 24HC (5 µM), or 25HC (5 µM) for 24 h, then fixed and stained with Nile red(GlpBio).
Redox Biology (2023): 102769. PMID: 37285742 IF: 10.7865 -
Related Biological Data
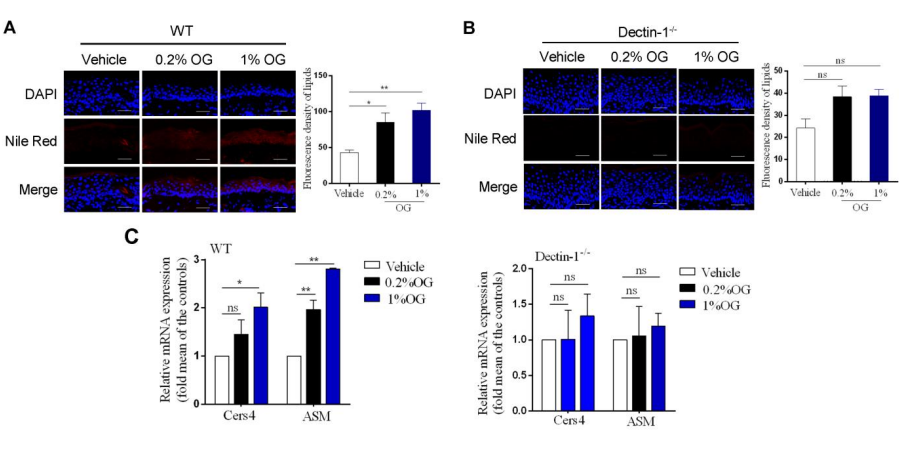
Effects of OG on lipid synthesis in the damaged epidermal barrier. (A, B) Nile red fluorescence staining and quantitative analysis of neutral lipid in the WT (A) and Dectin-1(B) mice.
The stained slices were then stained with Nile Red Fluorescent Dye Working Solution (Glpbio) for 20 min, and finally mounted with glycerol gelatin and examined with a confocal laser scanning microscope.
Brit J Pharmacol (2023). PMID: 38124222 IF: 7.3003 -
Related Biological Data
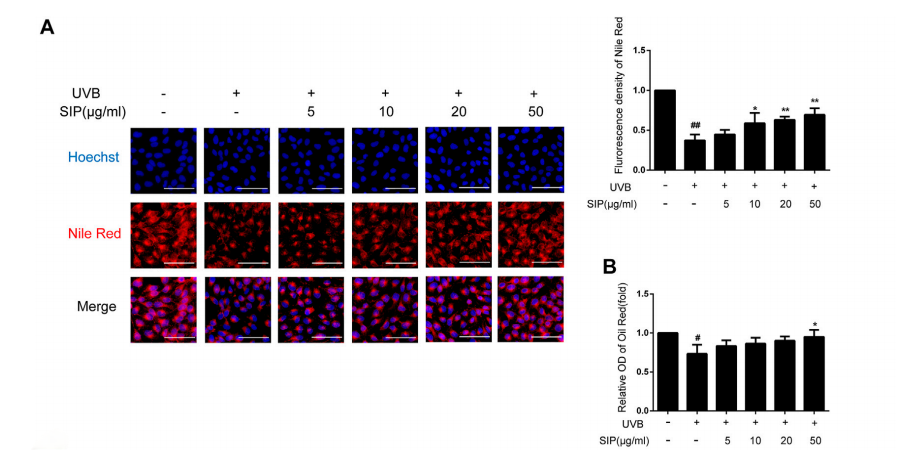
Effects of SIP on keratinocyte lipid synthesis. (A) Changes in neutral lipid level of HaCaT cells as examined by Nile red fluorescence staining. The plots beside the images show the quantitation analysis of neutral lipids fluorescence intensity. (B) Detection of lipid content in HaCaT cells by oil-red O.
The slices were incubated with Hoechst solution and then in Nile Red Fluorescent Dye Working Solution (Glpbio).
Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2023, 14. PMID: 36733502 IF: 5.9879 -
Related Biological Data
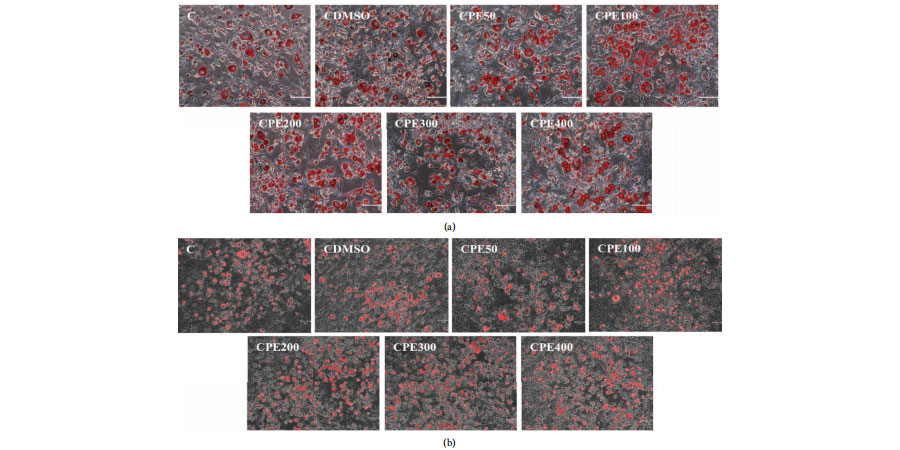
Oil Red O staining, Nile Red staining, and quantifcation of Oil Red O staining in 3T3-L1 cells treated with Citrus sunki peel extract. (a) 3T3-L1 cells, stained with Oil Red O, were visualized in optical microscopy. (b) 3T3-L1 cells, stained with Nile Red, were visualized in optical microscopy.
Nile Red working solution was prepared by diluting nile red dye (GLPBIO) in PBS to a concentration of 1 μg/mL. Cells were treated with nile red working solution for 30 min at room temperature.
J Food Biochem 2024 (2024). IF: 4 -
Related Biological Data
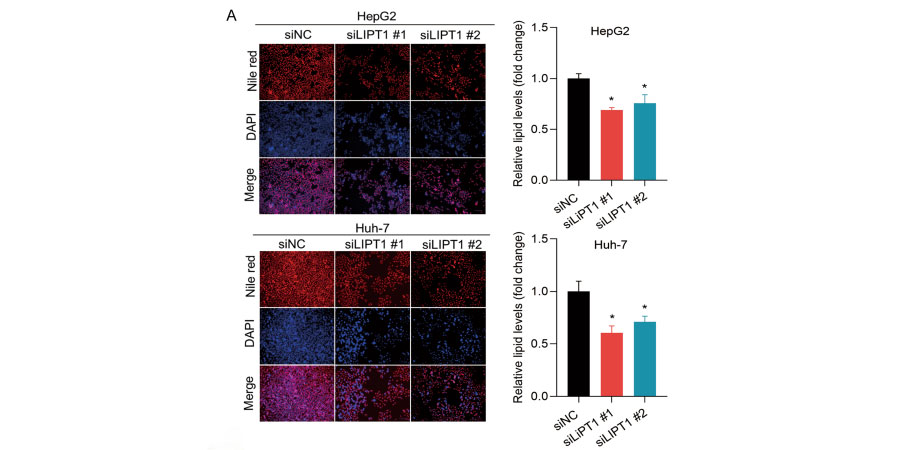
Downregulation of LIPT1 reduces lipid deposition in HCC cells. A Nile red staining analysis showed a signifcant decrease in lipid content in LIPT1-silenced cells.
Briefy, the transfected cells in 96-well plates (3× 103 cells/well) were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min and incubated with 0.1 μg/mL Nile red(GlpBio) for 10 min, then washing the plates with PBS twice, followed by DAPI staining for 10 min.
J Cancer Res Clin (2023): 1-17. PMID: 37668796 IF: 3.5999




